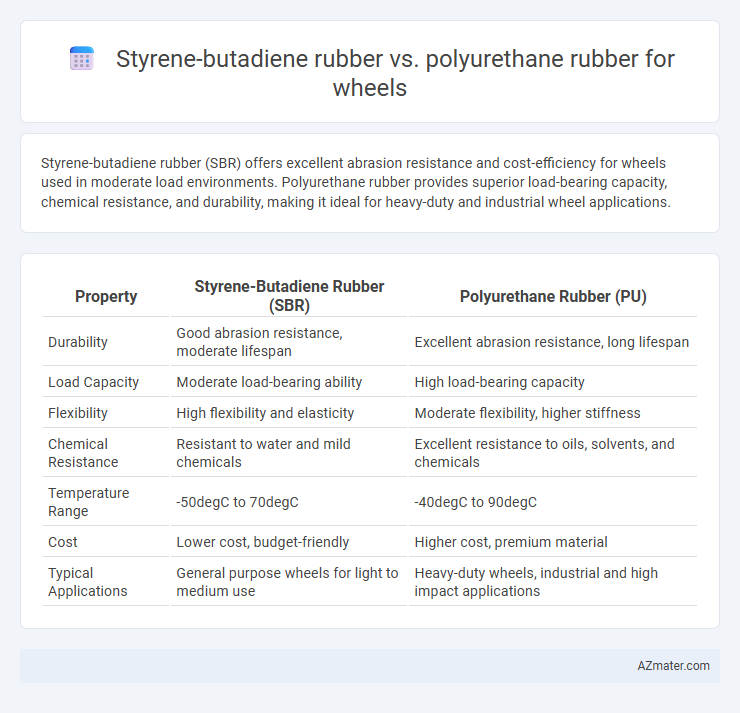
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and cost-efficiency for wheels used in moderate load environments. Polyurethane rubber provides superior load-bearing capacity, chemical resistance, and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty and industrial wheel applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) | Polyurethane Rubber (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Good abrasion resistance, moderate lifespan | Excellent abrasion resistance, long lifespan |
| Load Capacity | Moderate load-bearing ability | High load-bearing capacity |
| Flexibility | High flexibility and elasticity | Moderate flexibility, higher stiffness |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to water and mild chemicals | Excellent resistance to oils, solvents, and chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 70degC | -40degC to 90degC |
| Cost | Lower cost, budget-friendly | Higher cost, premium material |
| Typical Applications | General purpose wheels for light to medium use | Heavy-duty wheels, industrial and high impact applications |
Introduction to Wheel Rubber Materials
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and polyurethane (PU) rubber are widely used materials for wheel manufacturing due to their unique physical properties and performance characteristics. SBR offers excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for general-purpose wheels in industrial and commercial applications. Polyurethane rubber provides superior load-bearing capacity, enhanced chemical resistance, and greater elasticity, making it suitable for high-performance wheels used in harsh environments and heavy-duty machinery.
Overview of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a synthetic elastomer widely used in wheel applications due to its excellent abrasion resistance, aging stability, and cost-effectiveness. It offers a balanced combination of toughness and flexibility, making it suitable for high-impact and high-wear environments such as industrial casters and conveyor wheels. Compared to polyurethane rubber, SBR provides better resistance to heat and oxidation but generally has lower load-bearing capacity and chemical resistance.
Overview of Polyurethane Rubber (PU)
Polyurethane rubber (PU) offers superior abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity compared to Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for wheels in industrial applications subject to heavy wear. PU exhibits excellent chemical resistance and elasticity, enhancing wheel durability and performance on diverse surfaces. Its ability to withstand harsh environments and maintain structural integrity under high stress ensures longer service life and reduced maintenance costs.
Key Properties Comparison: SBR vs PU
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and good aging stability, making it ideal for wheels requiring durability on rough surfaces. Polyurethane (PU) rubber provides superior load-bearing capacity, chemical resistance, and elasticity, resulting in enhanced shock absorption and longer service life under heavy loads. While SBR excels in cost-effectiveness and general wear resistance, PU outperforms in mechanical strength and resistance to oils and solvents, crucial for industrial wheel applications.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and moderate durability, making it suitable for wheels exposed to rough surfaces and general wear. Polyurethane rubber exceeds SBR in durability and wear resistance, providing superior load-bearing capacity and resistance to cuts, oils, and chemicals, which enhances wheel lifespan in industrial and heavy-duty applications. The choice between SBR and polyurethane depends on the specific operational conditions and required performance, with polyurethane favored for high-stress environments demanding prolonged wear resistance.
Traction and Performance Differences
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and good traction on dry surfaces, making it suitable for durable wheel applications in moderate conditions, while polyurethane rubber provides enhanced grip on wet and oily surfaces due to its higher coefficient of friction and elasticity. Polyurethane wheels excel in performance with better load-bearing capacity and resilience, which contributes to improved shock absorption and reduced rolling resistance compared to SBR wheels. These differences in traction and mechanical properties influence the choice between SBR for cost-effective durability and polyurethane for high-performance, high-traction wheel applications.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers a cost-effective option for wheels due to its lower raw material and manufacturing expenses compared to polyurethane rubber, which tends to be pricier because of its specialized chemical composition and production process. SBR is widely available in global markets, benefiting from established supply chains and large-scale production, whereas polyurethane rubber may face limited availability and higher lead times owing to its more complex synthesis and niche applications. Cost-sensitive industries often prefer SBR wheels for budget constraints, while polyurethane wheels, despite higher costs, provide enhanced durability and abrasion resistance that justify their price in specialized uses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is derived from petroleum-based sources, contributing to higher carbon emissions and non-biodegradability issues compared to polyurethane rubber, which often incorporates bio-based polyols to reduce environmental footprint. Polyurethane rubber offers superior durability and longer lifespan for wheels, decreasing the frequency of replacements and overall material consumption, enhancing sustainability. Recycling processes for polyurethane are more advanced, enabling better recovery and reuse, while SBR recycling remains limited and energy-intensive.
Typical Applications in Wheel Manufacturing
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is widely used in wheel manufacturing for applications requiring excellent abrasion resistance and good aging properties, such as casters, trolley wheels, and conveyor rollers. Polyurethane rubber offers superior load-bearing capacity and resistance to oils, solvents, and chemicals, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial wheels, such as forklift wheels and heavy machinery casters. The choice between SBR and polyurethane depends on the specific operational environment, with polyurethane preferred for higher durability and SBR favored for cost-effective, general-purpose wheels.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Wheels
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for wheels used in moderate load and everyday environments. Polyurethane rubber provides superior durability, higher load-bearing capacity, and excellent chemical resistance, suitable for heavy-duty industrial wheels exposed to harsh conditions. Selecting the right rubber depends on application-specific factors such as load requirements, operating environment, and desired wheel lifespan.
Infographic: Styrene-butadiene rubber vs Polyurethane rubber for Wheel
 azmater.com
azmater.com