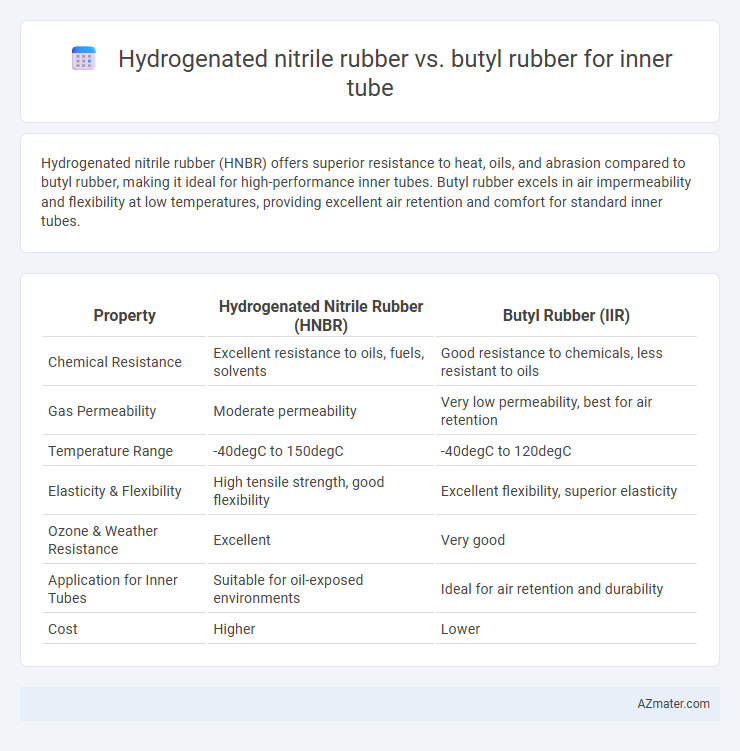
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oils, and abrasion compared to butyl rubber, making it ideal for high-performance inner tubes. Butyl rubber excels in air impermeability and flexibility at low temperatures, providing excellent air retention and comfort for standard inner tubes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Butyl Rubber (IIR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, solvents | Good resistance to chemicals, less resistant to oils |
| Gas Permeability | Moderate permeability | Very low permeability, best for air retention |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Elasticity & Flexibility | High tensile strength, good flexibility | Excellent flexibility, superior elasticity |
| Ozone & Weather Resistance | Excellent | Very good |
| Application for Inner Tubes | Suitable for oil-exposed environments | Ideal for air retention and durability |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Inner Tube Materials
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior abrasion resistance, oil resistance, and temperature stability, making it ideal for inner tubes exposed to harsh conditions and high-performance requirements. Butyl rubber remains a popular choice due to its excellent air retention, flexibility, and resistance to moisture permeation, ensuring long-lasting inflation in inner tubes. Selecting between HNBR and Butyl rubber depends on specific performance needs such as durability, chemical exposure, and service temperature ranges.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) offers exceptional resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals, making it highly suitable for inner tubes exposed to harsh environments. Its enhanced tensile strength and durability surpass Butyl rubber, providing improved abrasion resistance and longer service life. HNBR's ability to maintain flexibility at low temperatures ensures reliable performance in diverse conditions compared to conventional Butyl rubber.
Overview of Butyl Rubber (IIR)
Butyl rubber (IIR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its exceptional air impermeability, making it ideal for inner tube applications where airtightness and durability are critical. Its chemical composition includes copolymers of isobutylene with a small amount of isoprene, providing superior resistance to heat, ozone, and chemicals compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR). The inherent flexibility and excellent retentive properties of butyl rubber contribute to longer-lasting inner tubes, especially in automotive and bicycle tires.
Chemical Resistance: HNBR vs Butyl Rubber
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior chemical resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents compared to butyl rubber, making it ideal for inner tubes exposed to harsh automotive fluids. Butyl rubber provides excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and gas permeability but is less effective against hydrocarbon-based chemicals. The enhanced saturation of HNBR's polymer backbone results in improved durability and swelling resistance, outperforming butyl rubber in chemically aggressive environments.
Air Retention and Permeability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior air retention and lower permeability compared to butyl rubber, making it a preferred material for inner tubes requiring enhanced airtightness. HNBR's molecular structure provides excellent resistance to gas diffusion, reducing air loss over time and extending tube lifespan. Butyl rubber, while effective in sealing, demonstrates higher gas permeability rates, leading to more frequent inflation needs and potentially shorter service intervals.
Temperature Resistance Comparison
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior temperature resistance compared to butyl rubber, maintaining performance in continuous temperatures ranging from -40degC to 150degC, whereas butyl rubber typically withstands -40degC to 120degC. HNBR's enhanced thermal stability is due to its saturated polymer backbone, offering greater resistance to heat aging and oxidation, crucial for inner tubes exposed to fluctuating temperatures. This makes HNBR a preferable choice in applications demanding reliable durability and flexibility under higher temperature conditions.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Flexibility
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to butyl rubber, making it ideal for inner tubes requiring durability under high stress. Butyl rubber excels in flexibility and air retention due to its low permeability, enhancing comfort and reliability in inner tube applications. Balancing strength and flexibility, HNBR provides enhanced mechanical resilience, while butyl rubber ensures optimal elasticity and airtight performance.
Durability and Lifespan
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior durability and chemical resistance compared to butyl rubber, making HNBR inner tubes more resistant to abrasion, ozone, and heat aging. Butyl rubber provides excellent impermeability to gases, ensuring longer air retention and a consistently extended lifespan for inner tubes under normal conditions. The choice depends on the operating environment: HNBR excels in high-stress, high-temperature applications, while butyl rubber remains preferable for everyday use due to its exceptional air retention properties.
Cost and Availability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance and durability but comes at a higher cost compared to butyl rubber, which is more affordable and widely available. Butyl rubber's excellent impermeability to gases makes it the preferred choice for inner tubes in standard applications due to its cost-effectiveness and extensive market supply. HNBR is typically reserved for specialized inner tube uses where enhanced performance justifies its increased price and more limited availability.
Conclusion: Which Is Better for Inner Tubes?
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion, making it highly durable for inner tubes exposed to harsh conditions. Butyl rubber excels in air retention and impermeability, providing excellent sealing properties essential for maintaining tire pressure. For inner tubes requiring long-lasting air retention and flexibility, butyl rubber generally outperforms HNBR, though HNBR is preferred in high-stress or chemically aggressive environments.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Butyl rubber for Inner tube
 azmater.com
azmater.com