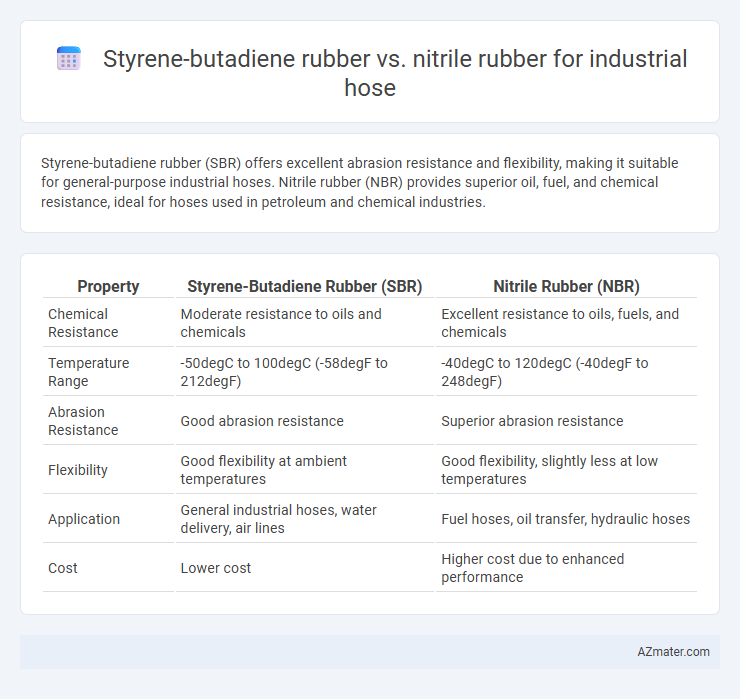
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility, making it suitable for general-purpose industrial hoses. Nitrile rubber (NBR) provides superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, ideal for hoses used in petroleum and chemical industries.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance to oils and chemicals | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 100degC (-58degF to 212degF) | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good abrasion resistance | Superior abrasion resistance |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at ambient temperatures | Good flexibility, slightly less at low temperatures |
| Application | General industrial hoses, water delivery, air lines | Fuel hoses, oil transfer, hydraulic hoses |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to enhanced performance |
Introduction to Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) and Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent abrasion resistance and good aging stability, making it a popular choice for industrial hose applications requiring durability and wear resistance. Nitrile rubber (NBR) excels in oil and fuel resistance due to its high resistance to petroleum-based fluids, which is essential for hoses used in fuel transfer and chemical handling. Both SBR and NBR offer distinct advantages in industrial hoses, with SBR providing superior mechanical strength and NBR delivering enhanced chemical resistance.
Key Characteristics of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance, good tensile strength, and outstanding aging stability, making it ideal for industrial hoses exposed to rough handling and mechanical stress. Its moderate resistance to heat and ozone enhances hose durability in challenging environments, while its relatively low cost supports efficient large-scale production. SBR's flexibility and high resilience contribute to reliable performance in applications requiring resistance to wear, impact, and weathering compared to nitrile rubber, which excels more in oil and chemical resistance.
Essential Properties of Nitrile Rubber
Nitrile rubber offers superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance compared to styrene-butadiene rubber, making it ideal for industrial hoses exposed to aggressive fluids. Its excellent abrasion resistance, high tensile strength, and temperature tolerance from -40degC to 120degC ensure durability in demanding environments. Nitrile rubber also provides enhanced compression set resistance and flexibility, maintaining hose integrity under mechanical stress and fluctuating temperatures.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate resistance to abrasion and some acids but displays poor tolerance to oils, fuels, and solvents, limiting its use in chemical-intensive industrial hoses. Nitrile rubber (NBR) excels in chemical resistance, particularly against petroleum-based oils, fuels, lubricants, and aliphatic hydrocarbons, making it an ideal choice for hoses exposed to oils and greases. While SBR is cost-effective for general industrial applications, NBR's superior resistance to oils and chemicals ensures longer hose life in harsh chemical environments.
Temperature Tolerance: SBR vs NBR
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) typically withstands temperatures ranging from -40degC to 100degC, making it suitable for moderate temperature industrial hose applications. Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior temperature tolerance, functioning effectively between -40degC and 120degC, which enhances its performance in hotter environments. The higher heat resistance of NBR makes it the preferred choice for industrial hoses exposed to oils, fuels, and elevated temperatures.
Abrasion and Wear Performance
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate abrasion resistance and good wear performance, making it suitable for industrial hoses exposed to general mechanical stress and mild abrasive conditions. Nitrile rubber (NBR) significantly outperforms SBR in abrasion resistance due to its superior oil and chemical resistance, enhancing durability in harsh environments with abrasive particles. For industrial hoses requiring enhanced longevity and resistance to wear from oils and chemicals, nitrile rubber is often the preferred material.
Oil and Fuel Resistance in Industrial Hoses
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate oil and fuel resistance but is generally less effective than nitrile rubber (NBR) in harsh industrial environments dealing with petroleum-based fluids. Nitrile rubber exhibits superior resistance to oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons, making it the preferred choice for industrial hoses exposed to aggressive chemical substances and high oil content. The enhanced oil resistance of NBR results in longer service life and reduced material degradation compared to SBR in demanding oil and fuel applications.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is generally more cost-efficient than nitrile rubber (NBR) due to its lower raw material costs and widespread production, making it a preferred choice for budget-sensitive industrial hose applications. Nitrile rubber offers superior resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, but its higher price and limited availability can lead to increased overall expenses in large-scale deployments. Availability of SBR is typically broader, ensuring faster supply and reduced lead times, whereas nitrile rubber may experience supply constraints depending on regional demand and manufacturing capacity.
Application Suitability: Industry Use Cases
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is widely used in industrial hoses for applications involving moderate abrasion resistance and oil exposure, making it ideal for water, air, and general-purpose chemical hoses in sectors like construction and agriculture. Nitrile rubber (NBR) excels in applications requiring superior resistance to petroleum oils, fuels, and chemicals, commonly utilized in automotive, oil refinery, and chemical processing industries. The choice between SBR and NBR hinges on the specific industrial environment, with NBR preferred for hydrocarbon-based fluids and SBR suited for dry abrasion and moderate chemical exposure.
Selecting the Right Rubber: SBR or NBR for Industrial Hoses
Selecting between Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and Nitrile rubber (NBR) for industrial hoses hinges on chemical resistance and temperature requirements. SBR offers strong abrasion resistance and good tensile strength, ideal for general industrial air or water hoses, while NBR excels in oil, fuel, and chemical exposure due to its superior oil resistance and temperature tolerance up to 120degC. For applications involving petroleum-based fluids or harsh chemicals, NBR provides durability and longevity unmatched by SBR, which suits less aggressive environments.
Infographic: Styrene-butadiene rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Industrial hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com