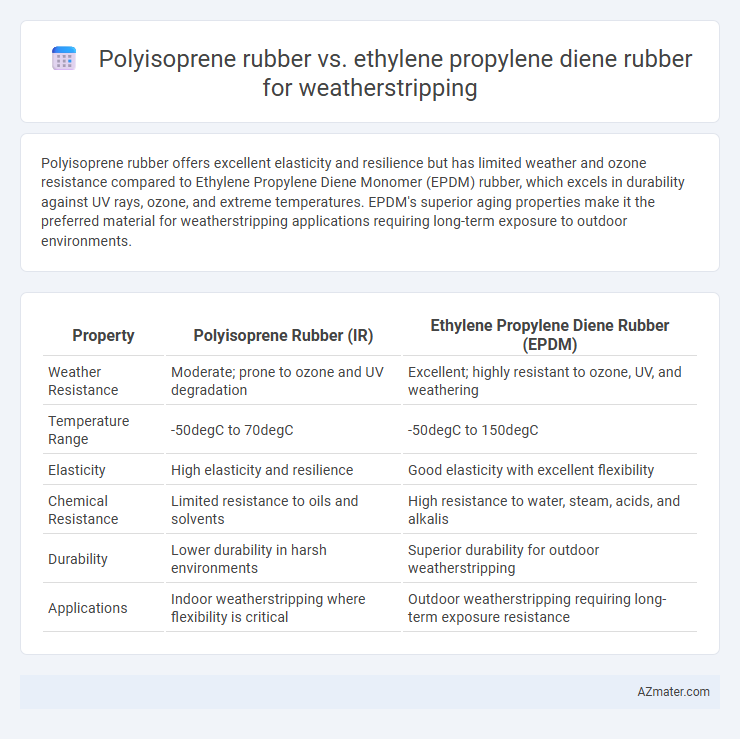
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and resilience but has limited weather and ozone resistance compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, which excels in durability against UV rays, ozone, and extreme temperatures. EPDM's superior aging properties make it the preferred material for weatherstripping applications requiring long-term exposure to outdoor environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyisoprene Rubber (IR) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Weather Resistance | Moderate; prone to ozone and UV degradation | Excellent; highly resistant to ozone, UV, and weathering |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 70degC | -50degC to 150degC |
| Elasticity | High elasticity and resilience | Good elasticity with excellent flexibility |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited resistance to oils and solvents | High resistance to water, steam, acids, and alkalis |
| Durability | Lower durability in harsh environments | Superior durability for outdoor weatherstripping |
| Applications | Indoor weatherstripping where flexibility is critical | Outdoor weatherstripping requiring long-term exposure resistance |
Introduction to Weatherstripping Materials
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance, making it suitable for flexible weatherstripping applications that require a tight seal against moisture and air. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in weather resistance, ozone, UV, and temperature tolerance, which ensures long-term durability in outdoor environments. Choosing between polyisoprene and EPDM depends on the specific demands of the weatherstripping application, including exposure conditions and mechanical stress.
Overview of Polyisoprene Rubber (IR)
Polyisoprene rubber (IR) is a synthetic elastomer closely resembling natural rubber in its molecular structure, offering excellent tensile strength, flexibility, and resilience ideal for weatherstripping applications. It demonstrates good abrasion resistance and dynamic properties but has limited resistance to heat, ozone, and chemical exposure compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber. Polyisoprene's superior elasticity and low compression set make it effective for creating tight seals in environments with moderate weathering conditions.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) is a synthetic elastomer known for exceptional resistance to weathering, ozone, and UV radiation, making it ideal for weatherstripping applications. Its chemical structure provides superior durability and flexibility across a wide temperature range, typically from -40degC to 150degC, outperforming natural polyisoprene rubber in outdoor environments. EPDM's resistance to water, steam, and various chemicals ensures long-lasting seals and reduced maintenance in automotive, construction, and industrial weatherstripping uses.
Key Properties Comparison: IR vs EPDM
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and tensile strength, closely resembling natural rubber, making it suitable for applications requiring flexibility and resilience in weatherstripping. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides superior resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and extreme weather conditions, ensuring long-lasting durability in outdoor environments. While polyisoprene excels in mechanical properties, EPDM outperforms in environmental resistance, making it the preferred choice for weatherstripping exposed to harsh climates.
Weather Resistance Capabilities
Polyisoprene rubber offers moderate weather resistance, exhibiting good flexibility but limited resistance to ozone and UV exposure, which may cause degradation over time in outdoor weatherstripping applications. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber demonstrates superior weather resistance, including excellent ozone, UV, heat, and moisture durability, making it ideal for prolonged outdoor use in weatherstripping. EPDM's chemical structure provides enhanced elasticity and longevity under harsh environmental conditions, outperforming polyisoprene in maintaining sealing effectiveness.
Durability and Longevity in Use
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent mechanical properties with a natural rubber-like elasticity, but it tends to degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and ozone, limiting its durability for outdoor weatherstripping applications. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber exhibits superior resistance to weathering, ozone, UV rays, and extreme temperatures, significantly enhancing its longevity in weatherstripping. EPDM's chemical stability ensures consistent performance and extended service life, making it a preferred choice for durable weather seals in automotive and construction industries.
Flexibility and Compression Set Performance
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent flexibility and low compression set, making it ideal for weatherstripping applications requiring durable sealing under repeated compression. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides superior resistance to weather, ozone, and temperature extremes but may exhibit a higher compression set compared to polyisoprene, potentially reducing long-term sealing effectiveness. Selecting between polyisoprene and EPDM depends on balancing flexibility needs with environmental durability for optimal weatherstripping performance.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Polyisoprene rubber offers a cost-effective solution for weatherstripping due to its natural origin and widespread availability, making it economically attractive for large-scale applications. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) tends to have a higher price point but benefits from extensive commercial availability and consistent supply owing to its synthetic production process. Choosing between these materials hinges on balancing budget constraints with the need for reliable sourcing in weather-resistant sealing applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyisoprene rubber, derived from natural latex, offers renewable sourcing with lower carbon footprints compared to synthetic Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, which relies on petrochemical feedstocks. EPDM exhibits superior resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and extreme weather, reducing replacement frequency and waste generation, supporting long-term sustainability in weatherstripping applications. Life cycle assessments highlight polyisoprene's biodegradability advantages, while EPDM's durability enhances environmental impact through longevity and reduced maintenance needs.
Best Applications for Polyisoprene and EPDM in Weatherstripping
Polyisoprene rubber excels in weatherstripping applications requiring high elasticity and excellent tensile strength, making it ideal for sealing automotive doors and windows where flexibility and precise sealing are critical. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber offers superior resistance to ozone, UV rays, and extreme weather conditions, making it the preferred choice for outdoor weatherstripping such as roofing seals, window gaskets, and industrial door seals exposed to harsh environments. EPDM's durability and resistance to aging significantly extend the lifespan of weatherstripping in construction and automotive applications, while polyisoprene's natural rubber properties provide superior comfort and fit in dynamic sealing scenarios.
Infographic: Polyisoprene rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Weatherstripping
 azmater.com
azmater.com