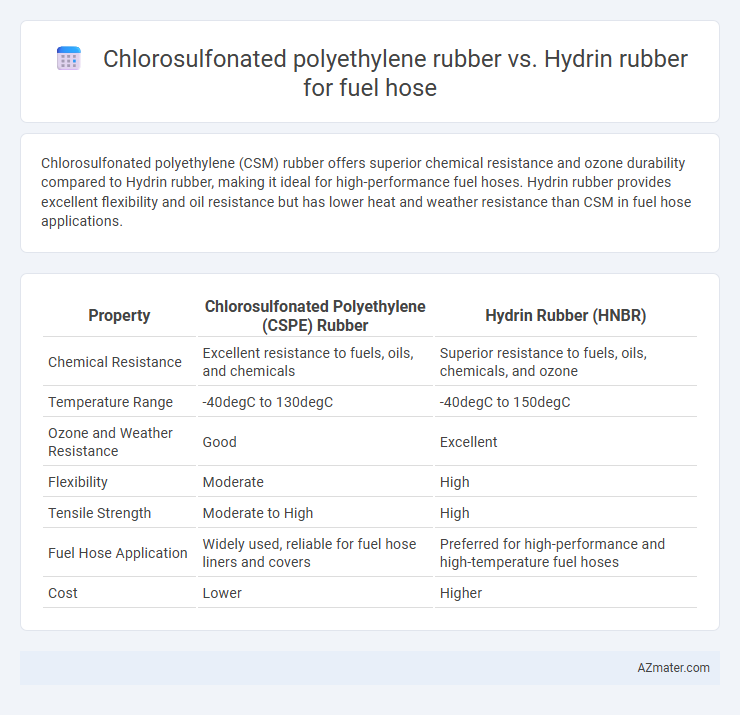
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers superior chemical resistance and ozone durability compared to Hydrin rubber, making it ideal for high-performance fuel hoses. Hydrin rubber provides excellent flexibility and oil resistance but has lower heat and weather resistance than CSM in fuel hose applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSPE) Rubber | Hydrin Rubber (HNBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to fuels, oils, and chemicals | Superior resistance to fuels, oils, chemicals, and ozone |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 130degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate to High | High |
| Fuel Hose Application | Widely used, reliable for fuel hose liners and covers | Preferred for high-performance and high-temperature fuel hoses |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Fuel Hose Materials
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber and Hydrin rubber are both crucial materials for fuel hose applications, prized for their chemical resistance and durability. CSM rubber offers excellent resistance to oils, fuels, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for harsh automotive environments. Hydrin rubber excels in fuel resistance and flexibility at low temperatures, ensuring reliable performance in varying climate conditions.
Overview of Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSM) Rubber
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers excellent resistance to fuels, oils, ozone, and weathering, making it a highly durable material for fuel hoses. Its unique chlorosulfonation process provides enhanced chemical stability and superior tensile strength compared to Hydrin rubber. CSM's combination of flexibility and resistance to degradation under exposure to hydrocarbons makes it a preferred choice in demanding automotive and industrial fuel hose applications.
Hydrin Rubber (Epichlorohydrin) Properties
Hydrin rubber, also known as epichlorohydrin rubber, exhibits excellent resistance to fuels, oils, and hydrocarbons, making it ideal for fuel hose applications. Its good low-temperature flexibility and strong resistance to heat and ozone outperform chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber, ensuring durability in harsh environments. The superior chemical stability and compression set resistance of epichlorohydrin rubber enhance fuel hose longevity and reliability in automotive and industrial fuel delivery systems.
Chemical Resistance Comparison: CSM vs Hydrin
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance to fuels, oils, and ozone, making it highly suitable for fuel hose applications where exposure to harsh hydrocarbons occurs. Hydrin rubber, a chlorinated copolymer of ethylene and propylene, offers excellent resistance to aliphatic hydrocarbons and weathering but is generally less resistant to aromatic and chlorinated solvents compared to CSM. The enhanced chemical resistance of CSM to a wider range of aggressive fuels and solvents makes it a preferred choice for demanding fuel hose environments requiring long-term durability and minimal degradation.
Fuel Permeability and Barrier Performance
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber exhibits superior fuel permeability resistance and enhanced barrier performance compared to Hydrin rubber, making it ideal for fuel hose applications requiring long-term durability. CSPE's chemical structure provides excellent resistance to hydrocarbon fuels, significantly reducing permeation rates and preventing fuel leakage. Hydrin rubber, while flexible and resistant to oils, generally shows higher fuel permeability and lower barrier efficiency, limiting its suitability for high-performance fuel hose systems.
Temperature Resistance in Fuel Hose Applications
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior temperature resistance in fuel hose applications, maintaining flexibility and structural integrity in a range from -40degC to 120degC, which makes it suitable for demanding automotive environments. Hydrin rubber, while offering good chemical resistance and low permeability to fuels, typically withstands temperatures only between -30degC and 90degC, limiting its use in high-temperature scenarios. The enhanced thermal stability of CSM rubber ensures better durability and performance under fluctuating engine heat conditions compared to Hydrin rubber.
Mechanical Properties and Flexibility
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior mechanical properties such as high tensile strength, excellent abrasion resistance, and outstanding resistance to heat and chemicals, making it ideal for fuel hose applications requiring durability. Hydrin rubber offers excellent flexibility and low temperature performance, maintaining flexibility in harsh environments and resisting fuel swelling and ozone degradation. While CSM excels in mechanical robustness and chemical resistance, Hydrin provides enhanced flexibility and resilience where hoses must withstand dynamic movements and extreme cold conditions.
Durability and Aging Performance
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits exceptional resistance to fuels, oils, and oxidative aging, making it highly durable for fuel hose applications exposed to harsh chemical environments. Hydrin rubber, a terpolymer of ethylene, chlorotrifluoroethylene, and vinyl chloride, offers superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and low-temperature flexibility, enhancing its aging performance under varying environmental conditions. CSM rubber tends to provide longer service life in fuel hoses subjected to high-temperature oxidative aging, while Hydrin rubber excels in maintaining elasticity and durability in colder climates.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber offers superior chemical resistance and weatherability for fuel hose applications but typically incurs higher manufacturing costs due to complex compounding and curing processes. Hydrin rubber, a chlorinated copolymer of ethylene and propylene, provides a cost-effective alternative with easier processing and faster production cycles, though it may have slightly lower fuel resistance and durability. Manufacturers must balance initial material expenses against long-term performance when selecting between CSPE and Hydrin for fuel hose production.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right Rubber
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber excels in fuel hose applications due to its superior resistance to fuels, oils, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for demanding automotive and industrial environments. Hydrin rubber offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility but may have lower ozone resistance and aging stability compared to CSM. Selecting between CSM and Hydrin depends on specific operational conditions such as exposure to aggressive fuels, temperature ranges, and durability requirements for optimized fuel hose performance.
Infographic: Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber vs Hydrin rubber for Fuel hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com