Nanocomposite rubber exhibits superior abrasion resistance and enhanced mechanical strength compared to synthetic rubber, making it ideal for durable shoe soles. Incorporating nanoparticles into the rubber matrix significantly improves wear resistance and flexibility, extending the lifespan of footwear.
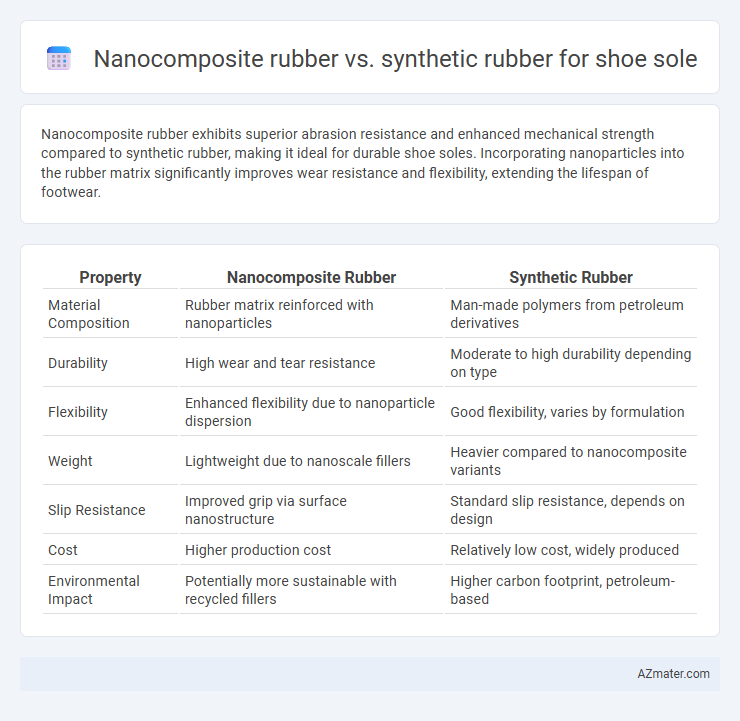
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nanocomposite Rubber | Synthetic Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Rubber matrix reinforced with nanoparticles | Man-made polymers from petroleum derivatives |
| Durability | High wear and tear resistance | Moderate to high durability depending on type |
| Flexibility | Enhanced flexibility due to nanoparticle dispersion | Good flexibility, varies by formulation |
| Weight | Lightweight due to nanoscale fillers | Heavier compared to nanocomposite variants |
| Slip Resistance | Improved grip via surface nanostructure | Standard slip resistance, depends on design |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Relatively low cost, widely produced |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially more sustainable with recycled fillers | Higher carbon footprint, petroleum-based |
Introduction to Rubber Materials for Shoe Soles
Nanocomposite rubber incorporates nanoscale fillers like silica or carbon nanotubes to enhance mechanical properties, durability, and abrasion resistance in shoe soles compared to traditional synthetic rubber. Synthetic rubber, typically composed of polymers such as styrene-butadiene or ethylene-propylene-diene monomer (EPDM), offers flexibility and resilience but may lack the improved strength and wear resistance found in nanocomposite blends. These advancements in nanocomposite rubber technology provide superior performance for high-demand footwear applications.
Defining Nanocomposite Rubber
Nanocomposite rubber is a type of rubber enhanced with nanoscale fillers such as clay, silica, or carbon nanotubes, which improve mechanical strength, abrasion resistance, and durability compared to traditional synthetic rubber used in shoe soles. Unlike synthetic rubber, which is typically made from polymers like styrene-butadiene or nitrile, nanocomposite rubber offers superior performance due to the uniform dispersion of nanoparticles that reinforce the polymer matrix at a molecular level. This advanced material results in shoe soles with enhanced flexibility, wear resistance, and longer lifespan, making it ideal for high-performance footwear applications.
Overview of Synthetic Rubber Types
Synthetic rubber types commonly used for shoe soles include styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), providing excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, and nitrile rubber (NBR), valued for oil and chemical resistance. Polyurethane (PU) offers superior flexibility and durability, while ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) is favored for lightweight cushioning and shock absorption. Nanocomposite rubber enhances these properties by integrating nanoscale fillers, improving mechanical strength and wear resistance compared to traditional synthetic rubbers.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Nanocomposite rubber exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to synthetic rubber due to the integration of nanoscale fillers such as silica or carbon nanotubes, which enhance tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and elasticity. Synthetic rubber soles, while flexible and durable, generally lack the reinforced microstructure provided by nanocomposites, resulting in lower resistance to wear and mechanical stress. The dispersion of nanoparticles within the rubber matrix significantly improves load distribution and crack resistance, making nanocomposite rubber an advanced material choice for high-performance shoe soles.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Nanocomposite rubber outperforms synthetic rubber in shoe sole applications due to its enhanced durability and superior wear resistance, achieved by incorporating nanoscale fillers such as silica or carbon nanotubes. These nanofillers improve the mechanical strength and abrasion resistance, leading to longer-lasting soles that maintain their structural integrity under repeated stress. Synthetic rubber, while flexible and cost-effective, generally exhibits lower resistance to wear and deformation compared to nanocomposite-enhanced alternatives.
Flexibility and Comfort Performance
Nanocomposite rubber enhances shoe sole flexibility by integrating nanoscale fillers, which improve elasticity and tensile strength without compromising softness. Synthetic rubber offers durability and basic flexibility but often lacks the advanced comfort and shock absorption provided by nanocomposite materials. The improved molecular structure of nanocomposite rubber allows better energy return and cushioning, resulting in superior comfort performance for prolonged wear.
Traction and Slip Resistance
Nanocomposite rubber enhances shoe sole traction and slip resistance by incorporating nanoscale fillers that improve surface grip and durability compared to traditional synthetic rubber. The uniform dispersion of nanoparticles increases the rubber's mechanical properties, reducing wear and maintaining consistent friction on various surfaces. Synthetic rubber soles, while durable, typically lack the advanced slip resistance and adaptive grip performance provided by nanocomposites in wet or oily conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nanocomposite rubber for shoe soles significantly reduces environmental impact by incorporating bio-based fillers and enhancing durability, which lowers the frequency of sole replacements and waste generation. Synthetic rubber, typically derived from petrochemicals, contributes to higher carbon emissions and ecological degradation during production and disposal stages. The sustainability of nanocomposite rubber is further amplified through improved recyclability and biodegradability compared to conventional synthetic rubber materials.
Cost-Effectiveness and Manufacturing Considerations
Nanocomposite rubber offers enhanced durability and abrasion resistance compared to traditional synthetic rubber, potentially reducing long-term replacement costs for shoe soles. Manufacturing nanocomposite rubber involves advanced dispersion techniques, which can increase initial production expenses but improve material performance and lifespan. Synthetic rubber remains more cost-effective for mass production due to simpler processing methods and established supply chains, making it preferable for budget-conscious footwear brands.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Rubber for Shoe Soles
Nanocomposite rubber offers enhanced mechanical strength, superior abrasion resistance, and improved elasticity compared to traditional synthetic rubber, making it ideal for high-performance shoe soles. Synthetic rubber remains cost-effective and provides good flexibility, but it may lack the durability and wear resistance of nanocomposite alternatives. Selecting the best rubber for shoe soles depends on balancing budget constraints with the need for longevity, comfort, and performance, where nanocomposite rubber generally outperforms synthetic rubber in demanding applications.
Infographic: Nanocomposite rubber vs Synthetic rubber for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com