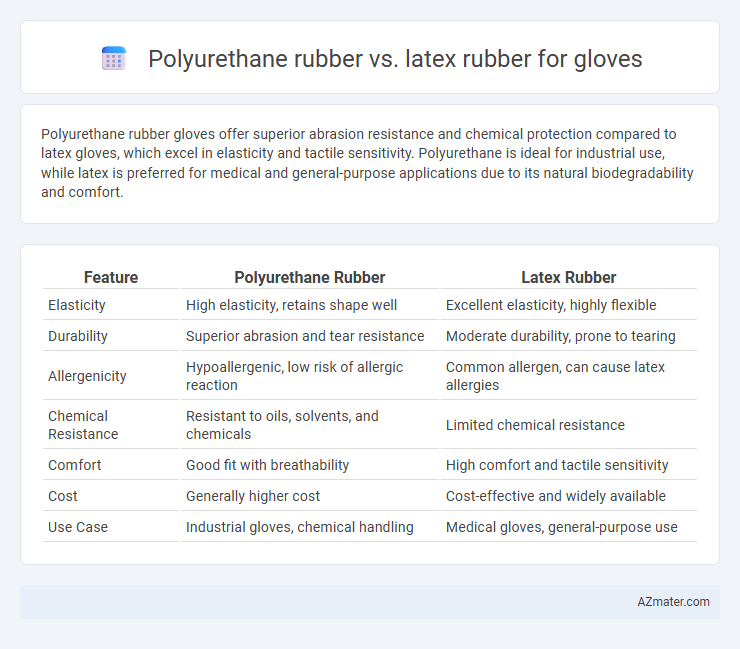
Polyurethane rubber gloves offer superior abrasion resistance and chemical protection compared to latex gloves, which excel in elasticity and tactile sensitivity. Polyurethane is ideal for industrial use, while latex is preferred for medical and general-purpose applications due to its natural biodegradability and comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyurethane Rubber | Latex Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Elasticity | High elasticity, retains shape well | Excellent elasticity, highly flexible |
| Durability | Superior abrasion and tear resistance | Moderate durability, prone to tearing |
| Allergenicity | Hypoallergenic, low risk of allergic reaction | Common allergen, can cause latex allergies |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils, solvents, and chemicals | Limited chemical resistance |
| Comfort | Good fit with breathability | High comfort and tactile sensitivity |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | Cost-effective and widely available |
| Use Case | Industrial gloves, chemical handling | Medical gloves, general-purpose use |
Introduction to Glove Materials: Polyurethane vs Latex
Polyurethane rubber offers superior tensile strength and resistance to oils and chemicals compared to latex rubber, making it ideal for industrial glove applications. Latex rubber excels in elasticity and provides a comfortable fit with excellent tactile sensitivity, preferred in medical and food handling gloves. Both materials deliver distinct advantages, with polyurethane gloves emphasizing durability while latex gloves prioritize flexibility and biodegradability.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Polyurethane rubber gloves consist of long chains of urethane linkages providing high abrasion resistance and chemical stability, making them ideal for handling oils and solvents. Latex rubber gloves are made from natural rubber latex, composed mainly of polyisoprene chains with superior elasticity and fit, but they are less resistant to organic solvents. The chemical structure of polyurethane offers greater durability against harsh chemicals, while latex provides better tactile sensitivity due to its flexible molecular network.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Polyurethane rubber gloves are produced through a dipping process where a fabric form is immersed in liquid polyurethane, followed by curing at controlled temperatures to form a thin, durable layer. Latex rubber gloves undergo a similar dipping process but use natural rubber latex, which coagulates on the form and is then vulcanized to enhance elasticity and strength. The key manufacturing difference lies in the curing methods and materials, with polyurethane requiring precise thermal curing, while latex relies on vulcanization for its elastomeric properties.
Physical Properties and Performance
Polyurethane rubber gloves offer superior tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and puncture durability compared to latex rubber gloves, making them ideal for high-performance industrial applications. Latex rubber gloves provide excellent elasticity, comfortable fit, and superior tactile sensitivity, but are more prone to degradation from oils and chemicals. Polyurethane gloves also exhibit better resistance to chemical solvents and oils, ensuring longer wear life in harsh environments.
Comfort and Fit Considerations
Polyurethane rubber gloves offer superior tactile sensitivity and a snug fit due to their thin, flexible material, making them ideal for tasks requiring precision and dexterity. Latex rubber gloves provide excellent elasticity and conform closely to the hand, ensuring a comfortable, secure fit but may cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. When prioritizing comfort and fit, polyurethane gloves excel in breathability and flexibility, while latex gloves deliver a more natural stretch and a trusted fit for extended wear.
Allergenicity and Skin Sensitivity
Polyurethane rubber gloves exhibit significantly lower allergenicity compared to latex rubber gloves, reducing the risk of Type I hypersensitivity reactions caused by natural latex proteins. Skin sensitivity incidents are less frequent with polyurethane gloves as they do not contain latex proteins or chemical accelerators commonly associated with allergic contact dermatitis. For users with latex allergies or sensitive skin, polyurethane gloves provide a safer alternative while maintaining flexibility and tactile sensitivity.
Durability and Puncture Resistance
Polyurethane rubber gloves offer superior durability and puncture resistance compared to latex rubber gloves, making them ideal for tasks involving sharp objects or abrasive surfaces. Polyurethane's molecular structure provides enhanced tensile strength and tear resistance, ensuring prolonged glove life under rigorous use. In contrast, latex gloves, while flexible and comfortable, are more prone to punctures and degradation when exposed to oils and chemicals.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Polyurethane rubber gloves exhibit lower biodegradability compared to latex rubber gloves, leading to longer environmental persistence and increased landfill waste. Natural latex gloves are derived from renewable resources and decompose more rapidly, reducing ecological footprint and minimizing toxic residue. The production of polyurethane involves petroleum-based materials, contributing to higher carbon emissions and environmental degradation relative to the sustainable harvesting of latex.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Polyurethane rubber gloves typically incur higher production costs than latex gloves due to more complex synthesis processes and raw material expenses. Latex rubber gloves maintain a widespread market availability driven by lower prices and established global manufacturing infrastructure. Cost-effectiveness and abundant supply make latex gloves a preferred choice in budget-sensitive industries, while polyurethane gloves are favored for specialized applications requiring enhanced chemical resistance.
Ideal Applications for Polyurethane and Latex Gloves
Polyurethane gloves excel in applications requiring high tactile sensitivity and chemical resistance, making them ideal for electronics assembly, food handling, and medical examinations. Latex gloves offer superior elasticity and biodegradability, preferred in healthcare settings and environments needing high flexibility and puncture resistance. The choice between polyurethane and latex gloves depends on specific industry demands, such as allergen concerns, durability, and exposure to oils or solvents.
Infographic: Polyurethane rubber vs Latex rubber for Glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com