Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat, oil, and chemical resistance compared to chloroprene rubber, making it ideal for high-performance hoses. Chloroprene rubber provides excellent weather, ozone, and abrasion resistance, suitable for outdoor hose applications requiring durability.
Table of Comparison
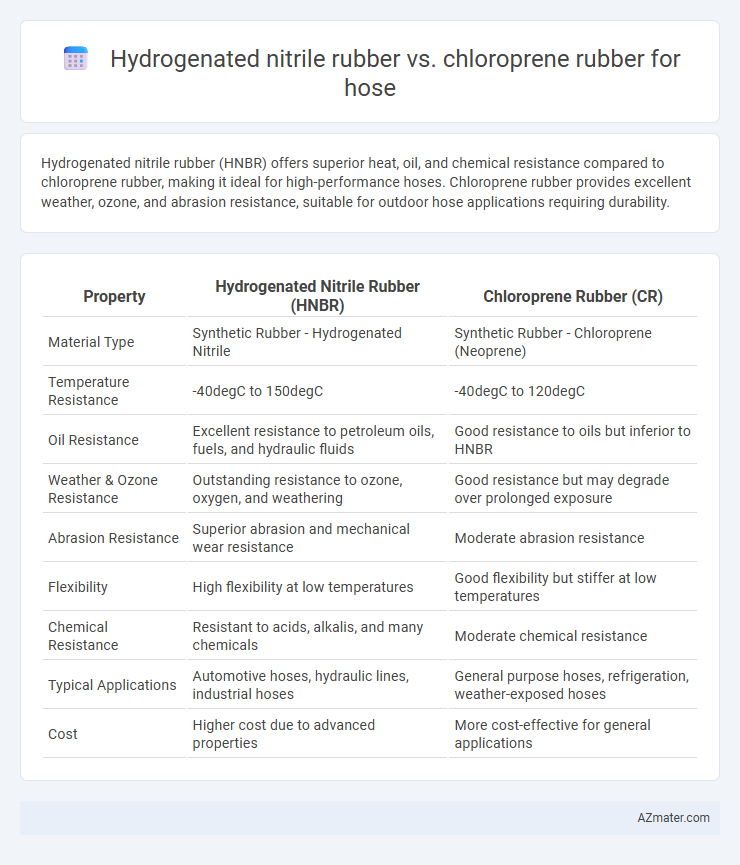
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic Rubber - Hydrogenated Nitrile | Synthetic Rubber - Chloroprene (Neoprene) |
| Temperature Resistance | -40degC to 150degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Oil Resistance | Excellent resistance to petroleum oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids | Good resistance to oils but inferior to HNBR |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | Outstanding resistance to ozone, oxygen, and weathering | Good resistance but may degrade over prolonged exposure |
| Abrasion Resistance | Superior abrasion and mechanical wear resistance | Moderate abrasion resistance |
| Flexibility | High flexibility at low temperatures | Good flexibility but stiffer at low temperatures |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids, alkalis, and many chemicals | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Typical Applications | Automotive hoses, hydraulic lines, industrial hoses | General purpose hoses, refrigeration, weather-exposed hoses |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | More cost-effective for general applications |
Introduction to Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber and Chloroprene Rubber
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance and heat stability compared to traditional nitrile compounds, making it ideal for demanding hose applications exposed to oils, fuels, and extreme temperatures. Chloroprene rubber (CR), known for its balanced properties of flexibility, weather resistance, and moderate chemical resistance, is widely used in versatile hose assembly processes. Both elastomers provide essential performance characteristics, with HNBR excelling in harsh industrial environments and CR favored for general-purpose, durable hose products.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) features a saturated polymer backbone derived from nitrile butadiene rubber that enhances its resistance to heat, oil, and chemical degradation, making it ideal for harsh environments in hose applications. Chloroprene rubber (CR) possesses a polychloroprene backbone with inherent chlorine atoms, offering excellent weather, ozone, and flame resistance but lower resistance to oils and solvents compared to HNBR. Both materials provide robust mechanical properties, yet HNBR excels in chemical stability and thermal resilience, while CR is favored for its durability and resistance to environmental aging.
Mechanical Performance in Hose Applications
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and chemical stability compared to chloroprene rubber (CR), making it ideal for high-pressure hose applications requiring durability against oils and fuels. Chloroprene rubber excels in flexibility and weather resistance but has lower mechanical strength and aging properties than HNBR, limiting its use in demanding mechanical environments. For hose applications requiring enhanced mechanical performance and extended service life, HNBR is preferred due to its exceptional resistance to heat, compression set, and mechanical wear.
Temperature Resistance: HNBR vs. Chloroprene
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior temperature resistance compared to chloroprene rubber, withstanding continuous temperatures up to 150degC and short-term exposure up to 165degC. Chloroprene rubber typically operates effectively within a temperature range of -40degC to 120degC, making it less suitable for high-temperature applications. HNBR's enhanced thermal stability and resistance to heat aging make it ideal for hose applications requiring prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures.
Oil, Fuel, and Chemical Resistance Capabilities
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior resistance to oils, fuels, and a broad range of chemicals compared to chloroprene rubber (CR), making it ideal for harsh environments requiring enhanced durability and thermal stability. HNBR maintains its mechanical properties across a wide temperature range and resists swelling and degradation from petroleum-based fluids, whereas chloroprene rubber offers moderate chemical resistance but is more susceptible to oils and certain solvents. For hoses exposed to aggressive fuels and chemical agents, HNBR provides longer service life and improved performance reliability.
Aging and Ozone Resistance in Industrial Environments
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior aging and ozone resistance compared to chloroprene rubber (CR) in industrial environments, maintaining mechanical properties and flexibility over extended exposure to heat, oxygen, and ozone. HNBR's saturated polymer backbone enhances its resistance to oxidative degradation, making it ideal for high-temperature and aggressive chemical conditions. Conversely, chloroprene rubber offers moderate ozone resistance but tends to harden and crack under prolonged ozone exposure, limiting its lifespan in demanding industrial applications.
Flexibility and Compression Set Characteristics
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior flexibility and excellent resistance to compression set, making it ideal for hoses subject to dynamic stress and repeated deformation. Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers good flexibility and moderate compression set resistance but tends to harden faster under prolonged compression, reducing its durability in high-stress hose applications. HNBR's enhanced chemical and thermal stability contributes to maintaining flexibility and dimensional integrity over extended service life compared to chloroprene.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to chloroprene rubber, resulting in longer hose lifespan and reduced replacement frequency, which enhances cost efficiency despite its higher upfront price. Chloroprene rubber hoses are generally more affordable and widely available due to established production and distribution networks, making them a cost-effective choice for standard applications with less exposure to extreme conditions. Selecting between HNBR and chloroprene rubber hoses depends on balancing initial material costs with long-term performance requirements and supply chain accessibility.
Typical Hose Application Areas
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) hoses excel in automotive fuel and oil transfer, hydraulic systems, and industrial applications due to superior resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion. Chloroprene rubber (CR) hoses are widely used for refrigerant and chemical transfer, air and water delivery, and general-purpose industrial hoses because of their excellent weather, ozone, and chemical resistance. Selection depends on application specifics such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress requirements.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Hose
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oils, and chemicals, making it ideal for hoses exposed to harsh industrial environments and high temperatures. Chloroprene rubber (CR), known for its excellent weather, ozone, and abrasion resistance, is suitable for outdoor applications where durability and flexibility are essential. Selecting the right rubber involves assessing the hose's operating conditions, such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress, to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Chloroprene rubber for Hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com