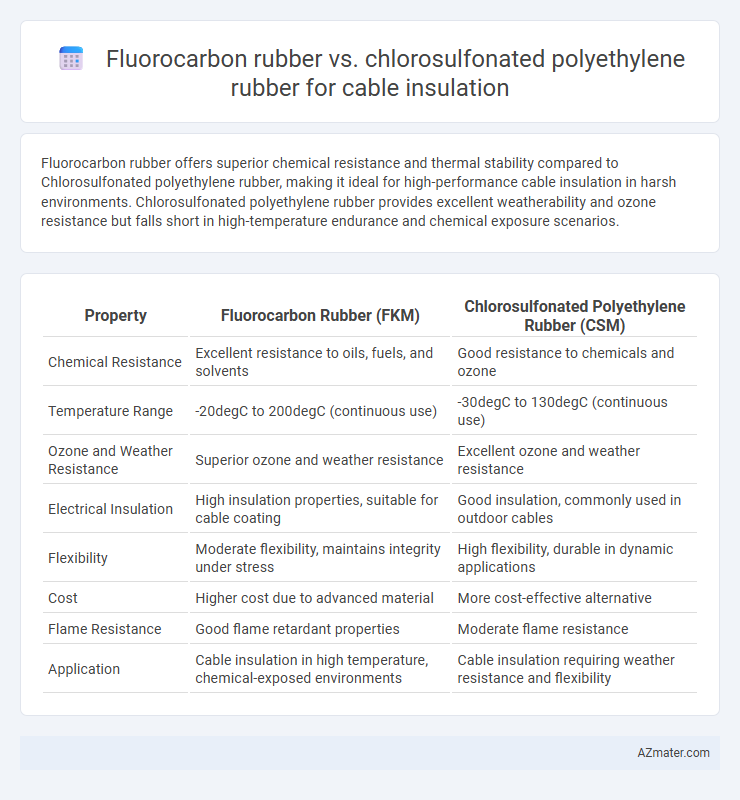
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber, making it ideal for high-performance cable insulation in harsh environments. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber provides excellent weatherability and ozone resistance but falls short in high-temperature endurance and chemical exposure scenarios.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluorocarbon Rubber (FKM) | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber (CSM) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents | Good resistance to chemicals and ozone |
| Temperature Range | -20degC to 200degC (continuous use) | -30degC to 130degC (continuous use) |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Superior ozone and weather resistance | Excellent ozone and weather resistance |
| Electrical Insulation | High insulation properties, suitable for cable coating | Good insulation, commonly used in outdoor cables |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, maintains integrity under stress | High flexibility, durable in dynamic applications |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced material | More cost-effective alternative |
| Flame Resistance | Good flame retardant properties | Moderate flame resistance |
| Application | Cable insulation in high temperature, chemical-exposed environments | Cable insulation requiring weather resistance and flexibility |
Introduction to Cable Insulation Materials
Fluorocarbon rubber offers excellent chemical resistance, high temperature stability up to 200degC, and superior weathering properties, making it ideal for demanding cable insulation applications exposed to harsh environments. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber provides good resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and moisture, with temperature tolerance typically up to 120degC, making it suitable for general-purpose cable insulation in outdoor and industrial settings. Both materials ensure electrical insulation and mechanical durability, but fluorocarbon rubber's enhanced performance is preferred for high-performance, critical cabling systems.
Overview of Fluorocarbon Rubber
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) is a high-performance elastomer widely used in cable insulation due to its exceptional resistance to heat, chemicals, and weathering. Its molecular structure provides superior flame retardance and excellent electrical insulation properties, making it ideal for harsh environments. Compared to chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM), FKM offers better durability, thermal stability up to 200degC, and resistance to oils and solvents, enhancing cable lifespan and reliability.
Overview of Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers exceptional resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemicals, making it highly suitable for durable cable insulation in harsh environments. Its excellent electrical insulation properties and strong resistance to oil and acid enhance cable performance and longevity compared to some fluorocarbon rubber variants. CSM's balance of flexibility, toughness, and chemical stability ensures reliable protection for cables used in industrial and outdoor applications.
Key Properties Comparison
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance, excellent thermal stability up to 200degC, and outstanding weathering and ozone resistance, making it ideal for high-performance cable insulation in harsh environments. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber provides good resistance to chemicals, ozone, and weathering but performs best at temperatures up to 120degC, with higher mechanical strength and flexibility at lower costs. Fluorocarbon rubber excels in maintaining electrical insulation properties under extreme conditions, while chlorosulfonated polyethylene balances durability and cost-effectiveness for medium-duty cable insulation applications.
Thermal Resistance Performance
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) exhibits superior thermal resistance performance for cable insulation, withstanding continuous temperatures up to 200-250degC and short-term peaks above 275degC, making it ideal for harsh environments. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) offers good thermal stability, typically enduring temperatures up to 125-150degC but degrades faster under prolonged high heat exposure. FKM's chemical structure provides enhanced resistance to thermal aging, oxidation, and heat-induced deformation, outperforming CSM in long-term thermal reliability for cable insulation applications.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Suitability
Fluorocarbon rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance to hydrocarbons, acids, and solvents, making it ideal for harsh chemical environments in cable insulation applications. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber offers excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and UV radiation, enhancing environmental durability for outdoor cable use. Fluorocarbon rubber's high-temperature tolerance contrasts with chlorine-based polyethylene's durability under prolonged environmental exposure, tailoring material choice to specific cable insulation demands.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Fluorocarbon rubber exhibits superior mechanical strength and exceptional resistance to chemicals, heat, and weathering, making it highly durable for cable insulation in harsh environments. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber offers good mechanical properties and notable resistance to ozone, sunlight, and moisture but generally falls short compared to fluorocarbon rubber in extreme temperature and chemical exposure conditions. The enhanced durability of fluorocarbon rubber translates to longer service life and reliability in demanding industrial and aerospace cable applications.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior electrical insulation capabilities for cable insulation, characterized by excellent dielectric strength and resistance to high temperatures and chemical exposure. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber provides good electrical insulation but is more prone to degradation under harsh environmental conditions, limiting its use in high-performance cable applications. Fluorocarbon rubber's stability under extreme conditions ensures long-term reliability in electrical insulation compared to chlorosulfonated polyethylene.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) offers superior chemical resistance and high-temperature stability for cable insulation but comes at a significantly higher cost and with limited availability compared to chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber. CSM provides a more economical solution with good weather and ozone resistance, benefiting from widespread production and easier procurement in bulk quantities. Industries prioritizing budget and supply chain reliability often choose CSM, while specialized applications requiring enhanced durability favor FKM despite its premium price and supply constraints.
Optimal Applications and Industry Recommendations
Fluorocarbon rubber excels in high-temperature and chemically aggressive environments, making it optimal for aerospace, automotive, and chemical processing cable insulation where resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents is critical. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber provides superior weathering, ozone, and UV resistance, making it ideal for outdoor electrical and telecommunications cables exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Industry recommendations favor fluorocarbon rubber for applications requiring extreme durability and chemical resistance, while chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber is preferred for cost-effective, weather-resistant insulation solutions in less chemically demanding settings.
Infographic: Fluorocarbon rubber vs Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber for Cable insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com