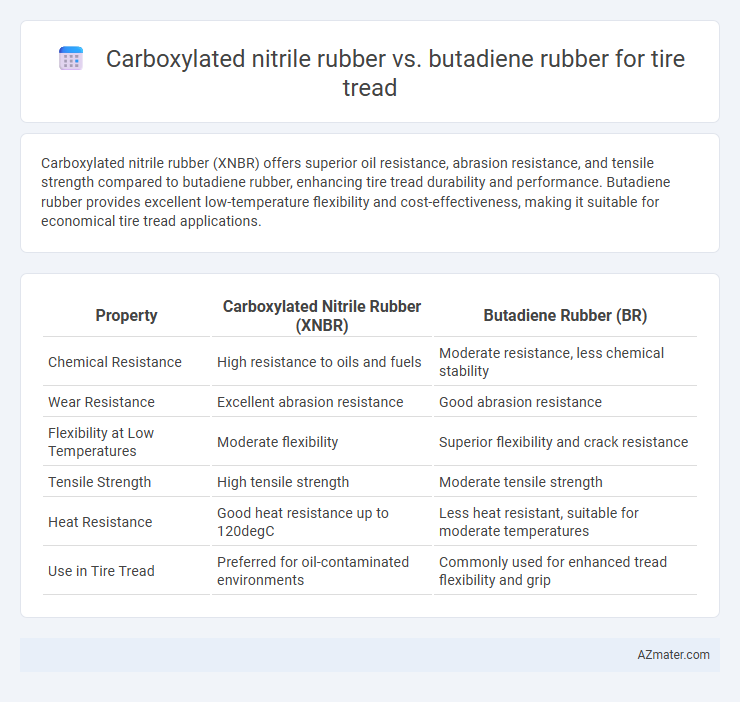
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance, abrasion resistance, and tensile strength compared to butadiene rubber, enhancing tire tread durability and performance. Butadiene rubber provides excellent low-temperature flexibility and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for economical tire tread applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) | Butadiene Rubber (BR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to oils and fuels | Moderate resistance, less chemical stability |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent abrasion resistance | Good abrasion resistance |
| Flexibility at Low Temperatures | Moderate flexibility | Superior flexibility and crack resistance |
| Tensile Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Heat Resistance | Good heat resistance up to 120degC | Less heat resistant, suitable for moderate temperatures |
| Use in Tire Tread | Preferred for oil-contaminated environments | Commonly used for enhanced tread flexibility and grip |
Introduction to Tire Tread Materials
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers enhanced abrasion resistance and oil resistance, making it suitable for demanding tire tread applications requiring durability and chemical stability. Butadiene rubber (BR) is valued for its excellent wear resistance and low rolling resistance, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and tread life in tires. The combination or selection between XNBR and BR depends on balancing elasticity, grip performance, and environmental resistance in tire tread formulations.
Overview of Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR)
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers enhanced tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and fuel resistance compared to traditional butadiene rubber, making it ideal for high-performance tire treads. The presence of carboxyl groups in XNBR improves cross-linking density, leading to superior durability and chemical resistance under harsh conditions. XNBR's balanced flexibility and resilience ensure better wet traction and longer tread life in automotive applications.
Overview of Butadiene Rubber (BR)
Butadiene rubber (BR) is a synthetic rubber known for its excellent abrasion resistance and high resilience, making it a preferred material for tire treads. It offers superior wear properties and low rolling resistance compared to carboxylated nitrile rubber, enhancing fuel efficiency and tire longevity. BR's unsaturated polymer structure provides good flexibility and traction under various road conditions, contributing to overall tire performance.
Key Performance Properties Comparison
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior abrasion resistance, oil resistance, and tensile strength compared to butadiene rubber (BR), making it highly suitable for tire tread applications demanding durability in harsh environments. Butadiene rubber delivers excellent wear resistance and low-temperature flexibility, contributing to improved grip and traction on dry and wet surfaces. The enhanced polarity and crosslink density of XNBR result in better heat resistance and reduced rolling resistance, optimizing tire performance and fuel efficiency.
Abrasion Resistance: XNBR vs BR
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior abrasion resistance compared to butadiene rubber (BR), making it a preferred choice for tire treads requiring enhanced durability under harsh conditions. The presence of carboxyl groups in XNBR facilitates stronger intermolecular bonding, resulting in improved wear resistance and longer tread life. BR, while providing good flexibility and grip, tends to exhibit higher wear rates, limiting its performance in high-abrasion applications relative to XNBR.
Wet and Dry Traction Differences
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior wet traction compared to butadiene rubber (BR) due to its enhanced polarity and improved interaction with water molecules, reducing hydroplaning risks. In dry conditions, butadiene rubber exhibits better abrasion resistance and higher tensile strength, resulting in improved durability and dry traction performance. The combination of XNBR's excellent wet grip and BR's robust dry traction makes them complementary materials often blended for optimized tire tread performance.
Aging and Weather Resistance
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior aging and weather resistance compared to butadiene rubber (BR) in tire tread applications, due to its enhanced polar functionality and crosslink density, which improve oxidation and ozone resistance. XNBR exhibits better retention of mechanical properties under prolonged exposure to UV radiation, heat, and atmospheric conditions, resulting in longer tire life and safer performance. In contrast, butadiene rubber is more prone to oxidative degradation and cracking, especially in harsh environments, limiting its effectiveness in weather-critical applications.
Processability for Tire Manufacturers
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior processability for tire manufacturers due to its enhanced dispersion of fillers and compatibility with various compounding ingredients, resulting in easier mixing and shaping compared to butadiene rubber (BR). XNBR exhibits better heat resistance and mechanical properties during processing, reducing cycle times and improving mold release in tire tread production. While BR provides good abrasion resistance and elasticity, its lower polarity makes filler dispersion more challenging, often necessitating additional processing steps to achieve optimal tire tread performance.
Cost-Effectiveness and Market Availability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers enhanced abrasion resistance and oil resistance compared to butadiene rubber (BR), making it more cost-effective in high-performance tire treads despite its higher raw material price. Butadiene rubber dominates tire tread applications due to its lower cost and widespread market availability, ensuring bulk procurement and stable supply chains for large-scale tire manufacturing. The balance between XNBR's superior durability and BR's affordability leads manufacturers to select blends or pure BR based on targeted performance and budget constraints.
Conclusion: Optimal Applications for XNBR and BR in Tire Tread
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior abrasion resistance, oil resistance, and enhanced mechanical strength, making it ideal for tire treads used in industrial and heavy-duty applications where durability and chemical exposure are critical. Butadiene rubber (BR) provides excellent flexibility, low rolling resistance, and better performance in cold conditions, making it optimal for passenger car tire treads that prioritize fuel efficiency and wear resistance. Selecting XNBR ensures longevity in harsh environments, while BR excels in providing balanced tread performance for everyday driving conditions.
Infographic: Carboxylated nitrile rubber vs Butadiene rubber for Tire tread
 azmater.com
azmater.com