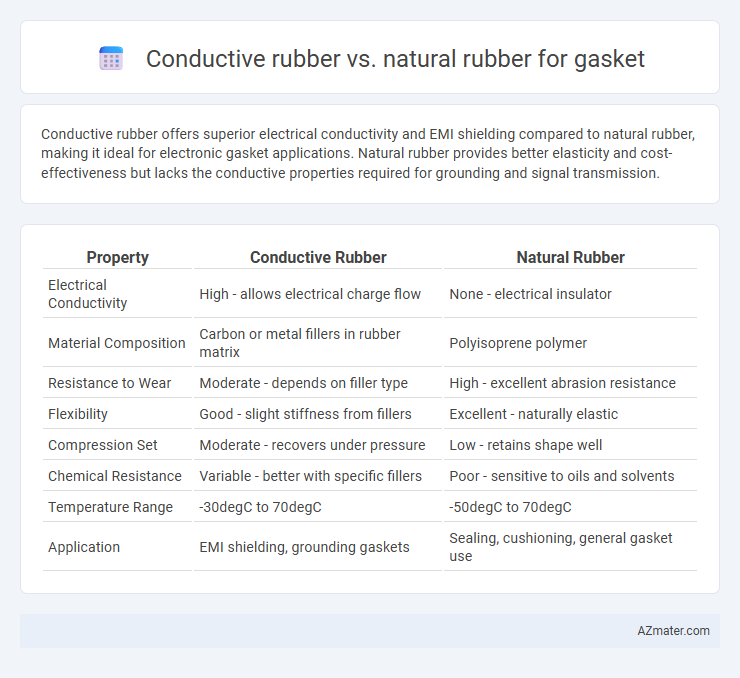
Conductive rubber offers superior electrical conductivity and EMI shielding compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for electronic gasket applications. Natural rubber provides better elasticity and cost-effectiveness but lacks the conductive properties required for grounding and signal transmission.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Conductive Rubber | Natural Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High - allows electrical charge flow | None - electrical insulator |
| Material Composition | Carbon or metal fillers in rubber matrix | Polyisoprene polymer |
| Resistance to Wear | Moderate - depends on filler type | High - excellent abrasion resistance |
| Flexibility | Good - slight stiffness from fillers | Excellent - naturally elastic |
| Compression Set | Moderate - recovers under pressure | Low - retains shape well |
| Chemical Resistance | Variable - better with specific fillers | Poor - sensitive to oils and solvents |
| Temperature Range | -30degC to 70degC | -50degC to 70degC |
| Application | EMI shielding, grounding gaskets | Sealing, cushioning, general gasket use |
Introduction to Gasket Materials
Gasket materials commonly include conductive rubber and natural rubber, each offering unique properties for sealing applications. Conductive rubber provides excellent electrical conductivity and electromagnetic shielding, making it ideal for electronic enclosures. Natural rubber, known for its superior elasticity and resistance to wear, is widely used in general sealing applications where electrical properties are not critical.
What is Conductive Rubber?
Conductive rubber is a specialized elastomer infused with conductive particles such as carbon black, metal flakes, or graphene, providing electrical conductivity while maintaining flexibility. It is used in gaskets to ensure effective grounding, EMI shielding, and static dissipation in electronic devices. Unlike natural rubber, which lacks inherent conductivity and serves primarily as a sealing material, conductive rubber combines sealing properties with electrical performance for advanced applications.
What is Natural Rubber?
Natural rubber is an elastomer derived from the latex sap of rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis), prized for its excellent tensile strength, elasticity, and resilience. Unlike conductive rubber, which incorporates carbon or metal fillers to enable electrical conductivity, natural rubber provides superior flexibility and water resistance but lacks inherent electrical properties. Its biodegradability and excellent mechanical characteristics make it ideal for gasket applications requiring sealing, cushioning, and durability without electrical conductivity demands.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Conductive rubber gaskets exhibit higher electrical conductivity and enhanced resistance to electromagnetic interference compared to natural rubber, which is primarily valued for its excellent elasticity and tensile strength. Natural rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and resilience under dynamic stress, making it ideal for applications requiring flexibility and durability, while conductive rubber provides essential grounding and shielding functions in electronic assemblies. Thermal stability and chemical resistance vary widely between the two, with conductive rubber typically incorporating additives to improve these traits, whereas natural rubber's performance can degrade in harsh environments.
Electrical Conductivity Differences
Conductive rubber gaskets contain carbon black, metal particles, or conductive fillers that enable electrical conductivity, making them suitable for EMI shielding and grounding applications. Natural rubber gaskets lack these conductive additives, resulting in excellent insulation properties but negligible electrical conductivity. The key difference lies in their resistivity values; conductive rubber typically exhibits low resistivity (10^-3 to 10^2 ohm-cm), whereas natural rubber's resistivity exceeds 10^12 ohm-cm, preventing electrical current flow.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Suitability
Conductive rubber gaskets exhibit superior chemical resistance to oils, solvents, and corrosive compounds compared to natural rubber, making them ideal for harsh industrial applications. Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and resilience but tends to degrade faster when exposed to ozone, UV light, and certain chemicals, limiting its environmental suitability. For environments requiring both conductivity and robust chemical resistance, conductive rubber seals provide enhanced durability and longer service life.
Durability and Lifespan
Conductive rubber gaskets exhibit superior durability due to their resistance to wear, chemicals, and extreme temperatures, ensuring a longer lifespan in demanding applications compared to natural rubber. Natural rubber, while offering excellent elasticity and sealing properties, tends to degrade faster when exposed to ozone, UV light, and harsh chemicals, reducing its effective service life. Selecting conductive rubber enhances gasket reliability in electronics, automotive, and industrial environments where prolonged durability and stable conductivity are critical.
Cost and Availability
Conductive rubber gaskets typically cost more than natural rubber due to specialized materials like carbon or metal fillers that enhance electrical conductivity. Natural rubber gaskets offer broader availability and lower price points, making them suitable for general sealing applications without conductivity requirements. Cost-effectiveness and accessibility favor natural rubber, while conductive rubber is essential for applications needing electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding or static dissipation.
Common Applications in Industry
Conductive rubber gaskets are widely used in the electronics and automotive industries for EMI/RFI shielding and grounding applications, ensuring reliable electrical conductivity and static discharge prevention. Natural rubber gaskets find common use in plumbing, food processing, and general industrial machinery due to their excellent flexibility, sealing capability, and resistance to water and abrasion. Selection between conductive and natural rubber gaskets depends on specific requirements such as electrical conductivity, chemical resistance, and mechanical durability in industrial environments.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Gasket Needs
Conductive rubber offers excellent electrical conductivity and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding, making it ideal for electronic and grounding gasket applications. Natural rubber provides superior elasticity, resilience, and chemical resistance, which suits seals in dynamic or harsh environments. Selecting the right gasket material depends on your specific requirements for conductivity, mechanical performance, and environmental resistance to ensure optimal sealing and durability.
Infographic: Conductive rubber vs Natural rubber for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com