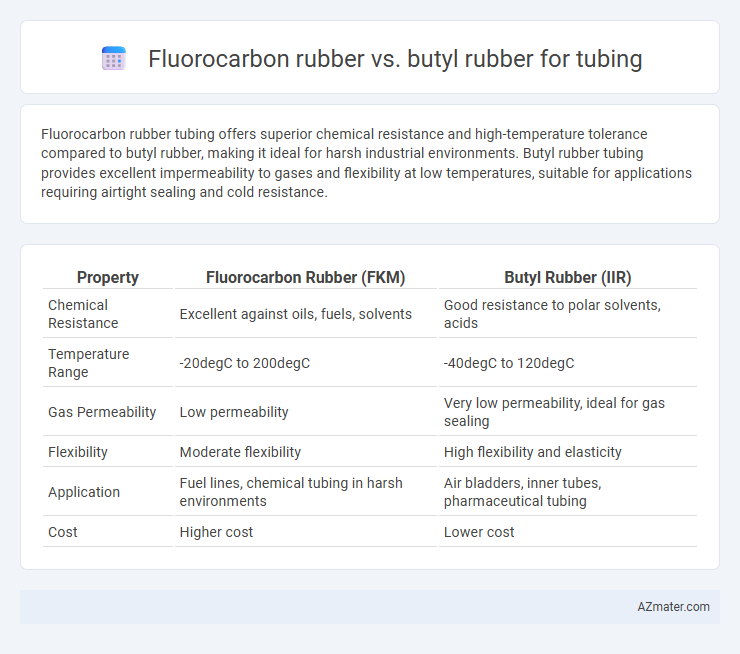
Fluorocarbon rubber tubing offers superior chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance compared to butyl rubber, making it ideal for harsh industrial environments. Butyl rubber tubing provides excellent impermeability to gases and flexibility at low temperatures, suitable for applications requiring airtight sealing and cold resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluorocarbon Rubber (FKM) | Butyl Rubber (IIR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against oils, fuels, solvents | Good resistance to polar solvents, acids |
| Temperature Range | -20degC to 200degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Gas Permeability | Low permeability | Very low permeability, ideal for gas sealing |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High flexibility and elasticity |
| Application | Fuel lines, chemical tubing in harsh environments | Air bladders, inner tubes, pharmaceutical tubing |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
Introduction to Fluorocarbon and Butyl Rubber Tubing
Fluorocarbon rubber tubing, known for its exceptional chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, is widely used in automotive, aerospace, and chemical processing industries where durability under harsh conditions is critical. Butyl rubber tubing offers excellent airtightness and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring resistance to gases, ozone, and weathering, such as medical devices and sealing components. Choosing between fluorocarbon and butyl rubber tubing depends on specific performance requirements like temperature range, chemical exposure, and environmental factors.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) contains copolymers of vinylidene fluoride and hexafluoropropylene, characterized by strong carbon-fluorine bonds that enhance its chemical resistance and thermal stability. Butyl rubber (IIR) is a copolymer of isobutylene with a small amount of isoprene, featuring a saturated hydrocarbon backbone that provides excellent impermeability and flexibility but lower resistance to solvents. The molecular structure of FKM's fluorinated chains grants superior resistance to oils, fuels, and aggressive chemicals, whereas butyl rubber's saturated hydrocarbon structure excels in gas retention and weather resistance but is less compatible with harsh chemical environments.
Temperature Resistance: Fluorocarbon vs Butyl Rubber
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) offers superior temperature resistance, withstanding continuous exposure up to 200-250degC, compared to butyl rubber's maximum temperature tolerance of around 120-150degC. This makes fluorocarbon tubing ideal for high-temperature applications such as chemical processing and automotive use. Butyl rubber excels in low-temperature flexibility but degrades faster under extreme heat, limiting its application in elevated temperature environments.
Chemical Resistance and Compatibility
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) offers superior chemical resistance compared to butyl rubber, excelling in environments with exposure to oils, fuels, and solvents due to its high fluorine content. Butyl rubber provides excellent resistance to water, acids, and alkalis but lacks the solvent and hydrocarbon resistance found in fluorocarbon rubber. When selecting tubing for chemical compatibility, fluorocarbon rubber is ideal for aggressive chemical applications, whereas butyl rubber suits applications requiring moisture and gas impermeability.
Physical Properties and Durability
Fluorocarbon rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance, high-temperature stability up to 200degC, and excellent abrasion resistance, making it ideal for harsh environments and aggressive fluids. Butyl rubber offers exceptional impermeability to gases, excellent flexibility at low temperatures, and outstanding resistance to weathering, ozone, and aging, though it degrades at temperatures above 120degC. In terms of durability, fluorocarbon rubber outperforms butyl rubber in extreme thermal and chemical conditions, while butyl rubber excels in maintaining elasticity and sealing performance in moderate temperature applications.
Flexibility and Elasticity Differences
Fluorocarbon rubber tubing exhibits superior chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance but has lower flexibility and elasticity compared to butyl rubber tubing. Butyl rubber offers excellent flexibility and elasticity, making it ideal for applications requiring repetitive stretching and compressive forces. The molecular structure of butyl rubber provides enhanced elongation and recovery, whereas fluorocarbon rubber's rigidity limits its use in highly dynamic environments.
Applications in Industrial and Medical Tubing
Fluorocarbon rubber exhibits exceptional chemical resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents, making it ideal for industrial tubing applications involving harsh chemical exposure and high temperatures. Butyl rubber offers superior impermeability to gases and excellent flexibility, which is critical for medical tubing requiring airtight seals and biocompatibility. Both materials fulfill demanding performance criteria, with fluorocarbon rubber preferred for solvent resistance and butyl rubber favored for gas barrier properties in specialized tubing solutions.
Cost Effectiveness and Availability
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance and temperature tolerance for tubing applications but comes with a higher cost compared to Butyl rubber, which is more budget-friendly and widely available. Butyl rubber excels in gas impermeability and flexibility, making it a cost-effective choice for general tubing needs where extreme chemical resistance is not required. Availability of Butyl rubber is broader globally, supporting faster procurement and lower operational expenses.
Maintenance and Lifespan Considerations
Fluorocarbon rubber tubing demonstrates superior chemical resistance and withstands high temperatures between -40degC to 205degC, resulting in lower maintenance requirements and a longer lifespan in harsh environments compared to butyl rubber. Butyl rubber tubing offers excellent impermeability to gases and good abrasion resistance but tends to degrade faster under UV exposure and elevated temperatures above 120degC, increasing maintenance frequency. Choosing fluorocarbon rubber over butyl rubber for tubing applications can reduce downtime and replacement costs due to its enhanced durability and resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents.
Choosing the Right Tubing Material: Key Takeaways
Fluorocarbon rubber offers exceptional chemical resistance, high temperature tolerance up to 200degC, and durability in harsh environments, making it ideal for tubing exposed to aggressive chemicals and oils. Butyl rubber provides superior impermeability to gases, excellent flexibility at low temperatures, and resistance to weathering, suitable for applications requiring airtight seals and resistance to ozone. Selecting the right tubing material depends on balancing chemical exposure, temperature range, and gas permeability requirements.
Infographic: Fluorocarbon rubber vs Butyl rubber for Tubing
 azmater.com
azmater.com