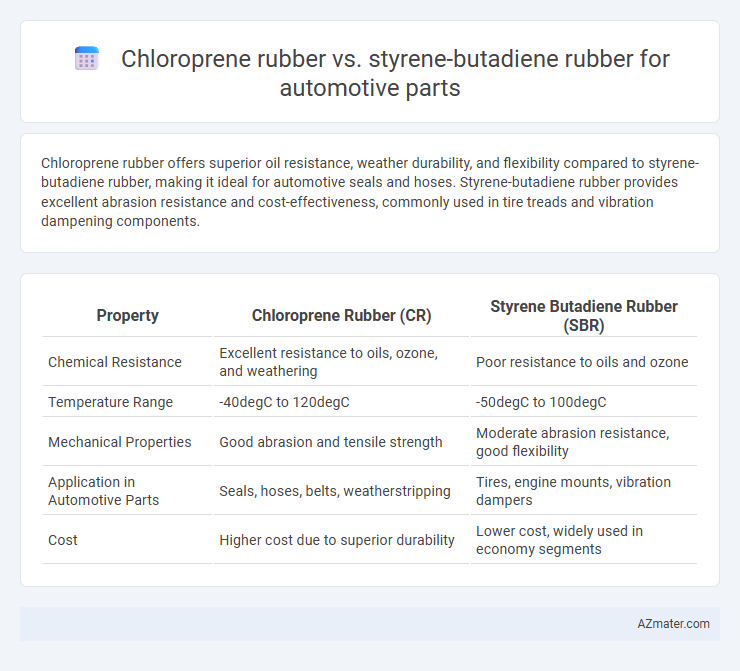
Chloroprene rubber offers superior oil resistance, weather durability, and flexibility compared to styrene-butadiene rubber, making it ideal for automotive seals and hoses. Styrene-butadiene rubber provides excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in tire treads and vibration dampening components.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, ozone, and weathering | Poor resistance to oils and ozone |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -50degC to 100degC |
| Mechanical Properties | Good abrasion and tensile strength | Moderate abrasion resistance, good flexibility |
| Application in Automotive Parts | Seals, hoses, belts, weatherstripping | Tires, engine mounts, vibration dampers |
| Cost | Higher cost due to superior durability | Lower cost, widely used in economy segments |
Introduction to Chloroprene Rubber and Styrene Butadiene Rubber
Chloroprene rubber (CR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent resistance to weathering, oils, and chemicals, making it ideal for automotive parts exposed to harsh environments. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) offers good abrasion resistance and aging stability, commonly used in tire treads and dynamic automotive components. Both CR and SBR provide valuable properties tailored to different performance requirements, with CR excelling in durability and SBR in wear resistance.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Chloroprene rubber (CR) consists of polychloroprene polymers with chlorine atoms enhancing chemical resistance and weatherability, making it suitable for automotive seals and hoses. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) comprises copolymers of styrene and butadiene, offering good abrasion resistance and aging properties primarily used in tire treads and interior components. The halogenated nature of chloroprene rubber provides superior oil and ozone resistance compared to the hydrocarbon backbone of SBR, influencing performance and durability in automotive applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Chloroprene rubber (CR) exhibits superior tensile strength and weather resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for automotive parts exposed to harsh environmental conditions. SBR offers excellent abrasion resistance and good aging stability, but its mechanical properties generally fall short of CR's performance in terms of tensile strength and elastomeric durability. For automotive applications requiring enhanced mechanical resilience and resistance to oils and ozone, CR is often preferred over SBR.
Heat and Temperature Resistance
Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers superior heat and temperature resistance compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), with CR capable of withstanding continuous temperatures up to 120degC and occasional spikes up to 150degC. SBR typically resists temperatures only up to 100degC, making it less suitable for automotive parts exposed to high thermal stress. The enhanced thermal stability of Chloroprene rubber ensures better durability and performance in engine mounts, seals, and hoses where heat resistance is critical.
Ozone and Weathering Resistance
Chloroprene rubber (CR) exhibits superior ozone and weathering resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for automotive parts exposed to harsh environmental conditions. CR's molecular structure provides excellent resistance to ozone cracking and UV degradation, ensuring longer durability in exterior applications such as seals and hoses. In contrast, SBR tends to degrade faster under ozone exposure, limiting its use primarily to interior or less exposed automotive components.
Oil and Chemical Resistance
Chloroprene rubber exhibits superior oil and chemical resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber, making it highly suitable for automotive parts exposed to harsh fluids and solvents. Its molecular structure provides enhanced stability against petroleum-based oils, hydraulic fluids, and various chemicals, ensuring prolonged durability and performance. In contrast, Styrene butadiene rubber tends to degrade faster under similar conditions, limiting its use in oil-exposed automotive applications.
Durability and Longevity in Automotive Applications
Chloroprene rubber exhibits superior durability and longevity in automotive parts due to its excellent resistance to abrasion, weathering, and ozone exposure compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR). Its enhanced chemical stability and oil resistance make it ideal for components subjected to harsh environmental conditions and mechanical stress. In contrast, SBR offers moderate wear resistance but tends to degrade faster under prolonged heat and oxidative exposure, limiting its service life in demanding automotive applications.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Chloroprene rubber (CR) typically incurs higher raw material and production costs compared to styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), impacting overall automotive part expenses. Despite the higher price, CR offers superior weather, oil, and chemical resistance, which can reduce long-term maintenance and replacement costs. SBR's lower cost and adequate performance in tire and seal applications make it economically favorable for large-scale automotive manufacturing where cost efficiency is critical.
Typical Automotive Parts Using Each Rubber
Chloroprene rubber is commonly used in automotive parts such as fuel hoses, gaskets, and vibration dampers due to its excellent oil, heat, and weather resistance. Styrene butadiene rubber is typically employed in tire treads, sidewalls, and underbody coatings for its superior abrasion resistance and low rolling resistance properties. Both rubbers are essential in automotive manufacturing, with chloroprene preferred for under-the-hood components and styrene butadiene for tire performance applications.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Automotive Parts
Chloroprene rubber offers superior oil, chemical, and weather resistance, making it ideal for automotive parts exposed to harsh environments such as hoses, seals, and gaskets. Styrene butadiene rubber provides excellent abrasion resistance and low-temperature flexibility, preferred in applications like tire treads and inner liners. Selecting the right rubber depends on specific automotive part requirements, with chloroprene favored for durability in dynamic and chemical-exposed components, while styrene butadiene excels in wear resistance and cost-effectiveness.
Infographic: Chloroprene rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Automotive part
 azmater.com
azmater.com