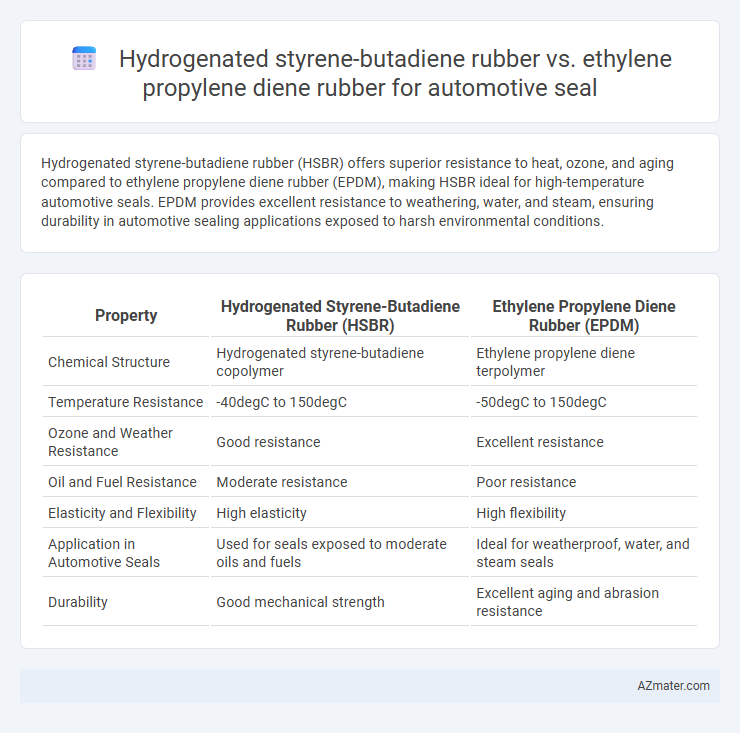
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior resistance to heat, ozone, and aging compared to ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM), making HSBR ideal for high-temperature automotive seals. EPDM provides excellent resistance to weathering, water, and steam, ensuring durability in automotive sealing applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene copolymer | Ethylene propylene diene terpolymer |
| Temperature Resistance | -40degC to 150degC | -50degC to 150degC |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Good resistance | Excellent resistance |
| Oil and Fuel Resistance | Moderate resistance | Poor resistance |
| Elasticity and Flexibility | High elasticity | High flexibility |
| Application in Automotive Seals | Used for seals exposed to moderate oils and fuels | Ideal for weatherproof, water, and steam seals |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength | Excellent aging and abrasion resistance |
Introduction to Automotive Seal Materials
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers enhanced resistance to heat, ozone, and oil, making it suitable for automotive seals exposed to harsh engine environments. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in weathering, ozone, and water resistance, ideal for exterior automotive seals requiring flexibility and durability. Selecting between HSBR and EPDM depends on specific automotive seal applications, balancing chemical resistance and environmental exposure.
Overview of Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR)
Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) is widely used in automotive seals due to its exceptional resistance to heat, oil, and ozone, making it ideal for under-the-hood applications. Its hydrogenation process enhances polymer saturation, significantly improving aging properties and mechanical strength compared to standard SBR. HSBR's superior chemical stability and durability ensure long-lasting performance in dynamic sealing environments commonly encountered in automotive engines.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber offers superior weather, ozone, and heat resistance, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Its excellent flexibility at low temperatures and resistance to water, steam, and polar solvents enhance durability and seal integrity in automotive applications. EPDM's molecular structure provides enhanced aging performance compared to Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR), resulting in longer-lasting seals for vehicles.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) is a selectively hydrogenated version of styrene-butadiene rubber, enhancing its saturation level and providing superior resistance to heat, oxidation, and ozone due to its reduced double bonds in the polymer chain. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber features a saturated ethylene-propylene backbone with unsaturation introduced by the diene component, offering excellent weathering, heat, and chemical resistance, particularly against polar substances. The chemical structure of HSBR allows for higher tensile strength and oil resistance, while EPDM's unique diene functionality provides enhanced flexibility and resistance to non-polar chemicals, making the choice dependent on specific automotive seal requirements such as temperature range and chemical exposure.
Mechanical Properties: HSBR vs EPDM
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), making it ideal for automotive seals requiring high durability. EPDM, however, provides excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, enhancing its longevity in harsh environmental conditions. For mechanical properties, HSBR excels in wear resistance and elasticity, whereas EPDM delivers better compression set and flexibility under fluctuating temperatures.
Weathering and Ozone Resistance in Automotive Seals
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior weathering and ozone resistance compared to ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) in automotive seals, making it ideal for long-term exposure to harsh environmental conditions. HSBR's saturated polymer backbone provides enhanced durability against UV radiation and oxidative degradation, ensuring prolonged seal performance. Although EPDM exhibits good ozone resistance, its unsaturated diene components can degrade faster under extreme weather exposure, reducing its lifespan in critical sealing applications.
Thermal Stability and Aging Performance
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits superior thermal stability compared to ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) due to its saturated polymer backbone, which effectively resists heat-induced degradation at temperatures up to 150degC. In automotive seal applications, HSBR maintains mechanical properties and elasticity over extended exposure to elevated temperatures, enhancing durability and service life. EPDM shows good aging resistance to weathering and ozone but generally has lower thermal stability, making HSBR the preferred choice for high-temperature sealing environments in engines and transmissions.
Processing and Fabrication Differences
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and thermal stability compared to ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM), allowing for easier processing under high-temperature vulcanization conditions commonly used in automotive seals. EPDM provides excellent weathering and ozone resistance with better elasticity, but it requires precise control of cure systems and temperatures to avoid over-curing during fabrication. The crosslinking mechanisms differ; HSBR relies on sulfur vulcanization with accelerator packages optimized for aromatic polymers, while EPDM utilizes peroxide curing systems tailored to its saturated backbone, influencing mold cycle times and post-curing requirements in automotive seal manufacturing.
Cost Analysis and Commercial Availability
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior wear resistance and thermal stability, making it a premium choice for automotive seals, but it typically comes at a higher cost due to complex hydrogenation processes. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber presents a more cost-effective alternative with excellent ozone resistance and flexibility, widely available from numerous commercial suppliers, thus reducing lead times and bulk purchase costs. Manufacturers often balance HSBR's performance advantages against EPDM's affordability and easier commercial availability when optimizing automotive seal production budgets.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right Rubber for Automotive Seals
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior heat resistance and oil stability, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to high temperatures and aggressive fluids. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in weathering resistance and flexibility, providing excellent performance in seals subjected to outdoor environments and low temperatures. Selecting between HSBR and EPDM depends on specific automotive seal requirements, such as thermal exposure, chemical resistance, and elasticity under varying environmental conditions.
Infographic: Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Automotive Seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com