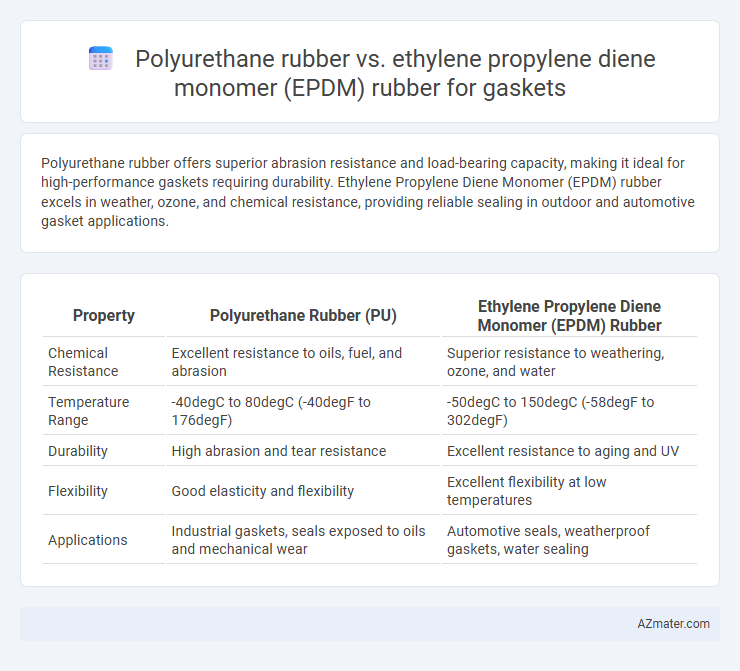
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for high-performance gaskets requiring durability. Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in weather, ozone, and chemical resistance, providing reliable sealing in outdoor and automotive gasket applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane Rubber (PU) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuel, and abrasion | Superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and water |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 80degC (-40degF to 176degF) | -50degC to 150degC (-58degF to 302degF) |
| Durability | High abrasion and tear resistance | Excellent resistance to aging and UV |
| Flexibility | Good elasticity and flexibility | Excellent flexibility at low temperatures |
| Applications | Industrial gaskets, seals exposed to oils and mechanical wear | Automotive seals, weatherproof gaskets, water sealing |
Introduction to Gasket Materials
Polyurethane rubber offers excellent abrasion resistance and tensile strength, making it ideal for gaskets requiring durability in harsh environments. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber provides superior weather, ozone, and chemical resistance, suited for gaskets exposed to outdoor conditions and aggressive chemicals. Selecting the appropriate gasket material depends on application-specific demands such as temperature range, pressure, and fluid compatibility, where polyurethane excels in mechanical properties while EPDM dominates in environmental resilience.
Overview of Polyurethane Rubber
Polyurethane rubber is a highly durable and flexible elastomer known for its excellent abrasion resistance, making it ideal for gasket applications exposed to mechanical stress. Its superior resistance to oils, solvents, and weathering ensures long-lasting performance in industrial and automotive sealing environments. Compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, polyurethane provides enhanced mechanical strength and tear resistance, although EPDM excels in ozone and heat resistance.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) Rubber
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber is a synthetic elastomer renowned for its exceptional resistance to heat, ozone, weathering, and aging, making it ideal for gasket applications in automotive and industrial environments. Unlike polyurethane rubber, EPDM offers superior flexibility at low temperatures and excellent chemical resistance to polar substances such as water, steam, and many acids and alkalis. Its outstanding electrical insulation properties and durability under harsh conditions position EPDM as a preferred choice for sealing solutions requiring long-term reliability and performance.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyurethane rubber exhibits superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, making it ideal for high-wear gasket applications. EPDM offers better flexibility and excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and heat, enhancing its sealing performance in outdoor environments. While polyurethane delivers higher tear strength and load-bearing capacity, EPDM provides greater elongation and compression set stability, crucial for maintaining gasket integrity under varying thermal conditions.
Chemical Resistance Differences
Polyurethane rubber offers superior resistance to oils, solvents, and abrasion, making it ideal for gaskets exposed to hydrocarbons and aggressive chemicals. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in resisting polar substances such as water, steam, and alkalis, providing excellent performance in outdoor and weather-exposed gasket applications. The chemical resistance differences dictate that polyurethane is preferred for sealing environments with hydrocarbons, while EPDM suits gaskets requiring robustness against polar chemicals and weathering.
Temperature Performance Analysis
Polyurethane rubber exhibits excellent abrasion resistance and tensile strength but has a limited temperature range, typically operating effectively between -40degC to 80degC, which restricts its use in high-temperature gasket applications. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber offers superior temperature performance, maintaining flexibility and sealing properties in a broader range of -50degC to 150degC, making it more suitable for gaskets exposed to extreme heat. EPDM's enhanced resistance to heat, steam, and weathering ensures reliable long-term performance in demanding thermal environments compared to polyurethane.
Durability and Longevity Insights
Polyurethane rubber exhibits superior abrasion resistance and higher tensile strength, making it highly durable for gasket applications exposed to mechanical wear and pressure. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber offers excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, enhancing gasket longevity in outdoor or high-temperature environments. While polyurethane provides enhanced physical durability, EPDM ensures extended lifespan in chemically aggressive or climatic conditions.
Typical Applications in Gasket Manufacturing
Polyurethane rubber offers exceptional abrasion resistance and tensile strength, making it ideal for gaskets in hydraulic systems, industrial machinery, and automotive seals exposed to mechanical wear. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber exhibits superior weather, ozone, and chemical resistance, commonly used for gaskets in outdoor applications, roofing systems, and water handling equipment. Both materials provide excellent sealing properties but are selected based on operational environments demanding durability against wear (polyurethane) or resilience to environmental degradation (EPDM).
Cost and Availability Considerations
Polyurethane rubber offers high abrasion resistance and durability but generally comes at a higher cost compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, which is more economical and widely available. EPDM gasket materials are favored in applications requiring excellent weather, ozone, and chemical resistance, contributing to their extensive market availability and cost-effectiveness. Cost-sensitive projects often select EPDM due to its lower price point and broad manufacturing sources, whereas polyurethane's performance benefits justify its premium pricing in specialized gasket applications.
Choosing the Right Rubber: Polyurethane vs. EPDM
Polyurethane rubber offers excellent abrasion resistance and high tensile strength, making it ideal for gaskets exposed to mechanical wear and dynamic stress. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, providing superior performance in outdoor and chemical environments. Selecting the right gasket material depends on the specific application requirements, with polyurethane suited for heavy-duty sealing and EPDM preferred for environmental durability.
Infographic: Polyurethane rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com