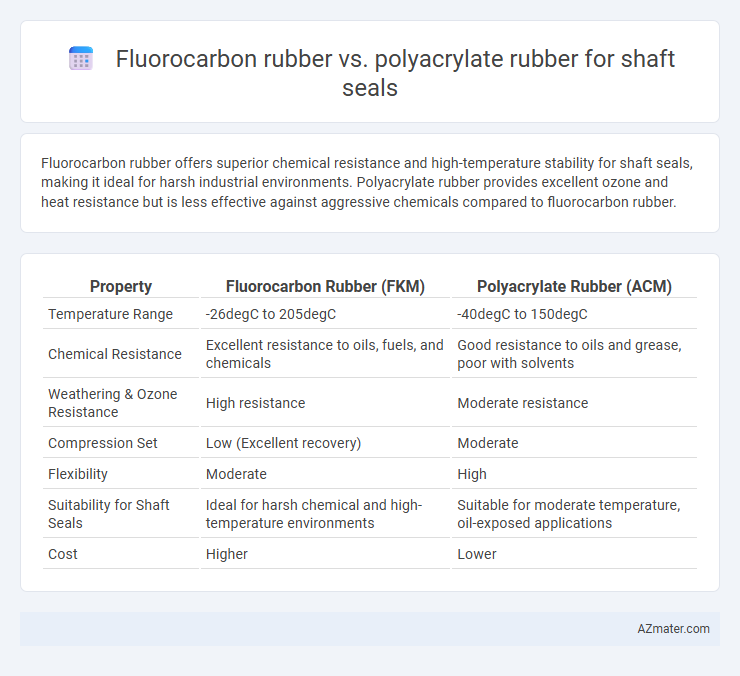
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance and high-temperature stability for shaft seals, making it ideal for harsh industrial environments. Polyacrylate rubber provides excellent ozone and heat resistance but is less effective against aggressive chemicals compared to fluorocarbon rubber.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluorocarbon Rubber (FKM) | Polyacrylate Rubber (ACM) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -26degC to 205degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Good resistance to oils and grease, poor with solvents |
| Weathering & Ozone Resistance | High resistance | Moderate resistance |
| Compression Set | Low (Excellent recovery) | Moderate |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High |
| Suitability for Shaft Seals | Ideal for harsh chemical and high-temperature environments | Suitable for moderate temperature, oil-exposed applications |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Shaft Seal Materials
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) offers superior chemical resistance, high-temperature stability up to 200degC, and excellent oil resistance, making it ideal for demanding shaft seal applications in automotive and industrial machinery. Polyacrylate rubber (ACM) provides good resistance to heat, oil, and ozone with an operating temperature range typically up to 150degC, suitable for moderate conditions requiring economical sealing solutions. Selecting between fluorocarbon and polyacrylate rubber depends on the specific chemical exposure, temperature requirements, and cost considerations in shaft seal performance.
Overview of Fluorocarbon Rubber (FKM)
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) offers exceptional chemical resistance, high-temperature stability up to 250degC, and superior durability in harsh environments, making it ideal for shaft seal applications requiring resistance to fuels, oils, and solvents. Its low gas permeability and excellent mechanical properties ensure long-lasting sealing performance under extreme conditions. Compared to polyacrylate rubber, FKM provides enhanced thermal and chemical resistance, suitable for demanding industrial and automotive sealing tasks.
Overview of Polyacrylate Rubber (ACM)
Polyacrylate rubber (ACM) is a synthetic elastomer known for excellent resistance to heat, oxidation, and oil, making it ideal for shaft seal applications in automotive and industrial machinery. Its superior aging resistance and flexibility at elevated temperatures, typically up to 150degC, provide enhanced durability compared to standard rubber materials. ACM seals maintain reliable sealing performance against mineral oils and synthetic lubricants, offering a cost-effective alternative to fluorocarbon rubber in moderate temperature environments.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Fluorocarbon rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polyacrylate rubber, particularly against strong acids, alkaline solutions, and hydrocarbon oils, making it ideal for harsh chemical environments. Polyacrylate rubber performs well in resisting oxidative oils, greases, and fuels but degrades faster when exposed to ketones, esters, and strong acids. Selecting fluorocarbon seals extends service life in aggressive chemical applications, while polyacrylate seals offer cost-effective performance in moderate oil and fuel environments.
Temperature Performance: FKM vs ACM
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) exhibits superior temperature resistance with an operational range typically between -26degC to 205degC, making it ideal for high-temperature shaft seal applications. In contrast, polyacrylate rubber (ACM) performs effectively within a narrower temperature spectrum of approximately -40degC to 150degC, limiting its use in extreme heat conditions. The higher thermal stability of FKM enables enhanced durability and reliability in demanding environments compared to ACM seals.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) offers superior chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, maintaining its mechanical strength in temperatures ranging from -26degC to 204degC, which enhances durability in harsh environments for shaft seals. Polyacrylate rubber (ACM) exhibits excellent resistance to heat and oxidation but operates effectively within a narrower temperature range of -40degC to 150degC, with moderate mechanical strength suitable for less aggressive applications. The enhanced tensile strength and abrasion resistance of fluorocarbon rubber make it more durable for dynamic sealing tasks involving aggressive fluids and elevated temperatures compared to polyacrylate rubber.
Oil and Fuel Compatibility
Fluorocarbon rubber exhibits exceptional oil and fuel resistance, maintaining stability and elasticity in high-temperature environments, making it ideal for shaft seals exposed to aggressive automotive fuels and synthetic oils. Polyacrylate rubber offers moderate oil resistance but degrades more quickly when exposed to hydrocarbons and aromatic fuels, limiting its use in long-term sealing applications within fuel systems. The superior chemical resistance and thermal stability of fluorocarbon rubber ensure enhanced durability and leak prevention in demanding oil and fuel seal environments.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance and high-temperature performance for shaft seals but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to polyacrylate rubber. Polyacrylate rubber provides a more cost-efficient solution with adequate resistance in moderate temperature and chemical environments, often making it the preferred choice for budget-sensitive applications. Availability of polyacrylate rubber is generally greater due to its widespread use, while fluorocarbon rubber may have longer lead times and limited suppliers, impacting overall procurement efficiency.
Typical Applications in Industries
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) is widely used in automotive, aerospace, and chemical processing industries due to its excellent resistance to high temperatures, oils, fuels, and aggressive chemicals, making it ideal for shaft seals in harsh environments. Polyacrylate rubber (ACM) is preferred in HVAC systems, automotive transmissions, and industrial equipment where moderate heat resistance and resistance to ozone, weathering, and oils are crucial for shaft seal performance. Each elastomer's typical applications leverage their unique chemical and thermal resistances to ensure reliable sealing in industry-specific conditions.
Choosing the Right Material for Shaft Seals
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance up to 200degC, and excellent durability, making it ideal for shaft seals exposed to harsh environments or aggressive chemicals. Polyacrylate rubber provides good resistance to oils and thermal stability around 150degC, suitable for medium-demand applications with moderate exposure. Selecting the right shaft seal material depends on factors like temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress, where fluorocarbon outperforms in extreme conditions while polyacrylate balances cost and performance for less severe environments.
Infographic: Fluorocarbon rubber vs Polyacrylate rubber for Shaft seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com