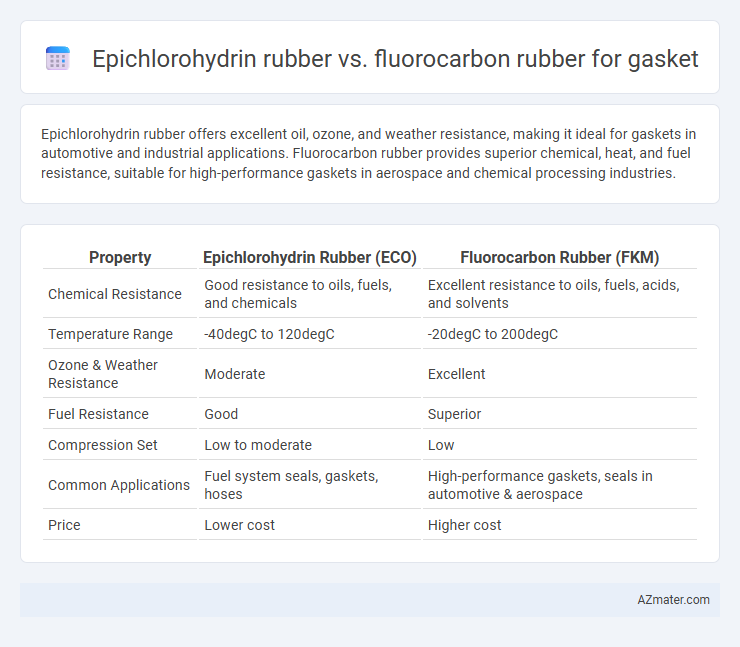
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent oil, ozone, and weather resistance, making it ideal for gaskets in automotive and industrial applications. Fluorocarbon rubber provides superior chemical, heat, and fuel resistance, suitable for high-performance gaskets in aerospace and chemical processing industries.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) | Fluorocarbon Rubber (FKM) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, acids, and solvents |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -20degC to 200degC |
| Ozone & Weather Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Fuel Resistance | Good | Superior |
| Compression Set | Low to moderate | Low |
| Common Applications | Fuel system seals, gaskets, hoses | High-performance gaskets, seals in automotive & aerospace |
| Price | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Epichlorohydrin Rubber and Fluorocarbon Rubber
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent resistance to oil, ozone, weathering, and heat, making it ideal for gaskets in automotive and industrial applications. Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) offers superior chemical resistance, high-temperature stability, and low permeability, often used in aerospace and chemical processing gasket seals. When selecting gasket materials, the choice between epichlorohydrin and fluorocarbon rubber depends on specific exposure conditions, including temperature range and chemical environment.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) features a saturated backbone with epoxy and chlorohydrin groups, providing excellent resistance to ozone, oils, and weathering, whereas fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) contains vinylidene fluoride and hexafluoropropylene units with strong carbon-fluorine bonds that deliver superior chemical and heat resistance. The chemical structure of ECO enables greater flexibility and gas impermeability, while FKM's highly fluorinated composition resists aggressive chemicals, fuels, and high temperatures beyond 200degC. These differences in molecular composition directly impact gasket performance, making ECO preferable for moderate temperature and oil resistance applications, and FKM optimal for harsh chemical and extreme thermal environments.
Mechanical Properties and Performance
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent flexibility, oil resistance, and moderate temperature tolerance, making it suitable for gaskets in automotive and refrigeration applications. Fluorocarbon rubber provides superior chemical resistance, high-temperature stability up to 200degC, and exceptional mechanical strength, ideal for gaskets exposed to harsh chemicals and extreme environments. While Epichlorohydrin excels in abrasion resistance and low gas permeability, Fluorocarbon delivers longer service life under aggressive media and higher thermal stress.
Temperature Resistance Capabilities
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent low-temperature flexibility down to -40degC and maintains stability up to approximately 120degC, making it ideal for applications requiring resistance to weathering and ozone exposure. Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) demonstrates superior high-temperature resistance, typically operating continuously between -20degC and 204degC, with short-term exposure up to 230degC, ensuring durability in harsh chemical and thermal environments. For gasket applications demanding broader temperature resilience, fluorocarbon rubber outperforms epichlorohydrin in extreme heat, while epichlorohydrin is preferable for moderate temperature conditions with enhanced cold resistance.
Chemical Resistance Analysis
Epichlorohydrin rubber demonstrates strong resistance to oils, ozone, and weathering, making it suitable for gaskets exposed to moderate chemical environments, especially in automotive and industrial applications. Fluorocarbon rubber, known for exceptional resistance to aggressive chemicals, fuels, acids, and high temperatures, provides superior gasket performance in harsh chemical environments such as fuel systems and chemical processing. Chemical resistance analysis highlights fluorocarbon rubber's advantage in resisting hydrocarbons, solvents, and oxidative degradation, whereas epichlorohydrin excels in resistance to polar solvents and oxygenated fluids.
Compatibility with Various Fluids
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent compatibility with a wide range of hydraulic fluids, oils, alcohols, and refrigerants, making it suitable for seals and gaskets in automotive and industrial applications. Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) provides superior resistance to aggressive chemicals, fuels, high-temperature oils, and acids, ensuring durability in harsh chemical environments and elevated temperatures. Selection between epichlorohydrin and fluorocarbon gaskets depends on the specific fluid exposure, temperature range, and chemical aggressiveness encountered in the application.
Aging, Weathering, and Ozone Resistance
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits excellent resistance to aging, weathering, and ozone, making it suitable for gaskets exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Fluorocarbon rubber outperforms Epichlorohydrin in chemical resistance and maintains superior stability against UV radiation, ozone, and extreme temperatures, ensuring longer gasket service life in aggressive environments. Both elastomers offer durable sealing solutions, but Fluorocarbon rubber is preferred for applications demanding higher resistance to oxidative and thermal degradation.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior cost efficiency compared to fluorocarbon rubber, making it a preferred choice for gasket applications with budget constraints. Availability of epichlorohydrin rubber is generally higher due to widespread production and more extensive supply chains, ensuring faster procurement and reduced lead times. Fluorocarbon rubber, while more expensive and less readily available, provides enhanced chemical resistance and temperature tolerance, but these benefits come at a premium cost and limited stock in many markets.
Typical Applications in Gasket Manufacturing
Epichlorohydrin rubber is widely used in gasket manufacturing for applications requiring excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and moderate chemical exposure, making it ideal for automotive and industrial seals exposed to oils and fuels. Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance, high-temperature stability, and excellent barrier properties, making it the preferred choice for gaskets in chemical processing, aerospace, and fuel system applications. Both materials provide durable sealing solutions, but fluorocarbon rubber is favored where aggressive chemical environments and elevated temperatures are common.
Selection Guidelines: Which Rubber for Your Gasket Needs?
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent oil, fuel, and ozone resistance, making it ideal for gaskets in automotive and fuel system applications where moderate chemical exposure is expected. Fluorocarbon rubber excels in high-temperature stability, exceptional chemical resistance to aggressive fluids, and superior weathering performance, making it suitable for gaskets in aerospace, chemical processing, and high-performance industrial environments. Selecting between Epichlorohydrin and Fluorocarbon rubbers depends on operational temperature range, chemical compatibility, and environmental exposure specific to your gasket application.
Infographic: Epichlorohydrin rubber vs Fluorocarbon rubber for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com