Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent adhesion for automotive seals, enhancing durability under extreme temperatures. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides exceptional resistance to weathering, ozone, and heat, making it ideal for long-lasting automotive sealing applications.
Table of Comparison
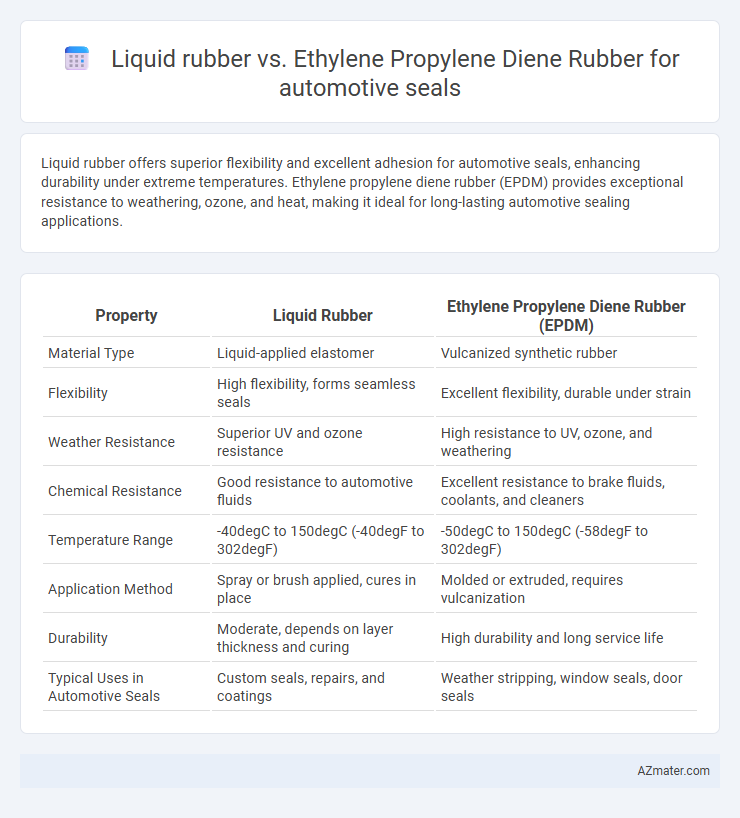
| Property | Liquid Rubber | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Liquid-applied elastomer | Vulcanized synthetic rubber |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, forms seamless seals | Excellent flexibility, durable under strain |
| Weather Resistance | Superior UV and ozone resistance | High resistance to UV, ozone, and weathering |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to automotive fluids | Excellent resistance to brake fluids, coolants, and cleaners |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC (-40degF to 302degF) | -50degC to 150degC (-58degF to 302degF) |
| Application Method | Spray or brush applied, cures in place | Molded or extruded, requires vulcanization |
| Durability | Moderate, depends on layer thickness and curing | High durability and long service life |
| Typical Uses in Automotive Seals | Custom seals, repairs, and coatings | Weather stripping, window seals, door seals |
Introduction to Automotive Seal Materials
Automotive seals require materials with excellent durability, weather resistance, and flexibility to withstand harsh environmental conditions. Liquid rubber offers superior adhesion and seamless application, making it ideal for complex shapes and irregular surfaces, while ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides exceptional resistance to ozone, UV, and temperature variations. Both materials are widely used, but EPDM's proven longevity in automotive sealing applications often sets the industry standard for weatherstripping, gaskets, and window seals.
Overview of Liquid Rubber: Properties and Applications
Liquid rubber exhibits excellent flexibility, superior chemical resistance, and strong adhesion, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to varying temperatures and harsh environments. Its seamless, waterproof coating properties prevent leaks and enhance durability in engine compartments, doors, and windows. Widely used in automotive sealing applications, liquid rubber ensures long-lasting performance and reduces maintenance costs compared to traditional Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber seals.
Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM): Key Features
Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) excels in automotive seals due to its superior resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, ensuring long-term durability in harsh environments. EPDM's excellent flexibility and compatibility with various fluids, including antifreeze and brake fluids, make it ideal for maintaining airtight and watertight seals. Compared to liquid rubber, EPDM offers enhanced mechanical strength and thermal stability, critical for automotive applications requiring reliable sealing performance.
Durability Comparison: Liquid Rubber vs EPDM
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent resistance to extreme temperatures and chemicals, enhancing the durability of automotive seals under harsh conditions. EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) rubber demonstrates outstanding resistance to ozone, UV rays, and weathering, maintaining seal integrity over prolonged exposure to environmental stressors. While both materials provide excellent durability, EPDM is often preferred for long-term outdoor applications due to its proven resistance to aging and erosion, whereas liquid rubber excels in applications requiring versatile adhesion and adaptability to complex surfaces.
Chemical Resistance: Performance in Harsh Conditions
Liquid rubber offers superior chemical resistance to automotive seals, effectively withstanding exposure to oils, fuels, and aggressive solvents, which ensures prolonged durability in harsh environments. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) exhibits excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering but is less effective against hydrocarbons and certain aggressive chemicals compared to liquid rubber. For automotive sealing applications demanding robust chemical resistance and exposure to diverse fluids, liquid rubber delivers enhanced performance and longevity over EPDM.
Flexibility and Elasticity: Which Offers Better Sealing?
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility due to its ability to form seamless, conforming seals that adapt to complex automotive surfaces, enhancing elasticity under varying temperatures and pressures. Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber provides excellent elasticity with robust resistance to weathering, ozone, and heat, maintaining a consistent seal in harsh conditions. For automotive seals requiring dynamic flexibility and stretch without compromising durability, liquid rubber generally delivers better sealing performance, especially in irregular or movable joints.
Ease of Application and Processing
Liquid rubber offers superior ease of application for automotive seals due to its pourable or sprayable form, enabling seamless coverage on complex geometries without the need for extensive molding equipment. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber requires more intricate processing, including vulcanization and molding, making it less flexible for on-demand or custom sealing solutions. The processing time and equipment costs are typically lower with liquid rubber, enhancing efficiency in automotive seal production.
Cost Analysis: Liquid Rubber vs EPDM
Liquid rubber typically offers lower upfront material costs and faster application processes compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM), reducing overall manufacturing expenses for automotive seals. EPDM, while more expensive initially, provides superior durability, chemical resistance, and temperature tolerance, potentially lowering long-term maintenance and replacement costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that liquid rubber suits budget-sensitive projects, whereas EPDM justifies higher investment through enhanced seal longevity in demanding automotive environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Liquid rubber and Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) both serve automotive seal applications with distinct environmental profiles. Liquid rubber offers enhanced sustainability due to its solvent-free, low VOC formulation and potential for reduced waste through precise, on-demand application. EPDM, while durable and resistant to weathering, involves energy-intensive manufacturing and challenges in recycling, making liquid rubber a more eco-friendly choice for automotive seals aiming to reduce environmental impact.
Final Recommendation: Choosing the Right Seal Material
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent adhesion for complex automotive seal applications, while Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber provides outstanding weather, ozone resistance, and durability under extreme temperatures. EPDM is often preferred for external seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions, whereas liquid rubber is ideal for intricate molds requiring seamless coverage and waterproofing. Selecting the right seal material depends on the specific performance requirements, with EPDM favored for longevity and liquid rubber excelling in adaptability and precision sealing.
Infographic: Liquid rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Automotive seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com