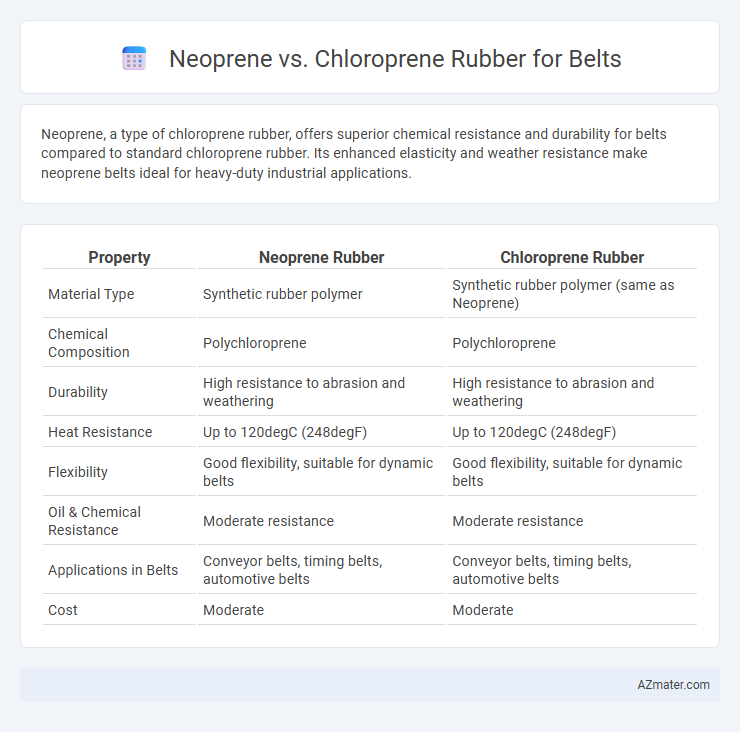
Neoprene, a type of chloroprene rubber, offers superior chemical resistance and durability for belts compared to standard chloroprene rubber. Its enhanced elasticity and weather resistance make neoprene belts ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Neoprene Rubber | Chloroprene Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic rubber polymer | Synthetic rubber polymer (same as Neoprene) |
| Chemical Composition | Polychloroprene | Polychloroprene |
| Durability | High resistance to abrasion and weathering | High resistance to abrasion and weathering |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 120degC (248degF) | Up to 120degC (248degF) |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility, suitable for dynamic belts | Good flexibility, suitable for dynamic belts |
| Oil & Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance | Moderate resistance |
| Applications in Belts | Conveyor belts, timing belts, automotive belts | Conveyor belts, timing belts, automotive belts |
| Cost | Moderate | Moderate |
Introduction to Neoprene and Chloroprene Rubber
Neoprene and chloroprene rubber are synthetic elastomers derived from the polymerization of chloroprene monomers, widely used in belt manufacturing for their durability and resistance to environmental factors. Neoprene offers excellent chemical stability and flexibility across varying temperatures, making it ideal for industrial belts subjected to wear, oil, and weather exposure, while chloroprene rubber retains similar properties but with enhanced toughness and resistance to abrasion. Both materials provide strong tensile strength and elasticity essential for conveyor, timing, and V-belts in automotive and manufacturing applications, with choice depending on specific mechanical and environmental requirements.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Neoprene rubber, also known as polychloroprene, consists of polymerized chloroprene monomers with a slightly higher crystallinity that enhances its tensile strength and chemical resistance, making it highly suitable for belts exposed to oils, heat, and weathering. Chloroprene rubber shares the same base chemical composition (C4H5Cl)n but often varies in polymerization methods and additive formulations, influencing properties like flexibility and aging resistance. The difference in molecular structure and cross-linking density between Neoprene and generic chloroprene rubber directly impacts belt durability under mechanical stress and environmental exposure.
Manufacturing Processes for Neoprene and Chloroprene Belts
Neoprene belts are manufactured using polymerization of chloroprene monomers followed by compounding with fillers, stabilizers, and plasticizers, with vulcanization enhancing durability and flexibility. Chloroprene rubber belts undergo similar polymerization but often feature modified processes to improve chemical resistance and elasticity, including controlled heat treatment and cross-linking adjustments. Both materials employ calendering, extrusion, or molding techniques, yet chloroprene belts generally require stricter quality control for consistent performance in harsh environments.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Flexibility
Neoprene rubber offers high tensile strength and excellent flexibility, making it resistant to wear and deformation under mechanical stress, ideal for belts subjected to dynamic loads. Chloroprene rubber, a synthetic variant of Neoprene, exhibits enhanced elasticity and superior resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering, ensuring durability in harsh environments. Both materials provide strong mechanical performance, but Chloroprene's slightly better balance of strength and flexibility contributes to longer-lasting belts in demanding industrial applications.
Resistance to Heat, Oil, and Weathering
Neoprene rubber exhibits superior resistance to heat, maintaining stability up to approximately 120degC, while chloroprene rubber offers similar heat resistance but excels in oil resistance due to its enhanced chemical structure. Both materials demonstrate excellent weathering resistance, with chloroprene rubber providing better performance against ozone and UV exposure, making it ideal for outdoor belt applications. The balance of heat tolerance, oil resistance, and durability against environmental factors defines the optimal choice between neoprene and chloroprene for industrial belts.
Durability and Lifespan in Industrial Applications
Neoprene rubber offers excellent durability with high resistance to oil, chemicals, and weathering, making it suitable for industrial belts exposed to harsh environments. Chloroprene rubber, a synthetic polymer similar to neoprene, provides superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength, enhancing belt lifespan under heavy mechanical stress. Both materials deliver long service life, but chloroprene often outperforms neoprene in durability for demanding industrial applications due to its enhanced elasticity and resistance properties.
Cost Analysis: Neoprene vs Chloroprene Belts
Neoprene belts typically offer a lower initial cost compared to chloroprene belts, making them a budget-friendly option for many industrial applications. Chloroprene belts, while more expensive, provide superior chemical resistance and durability, often resulting in lower long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including lifespan and performance under specific conditions, is crucial for selecting between neoprene and chloroprene belts.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Neoprene rubber, derived primarily from petroleum-based chloroprene monomers, has a higher environmental footprint due to energy-intensive production and limited biodegradability. Chloroprene rubber belts offer durability and chemical resistance, but their synthesis involves hazardous chemicals and generates toxic byproducts, challenging sustainability efforts. Recent advances in bio-based chloroprene alternatives and recycling methods aim to reduce ecological impact and promote circular economy in belt manufacturing.
Best Use Cases for Neoprene and Chloroprene Rubber Belts
Neoprene rubber belts excel in applications requiring excellent ozone, weather, and chemical resistance, making them ideal for automotive timing belts and conveyor belts in light-to-moderate industrial environments. Chloroprene rubber belts offer superior oil, heat, and abrasion resistance, best suited for heavy-duty industrial conveyors, agricultural machinery, and mining equipment requiring durability under harsh conditions. Selecting between neoprene and chloroprene rubber belts depends on the specific operating environment, with neoprene favored for outdoor exposure and mild chemicals, while chloroprene is preferred for environments with high oil exposure and mechanical stress.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Belt Applications
Neoprene provides superior weather resistance and excellent chemical stability, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial belt applications exposed to harsh environments. Chloroprene rubber offers enhanced flexibility and abrasion resistance, suited for belts requiring high durability and dynamic performance. Selecting the right rubber depends on specific operational demands such as exposure conditions, required elasticity, and wear resistance to ensure optimal belt longevity and efficiency.
Infographic: Neoprene vs Chloroprene rubber for Belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com