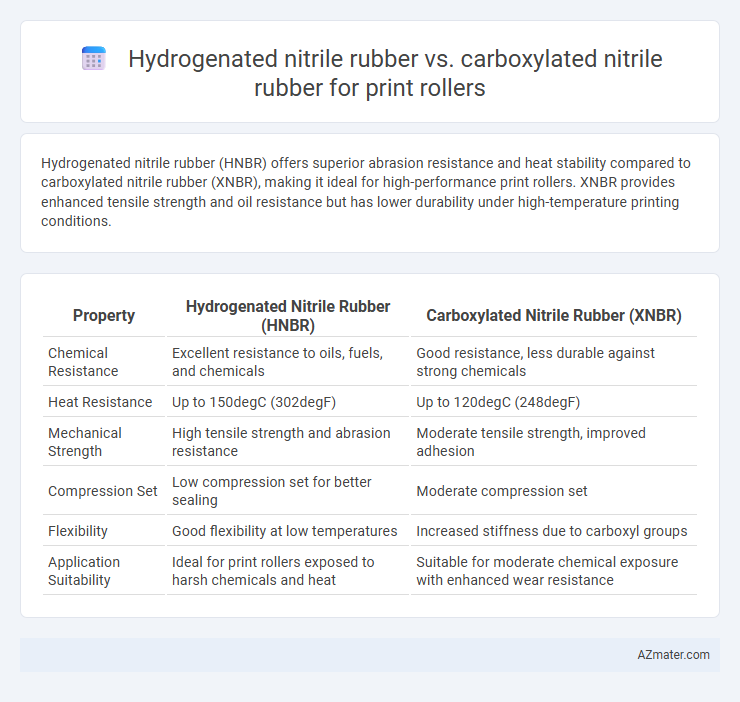
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and heat stability compared to carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR), making it ideal for high-performance print rollers. XNBR provides enhanced tensile strength and oil resistance but has lower durability under high-temperature printing conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Good resistance, less durable against strong chemicals |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 150degC (302degF) | Up to 120degC (248degF) |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and abrasion resistance | Moderate tensile strength, improved adhesion |
| Compression Set | Low compression set for better sealing | Moderate compression set |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at low temperatures | Increased stiffness due to carboxyl groups |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for print rollers exposed to harsh chemicals and heat | Suitable for moderate chemical exposure with enhanced wear resistance |
Introduction to Print Roller Elastomers
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior heat, oil, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for print rollers exposed to harsh printing environments and solvents. Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers enhanced tensile strength and abrasion resistance, improving roller durability under mechanical stress and frequent use. Selecting between HNBR and XNBR depends on specific printing conditions, balancing chemical resistance with mechanical performance for optimal print roller longevity.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) offers exceptional resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals, making it ideal for print roller applications requiring durability under harsh conditions. Its enhanced thermal stability and low compression set outperform Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR), ensuring longer service life and consistent performance. HNBR's superior mechanical properties and resistance to ozone and weathering also contribute to improved print quality and reduced maintenance cycles.
Overview of Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR)
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers enhanced abrasion resistance and improved tensile strength compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR), making it ideal for print roller applications that demand durability and high performance. XNBR's unique molecular structure, containing carboxyl groups, promotes superior adhesion and chemical resistance, particularly against oils, solvents, and printing inks. This combination ensures longer service life and consistent print quality in industrial roller environments.
Chemical Structure Differences: HNBR vs XNBR
Hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR) features a saturated hydrocarbon backbone with reduced double bonds, providing enhanced chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR), which contains carboxyl groups (-COOH) attached to the nitrile polymer chain for improved adhesion and mechanical strength. The hydrogenation process in HNBR reduces unsaturation, minimizing vulnerability to ozone and heat degradation, while the carboxyl groups in XNBR create ionic crosslinking sites that enhance abrasion resistance and tensile properties. These chemical structure differences directly influence print roller performance, where HNBR excels in high-temperature and solvent-rich environments, and XNBR offers superior wear resistance and strength under mechanical stress.
Mechanical Properties Comparison for Print Rollers
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior mechanical properties for print rollers, including higher tensile strength and enhanced abrasion resistance compared to carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR). HNBR's improved chemical stability and heat resistance result in longer service life under intensive printing operations. In contrast, XNBR provides excellent elasticity and adhesion, but its lower thermal endurance limits durability in high-temperature print roller applications.
Resistance to Chemicals and Solvents
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals and solvents, including petroleum oils, fuels, and aliphatic hydrocarbons, making it ideal for print rollers exposed to harsh industrial environments. Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits enhanced tensile strength and abrasion resistance but provides moderate chemical resistance, particularly vulnerable to strong acids and bases compared to HNBR. For print rollers requiring durability against aggressive solvents and chemical exposure, HNBR presents a more reliable choice due to its hydrogenation process improving saturation and oxidative stability.
Heat and Ozone Resistance in Printing Applications
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior heat resistance, maintaining physical properties at temperatures up to 150degC, making it ideal for high-temperature printing roller applications. Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers enhanced ozone resistance due to the polar carboxyl groups, which improve durability in outdoor or ozone-exposed printing environments. For print rollers exposed to elevated heat and ozone levels, HNBR provides better thermal stability while XNBR ensures longer service life against ozone-induced degradation.
Abrasion and Tear Performance
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior abrasion resistance and tear strength compared to carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR), making it ideal for print roller applications where durability is critical. HNBR's saturated polymer backbone enhances thermal stability and chemical resistance, reducing wear and extending roller life under repetitive mechanical stress. In contrast, XNBR offers improved elasticity and grip but typically falls short in abrasion endurance and tear resistance, limiting its performance in high-demand printing environments.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance and durability for print rollers but comes at a higher cost due to its complex manufacturing process. Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR), while slightly less resistant to harsh chemicals, is more cost-effective and widely available for large-scale production, making it a budget-friendly option. The choice between HNBR and XNBR often hinges on balancing long-term performance needs against immediate cost and supply considerations in the printing industry.
Selecting the Optimal Rubber for Print Roller Applications
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat resistance, chemical stability, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for print roller applications in high-temperature and aggressive chemical environments. Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) provides enhanced tensile strength and oil resistance but may fall short in extreme conditions compared to HNBR. Selecting the optimal rubber for print rollers depends on balancing the operating environment with material properties, where HNBR excels in durability and longevity under demanding printing processes.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Carboxylated nitrile rubber for Print roller
 azmater.com
azmater.com