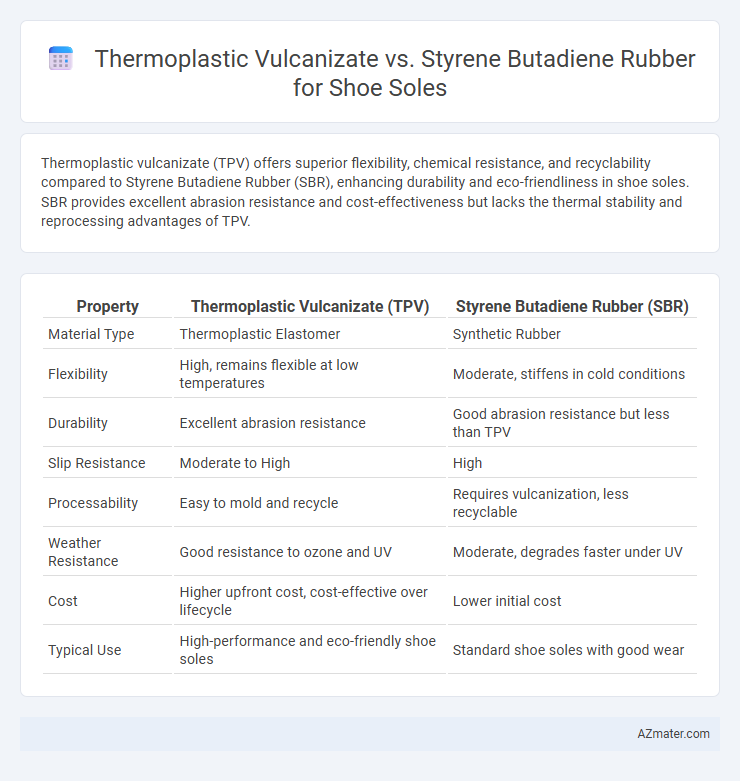
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and recyclability compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), enhancing durability and eco-friendliness in shoe soles. SBR provides excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness but lacks the thermal stability and reprocessing advantages of TPV.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Elastomer | Synthetic Rubber |
| Flexibility | High, remains flexible at low temperatures | Moderate, stiffens in cold conditions |
| Durability | Excellent abrasion resistance | Good abrasion resistance but less than TPV |
| Slip Resistance | Moderate to High | High |
| Processability | Easy to mold and recycle | Requires vulcanization, less recyclable |
| Weather Resistance | Good resistance to ozone and UV | Moderate, degrades faster under UV |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost, cost-effective over lifecycle | Lower initial cost |
| Typical Use | High-performance and eco-friendly shoe soles | Standard shoe soles with good wear |
Overview of Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV) and Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) is a blend of rubber and thermoplastic, offering excellent flexibility, durability, and resistance to heat and chemicals, making it ideal for lightweight and comfortable shoe soles. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) is a synthetic rubber known for its abrasion resistance, good aging stability, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in shoe soles requiring enhanced grip and toughness. Both materials deliver distinct performance benefits for footwear, with TPV excelling in elasticity and recyclability, while SBR provides superior wear resistance and impact absorption.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPVs) consist of a dynamically vulcanized rubber phase dispersed within a thermoplastic matrix, typically polypropylene, combining elastomeric properties with thermoplastic processability. Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a synthetic copolymer of styrene and butadiene, characterized by its amorphous rubbery nature and high abrasion resistance. The chemical structure of TPVs provides enhanced thermal stability and recyclability, while SBR offers superior elasticity and damping due to its unsaturated hydrocarbon chains and random copolymer composition.
Mechanical Properties: Strength, Flexibility, and Durability
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior flexibility and high tensile strength compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), making TPV ideal for dynamic shoe sole applications requiring resilience. SBR exhibits excellent abrasion resistance and maintains durability under repetitive impact, but its flexibility is lower than TPV's elastomeric behavior. For shoe soles subjected to varying mechanical stresses, TPV provides enhanced durability and cushioning without sacrificing strength, whereas SBR performs well in cost-sensitive designs with moderate flexibility requirements.
Wear Resistance and Longevity in Shoe Soles
Thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPVs) offer superior wear resistance compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) in shoe soles, attributed to their enhanced elastic recovery and abrasion resistance. TPV materials exhibit longer longevity under repetitive mechanical stress, maintaining sole integrity and cushioning properties over time. In contrast, SBR soles tend to degrade faster due to lower resistance to abrasion and environmental factors, resulting in reduced durability for high-performance footwear.
Comfort and Cushioning Performance
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior cushioning performance and resilience for shoe soles compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), providing enhanced shock absorption and long-lasting comfort during prolonged wear. TPV's unique blend of thermoplastic and elastomeric properties delivers excellent flexibility and energy return, reducing foot fatigue. In contrast, SBR, while cost-effective, tends to harden over time, diminishing its cushioning effect and comfort levels in high-impact footwear applications.
Processing Methods and Manufacturing Efficiency
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior processing efficiency over Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) due to its compatibility with injection and extrusion molding, enabling faster cycle times and reduced energy consumption. SBR requires longer vulcanization and curing steps, limiting production speed and increasing manufacturing costs. TPV's recyclability and reprocessability further enhance sustainability and cost-effectiveness in high-volume shoe sole manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers enhanced environmental sustainability for shoe soles due to its recyclability and lower energy consumption during manufacturing compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), which is derived from non-renewable petroleum-based sources and is less amenable to recycling. TPV's ability to be reprocessed reduces landfill waste, aligning with circular economy principles, while SBR soles typically generate more carbon emissions throughout their lifecycle due to vulcanization and limited end-of-life options. Choosing TPV materials can thus significantly reduce the ecological footprint of footwear production through improved resource efficiency and reduced pollutant output.
Cost Analysis: TPV vs SBR for Shoe Soles
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) generally incurs higher upfront material costs compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), but offers savings in manufacturing due to its thermoplastic processing advantages such as faster molding cycles and recyclability. SBR remains cost-effective for large-scale production because of its lower raw material price and well-established processing techniques, though it may result in higher post-processing expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership, TPV provides long-term benefits with durability and reduced waste, offsetting initial expenses for mid to premium shoe sole applications.
Applications and Suitability for Various Shoe Types
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers excellent flexibility, durability, and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for athletic and casual shoe soles requiring lightweight and cushioning properties. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides superior wear resistance and better grip, frequently used in work boots and outdoor footwear where toughness and traction are critical. TPV's recyclability and processability suit mass production and fashion footwear, while SBR's robustness favors heavy-duty and industrial shoe applications.
Future Trends and Innovations in Shoe Sole Materials
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) is gaining prominence in shoe sole manufacturing due to its enhanced durability, lightweight nature, and recyclability compared to traditional Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), making it a preferred choice for sustainable footwear innovation. Future trends emphasize TPV's compatibility with advanced manufacturing techniques such as 3D printing and injection molding, enabling complex sole designs that improve comfort and biomechanical performance. Innovations in polymer blends and nanocomposites are expected to further enhance TPV's abrasion resistance and elasticity, positioning it as a cutting-edge material for next-generation shoe soles.
Infographic: Thermoplastic vulcanizate vs Styrene Butadiene Rubber for Shoe Sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com