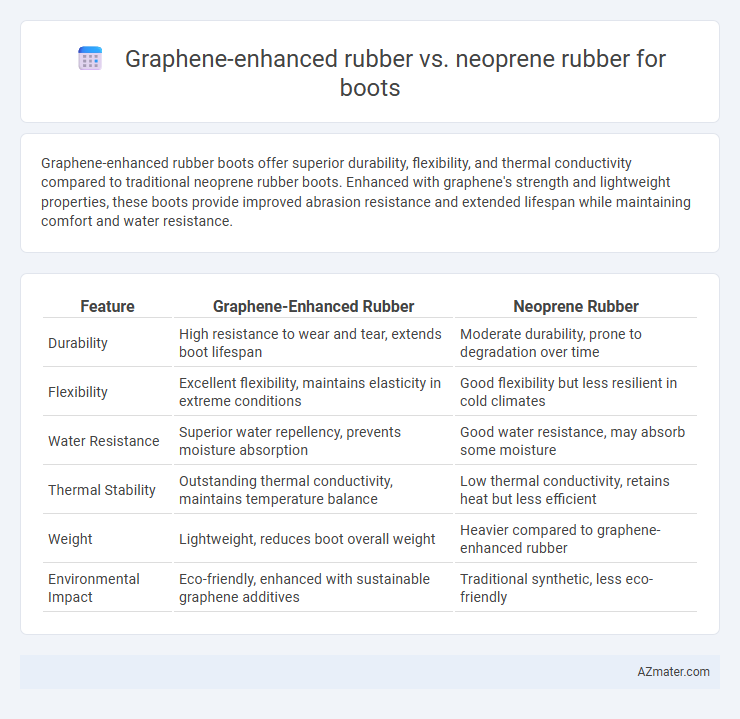
Graphene-enhanced rubber boots offer superior durability, flexibility, and thermal conductivity compared to traditional neoprene rubber boots. Enhanced with graphene's strength and lightweight properties, these boots provide improved abrasion resistance and extended lifespan while maintaining comfort and water resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Graphene-Enhanced Rubber | Neoprene Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to wear and tear, extends boot lifespan | Moderate durability, prone to degradation over time |
| Flexibility | Excellent flexibility, maintains elasticity in extreme conditions | Good flexibility but less resilient in cold climates |
| Water Resistance | Superior water repellency, prevents moisture absorption | Good water resistance, may absorb some moisture |
| Thermal Stability | Outstanding thermal conductivity, maintains temperature balance | Low thermal conductivity, retains heat but less efficient |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces boot overall weight | Heavier compared to graphene-enhanced rubber |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, enhanced with sustainable graphene additives | Traditional synthetic, less eco-friendly |
Introduction to Rubber Materials in Boot Manufacturing
Graphene-enhanced rubber in boot manufacturing offers superior tensile strength, enhanced durability, and improved thermal conductivity compared to traditional neoprene rubber, which is known for its excellent flexibility, water resistance, and chemical stability. The integration of graphene into rubber matrices significantly boosts abrasion resistance and extends the lifespan of boots used in demanding environments. Neoprene remains a popular choice for insulation and weatherproofing, but graphene-enhanced rubber provides advanced performance characteristics essential for high-end, durable footwear applications.
What is Graphene-Enhanced Rubber?
Graphene-enhanced rubber is a composite material integrating graphene nanosheets into traditional rubber matrices, offering superior mechanical strength, flexibility, and thermal conductivity compared to conventional rubbers like neoprene. This integration improves durability, abrasion resistance, and elasticity, making graphene-enhanced rubber ideal for performance boots exposed to harsh environments. Compared to neoprene rubber, graphene-enhanced rubber provides enhanced waterproofing and longevity, significantly extending the functional lifespan of footwear in demanding conditions.
Understanding Neoprene Rubber
Neoprene rubber, a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent chemical stability and flexibility over a wide temperature range, is widely used in boot manufacturing for its water resistance and durability. Graphene-enhanced rubber incorporates graphene nanoparticles, which significantly improve tensile strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance while maintaining neoprene's lightweight and insulating properties. Understanding neoprene's baseline performance helps highlight how graphene integration enhances the material's mechanical integrity, thermal conductivity, and lifespan in demanding boot applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Graphene-enhanced rubber exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to neoprene rubber, offering increased tensile strength and resistance to deformation under stress, which translates to enhanced durability for boots exposed to harsh conditions. The incorporation of graphene provides exceptional wear resistance and improved flexibility, reducing the likelihood of cracks or tears over prolonged use. Neoprene rubber, while known for good chemical resistance and flexibility, generally falls short in maintaining structural integrity and mechanical robustness under heavy or repetitive mechanical loads compared to graphene-enhanced composites.
Flexibility and Comfort: Graphene vs Neoprene
Graphene-enhanced rubber offers superior flexibility compared to traditional neoprene rubber, allowing boots to better conform to foot movements without compromising durability. The exceptional elasticity of graphene-infused materials reduces stiffness, enhancing overall comfort during extended wear. Neoprene provides adequate cushioning but lacks the advanced pliability and adaptive fit characteristics found in graphene-enhanced rubber.
Water and Chemical Resistance Performance
Graphene-enhanced rubber significantly improves water resistance and chemical stability compared to traditional neoprene rubber, providing superior durability in wet and corrosive environments. Its enhanced molecular structure reduces permeability, preventing water infiltration and resisting degradation from oils, solvents, and other chemicals commonly encountered in industrial or marine applications. Neoprene, while resistant to water and chemicals, performs less effectively under prolonged exposure or extreme conditions, making graphene-enhanced rubber the preferred choice for high-performance waterproof and chemical-resistant boots.
Thermal Insulation Abilities of Both Materials
Graphene-enhanced rubber exhibits superior thermal insulation properties compared to neoprene rubber due to graphene's exceptional heat conductivity and barrier capabilities, effectively reducing heat transfer in boots. Neoprene offers moderate thermal resistance by trapping air within its closed-cell structure, but it lacks graphene's enhanced heat dispersion and durability benefits. Boots made with graphene-enhanced rubber maintain warmth longer in extreme temperatures, making them ideal for cold-weather applications requiring advanced thermal regulation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Graphene-enhanced rubber offers improved durability and elasticity, significantly extending the lifespan of boots and reducing overall waste compared to traditional neoprene rubber. The production of graphene-infused rubber typically involves fewer toxic chemicals and generates lower carbon emissions, enhancing its environmental sustainability. Neoprene rubber, reliant on petroleum-based resources and energy-intensive manufacturing, presents higher ecological concerns due to its limited biodegradability and higher pollutant release.
Cost Analysis: Graphene-Enhanced vs Neoprene Rubber Boots
Graphene-enhanced rubber boots typically incur higher initial costs due to advanced material synthesis and enhanced performance properties, such as improved durability and flexibility compared to standard neoprene rubber boots. While neoprene boots offer lower upfront expenses, their shorter lifespan and reduced resistance to wear may lead to increased long-term replacement costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that graphene-enhanced rubber boots provide better value through extended service life and lower maintenance requirements despite the premium price.
Which Boot Material is Best for Your Needs?
Graphene-enhanced rubber offers superior strength, flexibility, and thermal conductivity compared to neoprene rubber, making boots more durable and suitable for extreme weather conditions. Neoprene rubber, known for its excellent insulation and water resistance, provides comfort and protection in wet and cold environments but lacks the enhanced durability of graphene composites. Choosing between these materials depends on whether you prioritize long-lasting performance and advanced material technology or proven insulation and affordability.
Infographic: Graphene-enhanced rubber vs Neoprene rubber for Boot
 azmater.com
azmater.com