Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance, high-temperature stability up to 200degC, and excellent durability for gasket applications compared to natural rubber, which provides better elasticity and is more cost-effective but less resistant to oils, solvents, and heat. Choosing fluorocarbon rubber enhances gasket performance in aggressive environments, while natural rubber suits general sealing needs with moderate temperature ranges.
Table of Comparison
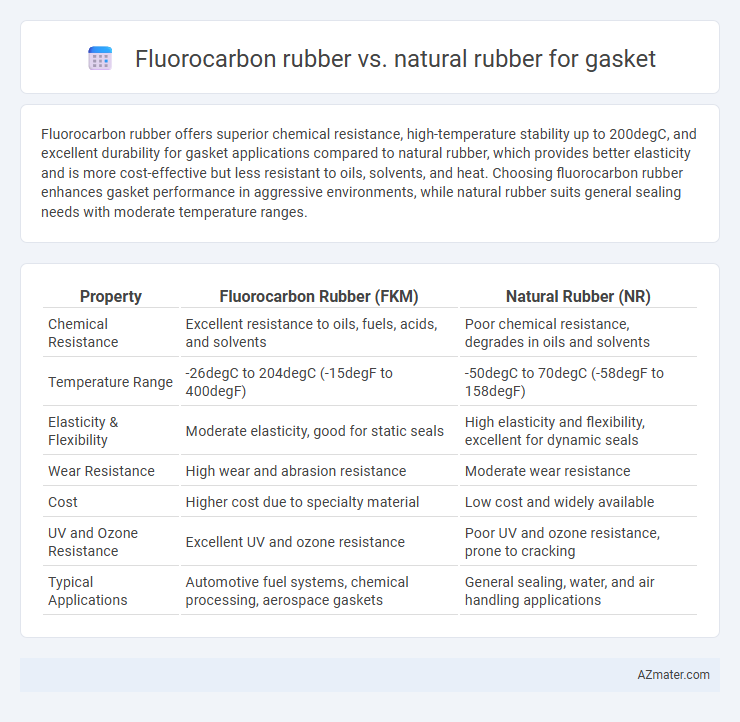
| Property | Fluorocarbon Rubber (FKM) | Natural Rubber (NR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, acids, and solvents | Poor chemical resistance, degrades in oils and solvents |
| Temperature Range | -26degC to 204degC (-15degF to 400degF) | -50degC to 70degC (-58degF to 158degF) |
| Elasticity & Flexibility | Moderate elasticity, good for static seals | High elasticity and flexibility, excellent for dynamic seals |
| Wear Resistance | High wear and abrasion resistance | Moderate wear resistance |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialty material | Low cost and widely available |
| UV and Ozone Resistance | Excellent UV and ozone resistance | Poor UV and ozone resistance, prone to cracking |
| Typical Applications | Automotive fuel systems, chemical processing, aerospace gaskets | General sealing, water, and air handling applications |
Introduction to Fluorocarbon Rubber and Natural Rubber
Fluorocarbon rubber, known for its exceptional chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, is commonly used in gasket applications requiring durability against oils, fuels, and harsh chemicals. Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and tensile strength, making it suitable for sealing applications where flexibility and abrasion resistance are critical. When selecting gasket materials, fluorocarbon rubber provides superior performance in extreme environments while natural rubber excels in applications with moderate conditions and dynamic sealing requirements.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Fluorocarbon rubber, composed of vinylidene fluoride and hexafluoropropylene monomers, features a highly fluorinated polymer chain providing superior chemical resistance and thermal stability up to 200degC, ideal for aggressive environments. In contrast, natural rubber consists primarily of cis-1,4-polyisoprene with a hydrocarbon backbone, offering excellent elasticity but limited resistance to oils, solvents, and heat above 80degC. The densely fluorinated structure of fluorocarbon rubber creates a non-polar, low-energy surface that resists permeation and degradation, whereas natural rubber's unsaturated carbon chains are prone to oxidation and swelling in chemical exposure.
Temperature Resistance Comparison
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) gaskets exhibit superior temperature resistance, operating effectively between -20degC to 250degC, making them ideal for high-heat applications. In contrast, natural rubber gaskets have a narrower temperature range, typically from -40degC to 70degC, limiting their use in environments with elevated temperatures. The enhanced thermal stability of fluorocarbon rubber ensures reliable sealing performance and prolonged gasket lifespan under extreme thermal conditions.
Chemical Resistance and Compatibility
Fluorocarbon rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to natural rubber, effectively withstanding harsh chemicals such as acids, fuels, and solvents, making it ideal for gaskets in aggressive environments. Natural rubber offers limited chemical compatibility, prone to swelling and degradation when exposed to oils, fuels, and many solvents, restricting its use in chemically demanding applications. Selecting fluorocarbon rubber gaskets ensures enhanced durability and longevity in chemical processing, automotive, and aerospace industries where resistance to diverse chemical agents is critical.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Fluorocarbon rubber exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to natural rubber, including higher tensile strength, excellent resistance to compression set, and outstanding elasticity retention under extreme temperatures. Its durability is significantly enhanced by exceptional chemical resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents, making it ideal for harsh industrial environments. Natural rubber, while offering good flexibility and abrasion resistance, tends to degrade faster due to lower resistance to heat, ozone, and chemical exposure, limiting its lifespan in demanding gasket applications.
Performance in Various Environments
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for gaskets exposed to aggressive fuels, oils, and solvents in automotive and aerospace industries. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance but degrades quickly in high-temperature or chemically harsh environments, limiting its use in industrial applications. For environments with extreme temperatures and exposure to chemicals, fluorocarbon rubber gaskets deliver longer service life and consistent performance compared to natural rubber.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical and temperature resistance compared to natural rubber, but it comes at a significantly higher cost, often 3 to 5 times more expensive per kilogram. Natural rubber remains the most economical choice for gaskets in low to moderate temperature applications, offering good flexibility and sealing at a fraction of the price. When balancing cost and performance, selecting natural rubber gaskets is ideal for budget-sensitive projects, while fluorocarbon rubber is favored in demanding environments where longevity justifies the premium expense.
Common Applications for Gaskets
Fluorocarbon rubber gaskets are widely used in automotive fuel systems, chemical processing, and aerospace industries due to their excellent resistance to fuels, oils, and high temperatures. Natural rubber gaskets are commonly found in water systems, food processing, and low-temperature sealing applications, where elasticity and abrasion resistance are critical. The choice between fluorocarbon and natural rubber depends on the specific chemical exposure and operating temperature range required for the gasket.
Advantages and Disadvantages Overview
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance up to 200-250degC, and excellent sealing performance in aggressive environments, making it ideal for harsh industrial applications. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity, low cost, and good abrasion resistance but suffers from poor resistance to oils, solvents, and high temperatures, limiting its use in aggressive chemical or high-heat environments. While fluorocarbon rubber gaskets demonstrate longer service life and better stability, natural rubber remains preferred for general-purpose sealing where chemical exposure and temperature extremes are minimal.
How to Select the Right Rubber for Gasket Use
Selecting the right rubber for gasket use involves evaluating chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and durability requirements. Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior resistance to high temperatures (up to 200degC) and aggressive chemicals, making it ideal for automotive and aerospace applications. In contrast, natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance but performs poorly in oil exposure and elevated temperatures, thus suiting low-stress sealing environments.
Infographic: Fluorocarbon rubber vs Natural rubber for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com