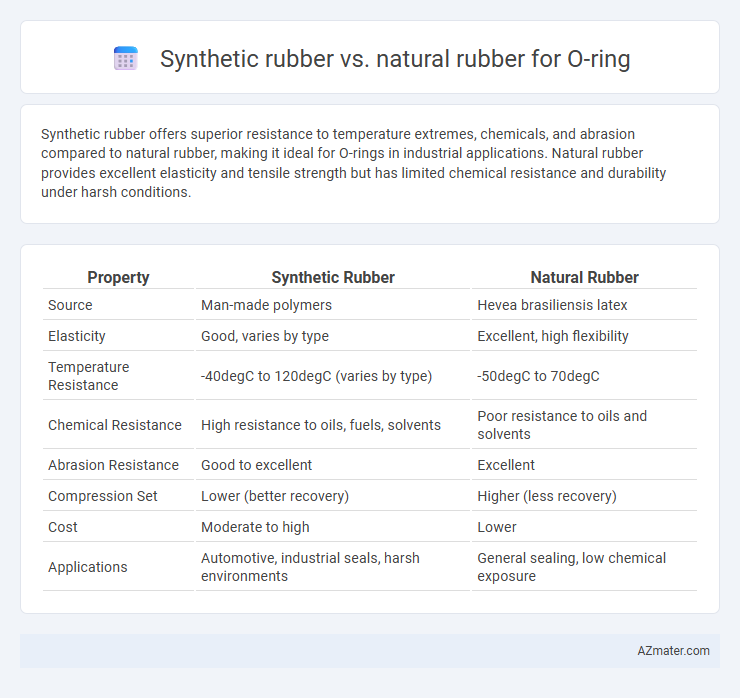
Synthetic rubber offers superior resistance to temperature extremes, chemicals, and abrasion compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for O-rings in industrial applications. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and tensile strength but has limited chemical resistance and durability under harsh conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Synthetic Rubber | Natural Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Man-made polymers | Hevea brasiliensis latex |
| Elasticity | Good, varies by type | Excellent, high flexibility |
| Temperature Resistance | -40degC to 120degC (varies by type) | -50degC to 70degC |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to oils, fuels, solvents | Poor resistance to oils and solvents |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good to excellent | Excellent |
| Compression Set | Lower (better recovery) | Higher (less recovery) |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Lower |
| Applications | Automotive, industrial seals, harsh environments | General sealing, low chemical exposure |
Introduction to O-Rings: Importance and Applications
O-rings, essential sealing components in various industries, rely on the material's properties to ensure performance and durability. Synthetic rubber O-rings offer superior resistance to chemicals, temperature extremes, and wear compared to natural rubber, making them ideal for automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications. Natural rubber O-rings provide excellent elasticity and flexibility but have limited resistance to oils, solvents, and harsh environments, restricting their use in specialized sealing applications.
Overview of Synthetic Rubber: Types and Properties
Synthetic rubber for O-rings includes materials like nitrile (NBR), silicone, fluorocarbon (FKM), and ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), each offering specific chemical resistance and temperature ranges. Nitrile excels in oil and fuel resistance, while silicone provides exceptional flexibility and temperature tolerance from -60degC to 230degC. Fluorocarbon offers superior chemical and heat resistance up to 250degC, making synthetic rubbers versatile for diverse industrial sealing applications compared to natural rubber's limited chemical and temperature resistance.
Overview of Natural Rubber: Characteristics and Sources
Natural rubber, derived from the latex of Hevea brasiliensis trees primarily grown in Southeast Asia, offers excellent elasticity, high tensile strength, and superior abrasion resistance ideal for O-ring applications. Its molecular structure provides outstanding resilience and flexibility, making it suitable for sealing under low to moderate temperatures and pressures. However, natural rubber is susceptible to degradation from oils, solvents, and ozone exposure, limiting its use in harsh chemical environments.
Performance Comparison: Durability and Flexibility
Synthetic rubber O-rings exhibit superior durability compared to natural rubber due to enhanced resistance to heat, chemicals, and abrasion, making them ideal for industrial applications. Natural rubber offers exceptional flexibility and elasticity, maintaining effective sealing in dynamic environments with frequent movement or vibration. Selecting between synthetic and natural rubber depends on specific performance requirements, with synthetic rubber favored for harsh conditions and natural rubber preferred for applications needing high elasticity.
Chemical Resistance: Synthetic vs Natural Rubber in O-Rings
Synthetic rubber O-rings exhibit superior chemical resistance compared to natural rubber, especially against oils, fuels, and solvents. Common synthetic materials like nitrile (NBR), Viton (FKM), and EPDM offer enhanced durability in aggressive chemical environments, whereas natural rubber tends to degrade faster when exposed to hydrocarbons and ozone. This makes synthetic rubber the preferred choice for O-rings in industrial applications requiring robust chemical stability.
Temperature Tolerance: Which Material Performs Better?
Synthetic rubber O-rings, such as those made from silicone or Viton, typically offer superior temperature tolerance ranging from -60degC to 250degC, outperforming natural rubber which generally withstands temperatures between -40degC and 70degC. This makes synthetic rubber ideal for applications involving extreme heat or cold, maintaining elasticity and structural integrity where natural rubber may harden or degrade. High-performance synthetic elastomers ensure reliable sealing under fluctuating temperature conditions, extending the lifespan and effectiveness of O-rings in industrial environments.
Cost Efficiency: Price Differences and Economic Impact
Synthetic rubber O-rings generally offer better cost efficiency due to their lower and more stable prices compared to natural rubber, which is subject to price volatility from agricultural factors. The economic impact favors synthetic options in large-scale manufacturing where consistent supply and predictable costs reduce overall production expenses. Price differences often lead industries to prefer synthetic O-rings for budget-sensitive applications without compromising performance in varying environmental conditions.
Environmental Considerations: Sustainability and Sourcing
Synthetic rubber O-rings, derived from petrochemical sources, pose environmental challenges due to non-renewable resource dependence and complex recycling processes, whereas natural rubber O-rings, sourced from rubber tree latex, offer better biodegradability and renewable sourcing but face concerns related to deforestation and land use. Sustainable practices in natural rubber production, such as certified plantations and agroforestry, enhance environmental benefits by promoting biodiversity and reducing carbon footprints. Life cycle assessments often highlight natural rubber's lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to synthetic options, though ongoing innovations in bio-based synthetic rubbers aim to balance performance with eco-friendly sourcing.
Industry-Specific Suitability: Choosing the Right O-Ring Material
Synthetic rubber O-rings, such as nitrile, EPDM, and Viton, offer enhanced resistance to chemicals, temperature extremes, and abrasion, making them ideal for automotive, aerospace, and chemical processing industries. Natural rubber O-rings excel in applications requiring high elasticity and resilience, commonly used in food processing and certain hydraulic systems where flexibility and compression set resistance are crucial. Selecting the correct O-ring material requires evaluating operational conditions, chemical exposure, and temperature demands specific to the industry to ensure optimal performance and durability.
Conclusion: Selecting the Best Rubber for O-Ring Applications
Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and resilience, making it suitable for dynamic O-ring applications with moderate temperatures and pressures. Synthetic rubber varieties like Nitrile (NBR), Viton (FKM), and EPDM provide superior chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and durability in harsh environments. Selecting the best rubber for O-rings depends on specific application requirements, including temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stresses to ensure optimal sealing performance and longevity.
Infographic: Synthetic rubber vs Natural rubber for O-ring
 azmater.com
azmater.com