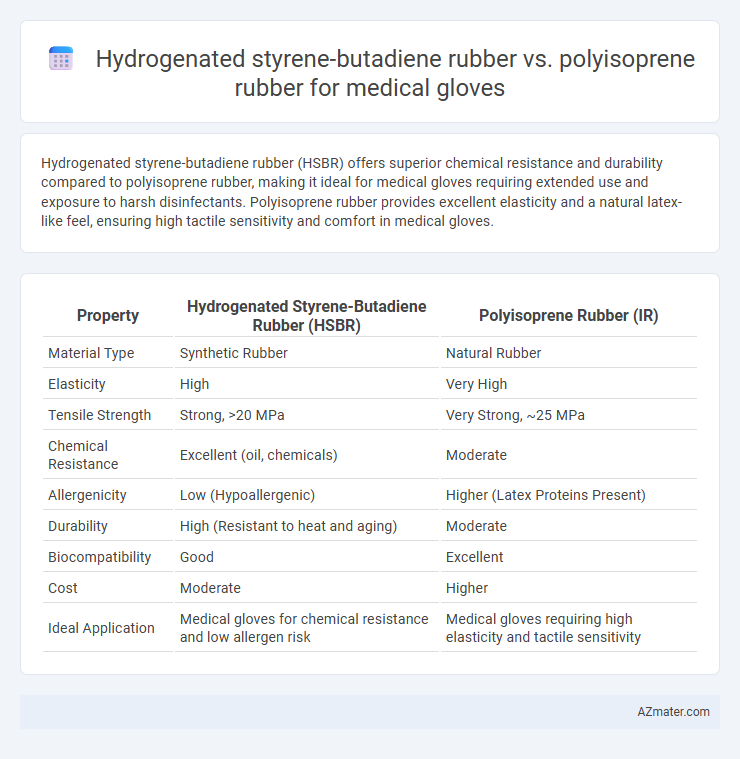
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to polyisoprene rubber, making it ideal for medical gloves requiring extended use and exposure to harsh disinfectants. Polyisoprene rubber provides excellent elasticity and a natural latex-like feel, ensuring high tactile sensitivity and comfort in medical gloves.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) | Polyisoprene Rubber (IR) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic Rubber | Natural Rubber |
| Elasticity | High | Very High |
| Tensile Strength | Strong, >20 MPa | Very Strong, ~25 MPa |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (oil, chemicals) | Moderate |
| Allergenicity | Low (Hypoallergenic) | Higher (Latex Proteins Present) |
| Durability | High (Resistant to heat and aging) | Moderate |
| Biocompatibility | Good | Excellent |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
| Ideal Application | Medical gloves for chemical resistance and low allergen risk | Medical gloves requiring high elasticity and tactile sensitivity |
Introduction to Medical Glove Materials
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers enhanced chemical resistance and durability compared to traditional polyisoprene rubber, making it suitable for medical gloves requiring prolonged exposure to disinfectants. Polyisoprene rubber mimics natural latex's softness and elasticity, providing superior comfort and tactile sensitivity for healthcare professionals. The choice between HSBR and polyisoprene in medical glove manufacturing balances factors such as allergenicity, mechanical performance, and resistance to chemical degradation.
Overview of Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR)
Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) offers enhanced chemical resistance, improved thermal stability, and superior abrasion resistance compared to traditional styrene-butadiene rubber, making it suitable for medical gloves requiring durability and protection against harsh disinfectants. Its hydrogenation process saturates the polymer backbone, reducing susceptibility to oxidative degradation and extending glove lifespan in clinical environments. While Polyisoprene rubber excels in elasticity and tactile sensitivity, HSBR provides a balance of mechanical strength and resistance to chemical exposure essential for certain medical applications.
What is Polyisoprene Rubber?
Polyisoprene rubber is a synthetic elastomer that closely mimics natural latex, offering excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and biocompatibility, making it ideal for medical gloves requiring high sensitivity and comfort. Unlike hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber, polyisoprene provides superior allergen-free properties, reducing the risk of latex allergy reactions in sensitive patients. This material also demonstrates enhanced tactile performance and chemical resistance, crucial for medical environments demanding durability and precision.
Key Differences in Chemical Structure
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) consists of saturated polybutadiene segments with styrene units, enhancing chemical resistance and reducing unsaturation compared to standard SBR. Polyisoprene rubber (IR) closely mimics natural rubber's cis-1,4-polyisoprene structure, providing excellent elasticity and tactile sensitivity crucial for medical gloves. The key difference lies in HSBR's hydrogenated backbone offering superior oxidative stability, whereas polyisoprene's chemical structure delivers greater flexibility and biodegradability.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength compared to polyisoprene rubber (IR), making it highly durable for medical gloves subjected to rigorous use. Polyisoprene rubber provides enhanced elasticity and higher elongation at break, offering better flexibility and comfort for sensitive medical tasks. The choice between HSBR and IR depends on the balance required between mechanical durability and tactile sensitivity in medical glove applications.
Biocompatibility and Allergenicity
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers enhanced biocompatibility with reduced protein content, significantly lowering the risk of allergenic reactions compared to polyisoprene rubber, which contains natural latex proteins linked to Type I latex allergies. Polyisoprene rubber closely mimics natural latex in elasticity and tactile sensitivity but presents a higher potential for allergenicity due to residual latex proteins despite advanced purification. HSBR gloves are preferred in medical settings where latex allergies are a concern, providing a hypoallergenic alternative with durable polymer stability and resistance to chemical degradation.
Resistance to Chemicals and Degradation
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits superior resistance to oils, chemicals, and oxidative degradation compared to polyisoprene rubber, making it more durable for medical glove applications involving exposure to harsh substances. Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and tactile sensitivity but is more susceptible to degradation from ozone, UV light, and solvents. Selecting HSBR for medical gloves enhances chemical resistance and longevity, while polyisoprene prioritizes comfort and fit.
Comfort and Fit in Medical Applications
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers enhanced durability and chemical resistance compared to polyisoprene rubber, which is known for its superior elasticity and natural latex-like softness, providing a more comfortable fit for prolonged medical glove use. Polyisoprene gloves exhibit excellent tactile sensitivity and conform closely to hand movements, reducing hand fatigue and improving precision during intricate medical procedures. While HSBR gloves excel in resilience and protection, polyisoprene remains the preferred choice for medical applications prioritizing comfort and ergonomic fit.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers cost advantages over polyisoprene rubber due to its synthetic origin and consistent supply chain, reducing price volatility in medical glove production. Manufacturing HSBR gloves involves simpler processing and greater chemical stability, which enhances shelf life and reduces production defects compared to the more delicate natural polyisoprene rubber. While polyisoprene provides superior elasticity and tactile sensitivity, the higher raw material cost and more complex handling requirements increase overall manufacturing expenses.
Future Trends in Medical Glove Materials
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers enhanced chemical resistance and durability, making it a promising candidate for medical gloves in environments requiring prolonged wear and exposure to harsh substances. Polyisoprene rubber, known for its excellent elasticity and natural latex-like properties, continues to be favored for its comfort and low allergenic potential. Future trends emphasize blending these materials or developing new composites to achieve superior barrier protection, biodegradability, and user safety in medical glove applications.
Infographic: Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber vs Polyisoprene rubber for Medical glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com