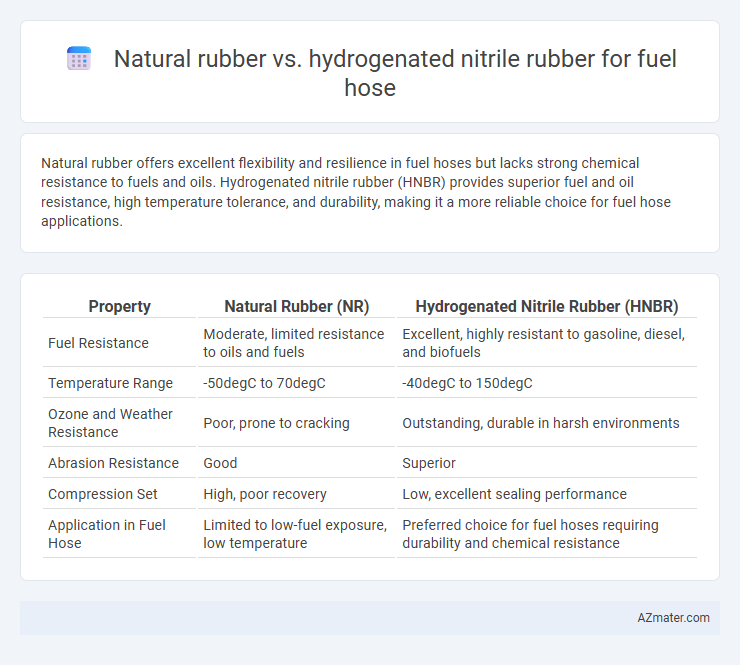
Natural rubber offers excellent flexibility and resilience in fuel hoses but lacks strong chemical resistance to fuels and oils. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior fuel and oil resistance, high temperature tolerance, and durability, making it a more reliable choice for fuel hose applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Natural Rubber (NR) | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Resistance | Moderate, limited resistance to oils and fuels | Excellent, highly resistant to gasoline, diesel, and biofuels |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 70degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Poor, prone to cracking | Outstanding, durable in harsh environments |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Superior |
| Compression Set | High, poor recovery | Low, excellent sealing performance |
| Application in Fuel Hose | Limited to low-fuel exposure, low temperature | Preferred choice for fuel hoses requiring durability and chemical resistance |
Introduction to Natural Rubber and Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber
Natural rubber, derived from latex of Hevea brasiliensis, offers excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and resistance to wear, making it suitable for fuel hose applications requiring flexibility and durability. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for superior heat, oil, and chemical resistance, maintaining performance at elevated temperatures and in harsh fuel environments. Both materials provide distinct advantages for fuel hoses, with natural rubber favored for flexibility and cost-effectiveness, while HNBR excels in long-term stability and fuel resistance.
Key Properties of Natural Rubber
Natural rubber exhibits excellent resilience, high tensile strength, and superior abrasion resistance, making it ideal for fuel hose applications requiring flexibility and durability. Its outstanding elasticity allows it to maintain performance under dynamic stresses and varying temperatures, while its natural resistance to wear and tear ensures prolonged hose lifespan. Despite limited chemical resistance compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber, natural rubber excels in scenarios involving high mechanical strain and moderate exposure to fuels.
Key Properties of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for fuel hose applications exposed to harsh environments. Its high tensile strength and excellent abrasion resistance extend the durability and performance of fuel hoses in automotive and industrial settings. HNBR's low permeability to fuels and its ability to maintain flexibility at low temperatures ensure reliable sealing and long service life under variable operating conditions.
Fuel Hose Applications: Requirements and Challenges
Natural rubber offers excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance for fuel hoses but struggles with fuel permeability and chemical degradation, limiting its durability in fuel system applications. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior resistance to hydrocarbons, high temperatures, and oxidative aging, making it more reliable for demanding fuel hose environments such as automotive and industrial fuel delivery. The key challenge in fuel hose design is balancing elasticity, fuel compatibility, and long-term thermal stability, where HNBR generally outperforms natural rubber in meeting stringent fuel hose performance requirements.
Chemical Resistance: Natural Rubber vs HNBR
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance compared to natural rubber, especially against oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons commonly encountered in fuel hose applications. Natural rubber tends to degrade quickly when exposed to petroleum-based fluids, resulting in swelling and loss of mechanical integrity. HNBR's enhanced molecular structure provides excellent resistance to oxidative degradation and retains flexibility and strength under harsh chemical exposure, making it the preferred material for fuel hoses in automotive and industrial environments.
Temperature Tolerance Comparison
Natural rubber exhibits temperature tolerance typically ranging from -50degC to 70degC, making it suitable for moderate conditions but less effective under extreme heat exposure. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior thermal stability withstanding temperatures from -40degC up to 150degC, providing enhanced resistance to heat aging and thermal degradation. For fuel hose applications requiring prolonged exposure to high temperatures, HNBR outperforms natural rubber by maintaining structural integrity and flexibility under harsh thermal conditions.
Durability and Longevity in Fuel Systems
Natural rubber offers excellent flexibility but has limited resistance to fuel and oil degradation, reducing its durability and longevity in fuel hoses. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior resistance to hydrocarbons, heat, and oxidative aging, significantly enhancing its lifespan and reliability within aggressive fuel system environments. Fuel hoses made from HNBR maintain structural integrity longer, minimizing maintenance and replacement costs in automotive and industrial fuel delivery applications.
Cost Effectiveness and Availability
Natural rubber offers cost-effective raw material sourcing and widespread availability, making it a budget-friendly option for fuel hoses in general applications. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR), while typically more expensive due to its specialized properties, provides superior chemical resistance and durability in harsh fuel environments. Choosing between the two depends on balancing upfront material costs against long-term performance and availability in specific fuel hose requirements.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to fuel, ozone, and heat compared to natural rubber, making it more durable and safer for fuel hose applications in harsh environments. Natural rubber, while biodegradable, degrades quickly when exposed to hydrocarbons and ozone, posing risks of hose failure and environmental contamination. The enhanced chemical stability of HNBR reduces the frequency of hose replacements, minimizing environmental waste and improving operational safety in fuel systems.
Conclusion: Optimal Rubber Choice for Fuel Hose Applications
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) outperforms natural rubber in fuel hose applications due to its superior resistance to heat, oil, and chemical degradation, ensuring longer service life and reliability. Natural rubber offers good flexibility but lacks the enhanced durability and fuel resistance required for modern fuel systems. Selecting HNBR optimizes performance and safety, making it the preferred material for high-demand fuel hose environments.
Infographic: Natural rubber vs Hydrogenated nitrile rubber for Fuel hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com