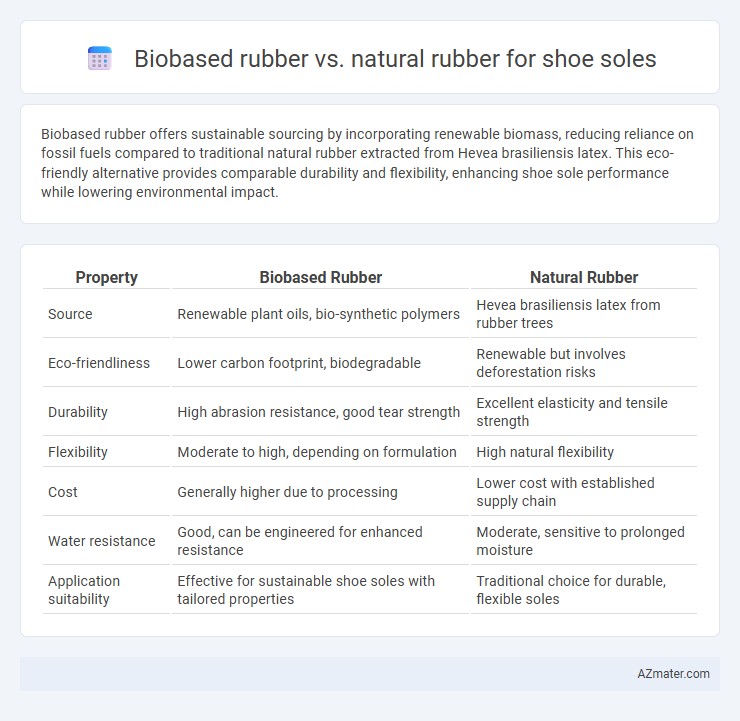
Biobased rubber offers sustainable sourcing by incorporating renewable biomass, reducing reliance on fossil fuels compared to traditional natural rubber extracted from Hevea brasiliensis latex. This eco-friendly alternative provides comparable durability and flexibility, enhancing shoe sole performance while lowering environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Biobased Rubber | Natural Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable plant oils, bio-synthetic polymers | Hevea brasiliensis latex from rubber trees |
| Eco-friendliness | Lower carbon footprint, biodegradable | Renewable but involves deforestation risks |
| Durability | High abrasion resistance, good tear strength | Excellent elasticity and tensile strength |
| Flexibility | Moderate to high, depending on formulation | High natural flexibility |
| Cost | Generally higher due to processing | Lower cost with established supply chain |
| Water resistance | Good, can be engineered for enhanced resistance | Moderate, sensitive to prolonged moisture |
| Application suitability | Effective for sustainable shoe soles with tailored properties | Traditional choice for durable, flexible soles |
Introduction to Rubber Types in Footwear
Biobased rubber and natural rubber both serve as essential materials for shoe soles, offering distinct properties that influence durability and comfort. Natural rubber, harvested from rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis), provides excellent elasticity and resilience, making it a traditional choice in footwear manufacturing. Biobased rubber, derived from renewable plant sources like guayule or dandelion, presents an eco-friendly alternative with comparable performance, aligning with sustainable footwear trends.
What is Biobased Rubber?
Biobased rubber is a sustainable alternative derived from renewable biomass sources such as guayule or dandelion roots, designed to reduce reliance on petroleum-based materials. Unlike natural rubber harvested from Hevea brasiliensis trees, biobased rubber can be produced with lower environmental impact and enhanced control over material properties, making it ideal for eco-friendly shoe soles. This innovative material offers comparable durability and elasticity while promoting a circular economy in the footwear industry.
Understanding Natural Rubber
Natural rubber, derived from the latex of Hevea brasiliensis trees, possesses excellent elasticity, resilience, and abrasion resistance, making it a preferred material for shoe soles. Its molecular structure consists of cis-1,4-polyisoprene, which provides superior flexibility and tensile strength compared to synthetic alternatives. Unlike biobased rubber, natural rubber offers consistent performance in wet conditions and maintains durability over prolonged use, key factors for high-quality footwear.
Sourcing and Sustainability Comparison
Biobased rubber for shoe soles is derived from renewable resources such as agricultural byproducts or engineered bio-polymers, reducing dependence on traditional rubber tree plantations that face deforestation and land degradation risks. Natural rubber, harvested from Hevea brasiliensis trees, provides high elasticity and durability but involves intensive land use and susceptibility to diseases affecting long-term supply stability. Sustainable sourcing of biobased rubber promotes circular economy principles, lower carbon footprints, and less environmental impact compared to conventional natural rubber, making it a more eco-friendly choice for footwear manufacturing.
Performance and Durability Differences
Biobased rubber for shoe soles offers enhanced sustainability with comparable elasticity and abrasion resistance to natural rubber, but it may exhibit slightly lower tensile strength under extreme stress. Natural rubber provides superior resilience and long-term durability due to its high molecular weight and natural polymer structure, ensuring better performance in demanding conditions. The choice between biobased and natural rubber influences shoe sole longevity, grip, and flexibility based on specific environmental and mechanical stress factors.
Environmental Impact: Biobased vs Natural
Biobased rubber for shoe soles offers a lower environmental impact by utilizing renewable feedstocks derived from agricultural waste or non-food biomass, reducing reliance on rubber tree plantations that contribute to deforestation. Natural rubber, sourced primarily from Hevea brasiliensis trees, involves land-intensive cultivation often linked to habitat loss and biodiversity decline. The production of biobased rubber typically results in lower greenhouse gas emissions and reduced water consumption compared to the natural rubber supply chain.
Processing and Manufacturing Considerations
Biobased rubber for shoe soles offers improved sustainability by utilizing renewable resources, but it often requires specialized compounding and curing processes to achieve performance parity with natural rubber. Natural rubber exhibits excellent elasticity and resilience, benefiting from well-established manufacturing techniques such as mastication and vulcanization that provide consistent quality and durability. Processing biobased rubber may involve modifications in temperature control and mixing times to optimize filler dispersion and crosslink density, impacting the final sole's wear resistance and flexibility.
Cost Analysis for Shoe Manufacturers
Biobased rubber, derived from renewable resources like plant oils or agricultural waste, often presents higher initial production costs compared to traditional natural rubber sourced from Hevea brasiliensis trees. Shoe manufacturers must consider the fluctuating raw material prices influenced by agricultural yields and market demand for both types, with biobased rubber potentially reducing long-term expenses through sustainability incentives and lower environmental compliance costs. Cost analysis reveals that while natural rubber benefits from established supply chains and lower upfront costs, biobased alternatives can offer competitive pricing when factoring in life-cycle cost savings and consumer preference for eco-friendly products.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Consumer perception increasingly favors biobased rubber for shoe soles due to its environmental benefits and sustainable sourcing, driving demand in eco-conscious markets. Natural rubber maintains strong recognition for durability and performance but faces challenges with deforestation concerns and supply volatility. Market trends reveal a growing shift towards biobased alternatives as brands emphasize carbon footprint reduction and circular economy principles in footwear production.
Future Outlook for Shoe Sole Materials
Biobased rubber for shoe soles is gaining traction due to its sustainable production from renewable resources, reducing dependency on fossil fuels and lowering carbon footprints compared to natural rubber sourced from Hevea brasiliensis. Advances in polymer science are enhancing the flexibility, durability, and wear resistance of biobased rubbers, making them viable contenders in high-performance footwear applications. Innovations in biodegradability and recyclability position biobased rubber as a future-proof material aligned with circular economy principles in the shoe sole industry.
Infographic: Biobased rubber vs Natural rubber for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com