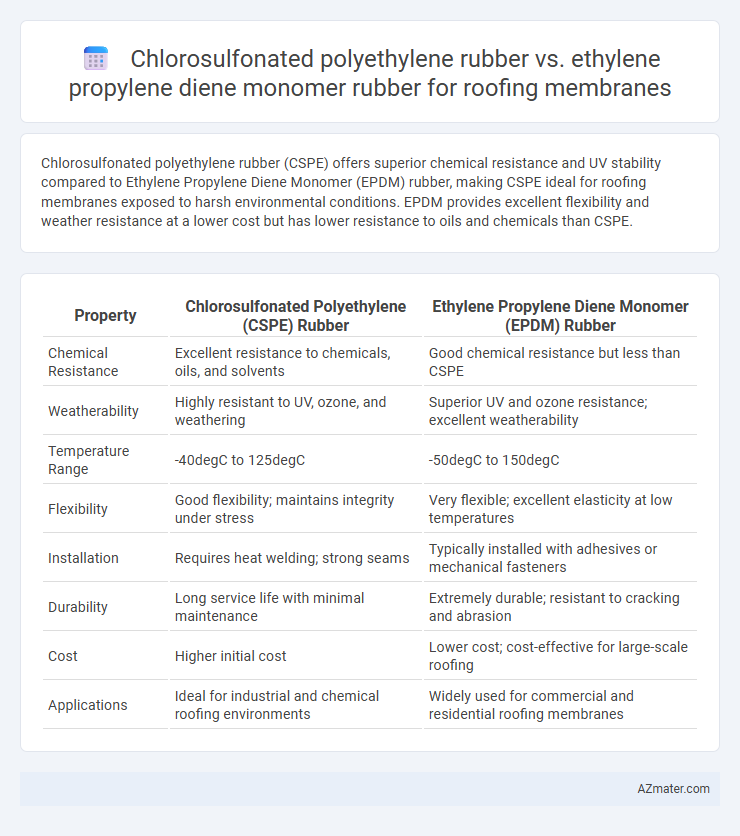
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSPE) offers superior chemical resistance and UV stability compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, making CSPE ideal for roofing membranes exposed to harsh environmental conditions. EPDM provides excellent flexibility and weather resistance at a lower cost but has lower resistance to oils and chemicals than CSPE.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSPE) Rubber | Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to chemicals, oils, and solvents | Good chemical resistance but less than CSPE |
| Weatherability | Highly resistant to UV, ozone, and weathering | Superior UV and ozone resistance; excellent weatherability |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 125degC | -50degC to 150degC |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility; maintains integrity under stress | Very flexible; excellent elasticity at low temperatures |
| Installation | Requires heat welding; strong seams | Typically installed with adhesives or mechanical fasteners |
| Durability | Long service life with minimal maintenance | Extremely durable; resistant to cracking and abrasion |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost; cost-effective for large-scale roofing |
| Applications | Ideal for industrial and chemical roofing environments | Widely used for commercial and residential roofing membranes |
Introduction to Roofing Membranes
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber offers exceptional resistance to weathering, UV radiation, and chemical exposure, making it a durable choice for roofing membranes. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber provides superior flexibility, excellent ozone and UV resistance, and long-term waterproofing performance. The selection between CSPE and EPDM roofing membranes depends on environmental conditions, installation requirements, and lifecycle cost considerations.
Overview of Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSPE) Rubber
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber offers exceptional chemical resistance, weatherability, and UV stability, making it highly suitable for roofing membranes exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Its molecular structure features chlorosulfonyl groups that enhance resistance to ozone, acids, and alkalis, outperforming many other elastomers in durability and lifespan. CSPE roofing membranes maintain flexibility across a wide temperature range, ensuring reliable waterproofing and resistance to mechanical stress.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) Rubber
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber is a synthetic elastomer widely used in roofing membranes due to its excellent resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and extreme weather conditions, ensuring long-term durability. Its superior elasticity and flexibility allow EPDM membranes to accommodate roof movement and thermal expansion without cracking or splitting. Compared to chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber, EPDM offers better chemical resistance and environmental stability, making it a preferred choice for sustainable roofing applications.
Material Properties: CSPE vs EPDM
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSPE) offers excellent resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and chemicals, making it highly durable for roofing membranes in harsh environmental conditions. Ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber (EPDM) is known for superior flexibility, weather resistance, and temperature tolerance, particularly withstanding extreme heat and cold without cracking. While CSPE provides strong resistance against oils and solvents, EPDM excels in elasticity and long-term aging performance, often influencing membrane selection based on specific climate and chemical exposure requirements.
Weather and UV Resistance Comparison
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber exhibits superior weather and UV resistance compared to ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber, maintaining flexibility and durability under prolonged exposure to sunlight and harsh environmental conditions. CSPE's chlorine content enhances its resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and oxidative degradation, making it less prone to cracking and aging over time. While EPDM also offers good weather resistance, it generally experiences faster surface degradation and reduced lifespan in high UV exposure scenarios relative to CSPE membranes.
Chemical and Ozone Resistance in Roofing Applications
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber demonstrates superior chemical resistance against oils, solvents, and acids, making it highly durable in roofing membranes exposed to harsh environmental contaminants. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in ozone resistance, maintaining elasticity and structural integrity under prolonged UV and ozone exposure, which is critical for outdoor roofing applications. While CSPE offers robust protection against a wider range of chemicals, EPDM is preferred for roofing membranes prioritizing ozone and weather resistance, ensuring long-term performance in diverse climatic conditions.
Installation Methods and Flexibility
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber roofing membranes are installed primarily using heat welding or adhesive bonding, providing strong seams resistant to weathering and chemicals, while Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber membranes typically rely on mechanical fastening, ballasting, or adhesives due to their inherent flexibility and ease of handling. CSPE offers excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability, making it suitable for complex roof shapes but requires more precise installation techniques to avoid membrane damage. EPDM exhibits superior elongation and flexibility, allowing for easier installation over irregular roof surfaces and accommodating thermal expansion without loss of waterproofing integrity.
Longevity and Maintenance Considerations
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber roofing membranes exhibit exceptional longevity due to their high resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and chemical exposure, often lasting over 30 years with minimal maintenance. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber offers strong durability but typically requires more frequent inspections and potential repairs due to susceptibility to punctures and seam failures over a 20-25 year lifespan. Maintenance for CSPE membranes is generally lower, as their superior chemical resistance reduces the likelihood of surface degradation and preserves membrane integrity in harsh environmental conditions.
Cost Analysis: CSPE vs EPDM Roofing Membranes
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) roofing membranes typically have a higher initial cost compared to ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) membranes due to their chemical composition and manufacturing process. EPDM offers a more cost-effective option with lower installation and maintenance expenses, making it favorable for budget-conscious projects. Despite the higher upfront investment, CSPE membranes provide superior chemical and UV resistance, potentially reducing long-term replacement costs in harsh environments.
Choosing the Right Rubber Membrane for Roofing
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSPE) offers exceptional chemical resistance, UV stability, and weathering durability, making it highly suitable for roofing membranes exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber is valued for its flexibility, excellent ozone resistance, and cost-effectiveness in roofing applications, particularly in variable climates with temperature fluctuations. Selecting the right rubber membrane involves evaluating factors like exposure to chemicals, UV intensity, temperature range, and budget constraints to determine whether CSPE's superior durability or EPDM's adaptability and economy best fit the project requirements.
Infographic: Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber for Roofing membrane
 azmater.com
azmater.com