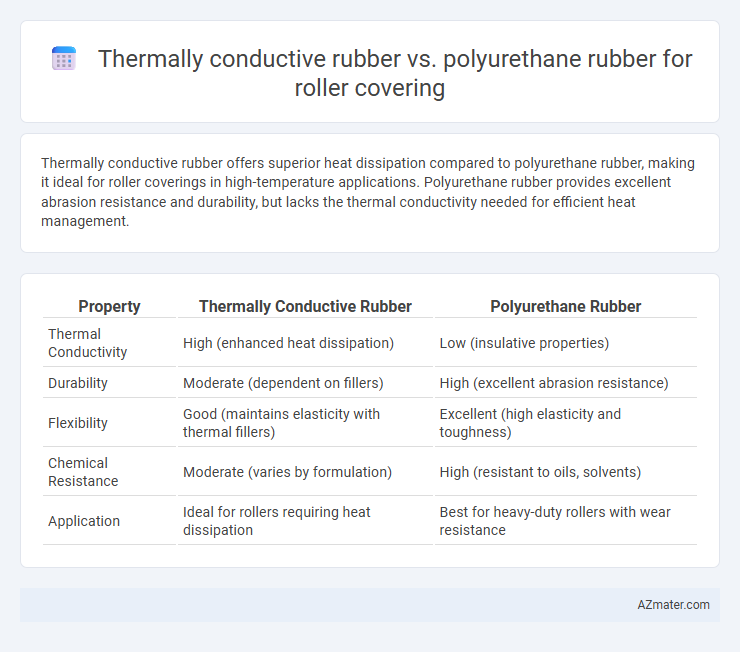
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior heat dissipation compared to polyurethane rubber, making it ideal for roller coverings in high-temperature applications. Polyurethane rubber provides excellent abrasion resistance and durability, but lacks the thermal conductivity needed for efficient heat management.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermally Conductive Rubber | Polyurethane Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | High (enhanced heat dissipation) | Low (insulative properties) |
| Durability | Moderate (dependent on fillers) | High (excellent abrasion resistance) |
| Flexibility | Good (maintains elasticity with thermal fillers) | Excellent (high elasticity and toughness) |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate (varies by formulation) | High (resistant to oils, solvents) |
| Application | Ideal for rollers requiring heat dissipation | Best for heavy-duty rollers with wear resistance |
Introduction to Roller Covering Materials
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior heat dissipation properties, making it ideal for roller coverings in high-temperature industrial applications, whereas polyurethane rubber is favored for its exceptional abrasion resistance and elasticity. Roller coverings require materials that balance durability, thermal management, and flexibility to ensure optimal performance and extended service life. Selecting between thermally conductive rubber and polyurethane rubber depends on specific operational demands such as heat exposure, mechanical stress, and required grip characteristics.
Importance of Thermal Conductivity in Rollers
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior heat dissipation compared to polyurethane rubber, crucial for maintaining optimal roller temperature and preventing overheating during high-speed or heavy-load applications. Enhanced thermal conductivity in roller coverings minimizes thermal expansion and deformation, extending roller lifespan and ensuring consistent material processing quality. Polyurethane rubber, while durable and wear-resistant, generally lacks the thermal management capabilities essential for applications with significant heat generation, making thermally conductive rubber preferable for precision industrial rollers.
Overview of Thermally Conductive Rubber
Thermally conductive rubber is engineered to efficiently dissipate heat while maintaining flexibility and durability, making it ideal for roller coverings that require temperature management. This material often incorporates fillers like boron nitride or graphite to enhance thermal conductivity without compromising mechanical performance. Its superior heat transfer properties prevent overheating and improve the longevity and operational efficiency of rollers in industrial applications compared to traditional polyurethane rubber.
Properties of Polyurethane Rubber
Polyurethane rubber for roller covering offers exceptional abrasion resistance and high tensile strength, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and longevity. Its excellent chemical resistance and flexibility enable it to maintain performance under varying temperatures and exposure to oils or solvents. Compared to thermally conductive rubber, polyurethane rubber provides superior mechanical properties that enhance roller lifespan and reduce maintenance frequency.
Heat Dissipation: Thermally Conductive Rubber vs Polyurethane
Thermally conductive rubber outperforms polyurethane rubber in roller covering applications by efficiently dissipating heat generated during high-speed rotation or frictional contact, reducing thermal degradation and extending roller lifespan. The intrinsic thermal conductivity of thermally conductive rubber facilitates rapid heat transfer away from critical contact surfaces, whereas polyurethane rubber exhibits comparatively lower thermal conductivity, often leading to heat accumulation and potential material breakdown. Optimizing roller covering with thermally conductive rubber enhances operational stability and prevents temperature-induced deformation common in polyurethane alternatives.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior mechanical strength with enhanced resistance to wear and tear compared to polyurethane rubber, making it ideal for high-performance roller coverings subjected to continuous friction. Polyurethane rubber provides good durability but tends to degrade faster under extreme thermal and mechanical stress, limiting its lifespan in heavy-duty applications. The thermally conductive variant ensures consistent performance and longevity by dissipating heat effectively, reducing the risk of material breakdown during prolonged operational cycles.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Thermally conductive rubber outperforms polyurethane rubber in roller covering applications exposed to high-temperature environments due to its superior heat dissipation properties, reducing thermal degradation and extending roller lifespan. Polyurethane rubber, while offering excellent abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, tends to soften and lose elasticity at elevated temperatures above 80degC, leading to increased wear and potential premature failure. Selecting thermally conductive rubber ensures consistent performance and operational efficiency in industrial processes involving sustained high heat, such as plastic extrusion or metal processing.
Cost and Longevity Analysis
Thermally conductive rubber offers enhanced heat dissipation properties that extend roller lifespan by preventing overheating, but it generally comes at a higher initial cost compared to polyurethane rubber. Polyurethane rubber provides excellent wear resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and budget-conscious solutions. The longevity of thermally conductive rubber often justifies its premium price in high-temperature environments, whereas polyurethane rubber excels in mechanical toughness and abrasion resistance for standard roller covering needs.
Industry Applications: Choosing the Right Material
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior heat dissipation, making it ideal for roller coverings in electronics manufacturing and automotive industries where temperature control is critical. Polyurethane rubber excels in abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, preferred in heavy-duty applications like printing presses and conveyor systems. Selecting the right material depends on the operational environment, with thermally conductive rubber suited for high-heat scenarios and polyurethane rubber favored for durability and mechanical stress resistance.
Conclusion: Selecting Optimal Roller Covering Material
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior heat dissipation and enhanced durability, making it ideal for high-temperature roller applications, whereas polyurethane rubber provides excellent abrasion resistance and elasticity, suitable for general-purpose rollers with moderate thermal demands. The choice depends on operational temperature, mechanical stress, and environmental exposure; thermally conductive rubber minimizes thermal degradation and improves process efficiency, while polyurethane ensures longevity under mechanical wear. Selecting the optimal roller covering material requires balancing thermal management needs with mechanical performance to maximize roller lifespan and functionality.
Infographic: Thermally conductive rubber vs Polyurethane rubber for Roller covering
 azmater.com
azmater.com