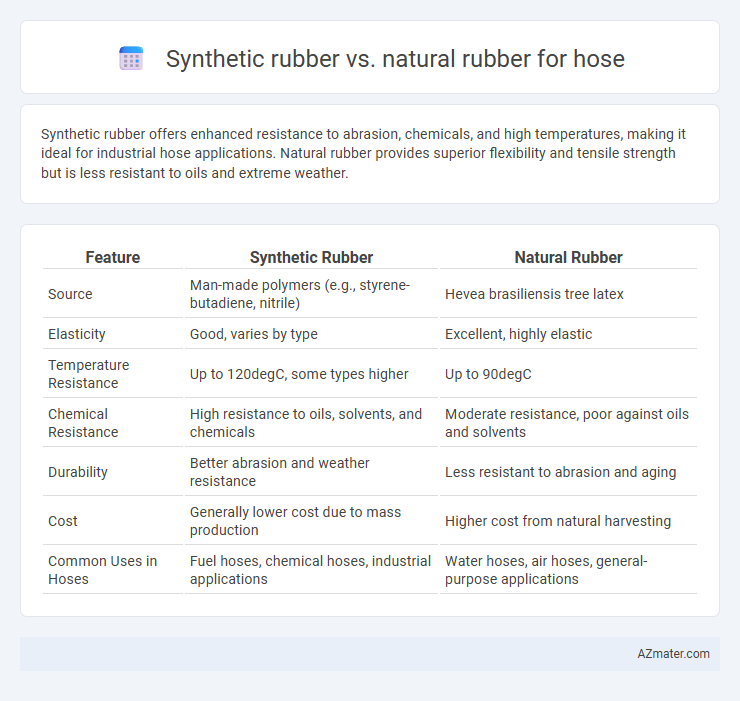
Synthetic rubber offers enhanced resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and high temperatures, making it ideal for industrial hose applications. Natural rubber provides superior flexibility and tensile strength but is less resistant to oils and extreme weather.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synthetic Rubber | Natural Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Man-made polymers (e.g., styrene-butadiene, nitrile) | Hevea brasiliensis tree latex |
| Elasticity | Good, varies by type | Excellent, highly elastic |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 120degC, some types higher | Up to 90degC |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to oils, solvents, and chemicals | Moderate resistance, poor against oils and solvents |
| Durability | Better abrasion and weather resistance | Less resistant to abrasion and aging |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to mass production | Higher cost from natural harvesting |
| Common Uses in Hoses | Fuel hoses, chemical hoses, industrial applications | Water hoses, air hoses, general-purpose applications |
Introduction to Rubber Types in Hose Manufacturing
Synthetic rubber, including varieties like SBR and NBR, offers enhanced resistance to oils, chemicals, and temperature extremes, making it ideal for industrial hose manufacturing. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity, flexibility, and abrasion resistance, primarily used in hoses requiring high resilience and durability. Selecting the appropriate rubber type significantly influences hose performance, longevity, and suitability for specific applications.
Chemical Composition: Synthetic vs Natural Rubber
Synthetic rubber, primarily composed of polymers like styrene-butadiene or nitrile butadiene, offers enhanced resistance to oils, chemicals, and temperature variations compared to natural rubber. Natural rubber consists mostly of polyisoprene, a polymer derived from latex sap, providing superior elasticity and tensile strength but limited chemical resistance. The chemical composition differences significantly affect hose performance, making synthetic rubber ideal for industrial applications where chemical exposure is high, while natural rubber suits environments requiring flexibility and abrasion resistance.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Synthetic rubber hoses generally exhibit superior mechanical properties compared to natural rubber, including higher tensile strength and enhanced abrasion resistance. Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and resilience but may degrade faster under harsh environmental conditions such as ozone and UV exposure. The choice depends on specific application needs, with synthetic rubber providing better durability and mechanical stability for demanding industrial hose applications.
Resistance to Chemicals and Abrasion
Synthetic rubber hoses exhibit superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals including oils, solvents, and acids, making them ideal for industrial applications where exposure to harsh substances is frequent. Natural rubber hoses offer excellent abrasion resistance due to their high elasticity and tensile strength, but they degrade faster when in contact with oils and certain chemicals. Choosing synthetic rubber enhances chemical resistance, while natural rubber prioritizes abrasion durability in hose construction.
Flexibility and Elasticity Differences
Synthetic rubber offers superior flexibility in hoses due to its engineered polymer structure, enabling consistent performance across a wider temperature range compared to natural rubber. Natural rubber exhibits higher elasticity, providing excellent stretch and recovery characteristics, which is ideal for applications requiring significant deformation and return to original shape. The choice between synthetic and natural rubber for hoses depends on operational conditions, with synthetic excelling in durability and temperature resistance, while natural rubber remains preferred for maximum elastic resilience.
Temperature Tolerance and Weather Resistance
Synthetic rubber hoses exhibit superior temperature tolerance, typically withstanding extreme temperatures ranging from -50degC to 150degC, compared to natural rubber's narrower range of approximately -40degC to 70degC. Weather resistance is significantly enhanced in synthetic rubber, which resists ozone, UV radiation, and oxidation more effectively than natural rubber, making it ideal for prolonged outdoor applications. The enhanced chemical composition of synthetic rubber ensures durability and flexibility under harsh environmental conditions, while natural rubber tends to degrade faster when exposed to weather elements.
Cost and Availability Factors
Synthetic rubber for hoses offers more consistent pricing due to stable manufacturing processes and raw material sources, whereas natural rubber is subject to price volatility influenced by climate and geopolitical factors affecting latex supply. Availability of synthetic rubber is higher and more reliable because it is produced industrially in large quantities worldwide, while natural rubber depends heavily on specific geographic regions, causing potential shortages. Cost considerations often favor synthetic rubber for large-scale hose production, as it provides economic predictability and reduced supply chain risks.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Synthetic rubber used in hoses typically derives from petrochemical sources, resulting in higher carbon emissions and less biodegradability compared to natural rubber, which is harvested from Hevea brasiliensis trees and is renewable and biodegradable. The production of natural rubber supports carbon sequestration in rubber plantations and reduces reliance on fossil fuels, promoting a smaller environmental footprint. However, issues like deforestation and land use change in natural rubber cultivation challenge its sustainability, while advances in bio-based synthetic rubbers aim to mitigate ecological impacts.
Typical Applications for Each Rubber Type
Synthetic rubber, such as nitrile and EPDM, is commonly used in hoses exposed to oil, chemicals, and extreme temperatures due to its superior resistance and durability in harsh environments. Natural rubber hoses excel in flexibility and abrasion resistance, making them ideal for air, water, and general-purpose industrial applications where elasticity and resilience are essential. Specific applications include fuel and hydraulic lines for synthetic rubber, while natural rubber is preferred for garden hoses, pneumatic lines, and material handling systems.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Hose Needs
Synthetic rubber offers superior resistance to chemicals, temperature extremes, and abrasion, making it ideal for industrial and heavy-duty hose applications. Natural rubber provides excellent flexibility, tensile strength, and resilience, suitable for hoses in agricultural and general-purpose uses. Selecting the right rubber depends on factors such as environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and specific performance requirements to ensure durability and efficiency.
Infographic: Synthetic rubber vs Natural rubber for Hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com