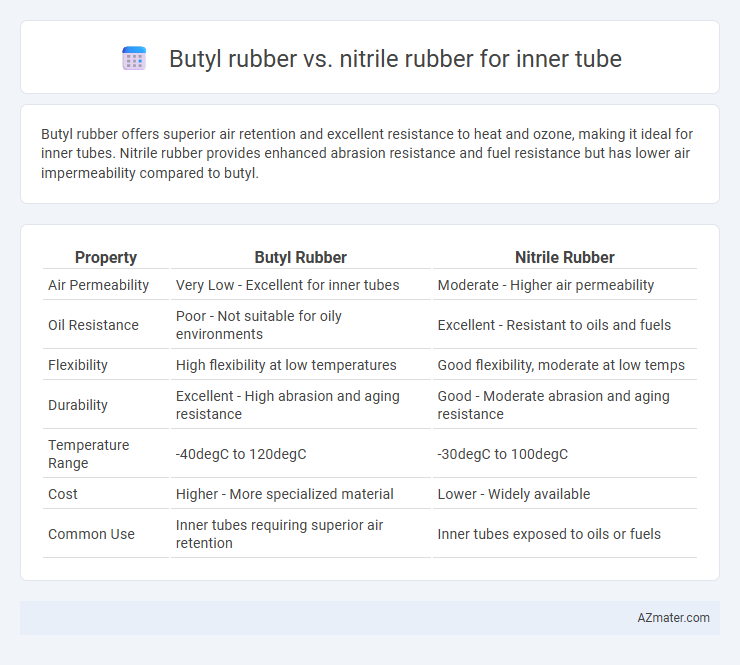
Butyl rubber offers superior air retention and excellent resistance to heat and ozone, making it ideal for inner tubes. Nitrile rubber provides enhanced abrasion resistance and fuel resistance but has lower air impermeability compared to butyl.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Butyl Rubber | Nitrile Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Air Permeability | Very Low - Excellent for inner tubes | Moderate - Higher air permeability |
| Oil Resistance | Poor - Not suitable for oily environments | Excellent - Resistant to oils and fuels |
| Flexibility | High flexibility at low temperatures | Good flexibility, moderate at low temps |
| Durability | Excellent - High abrasion and aging resistance | Good - Moderate abrasion and aging resistance |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -30degC to 100degC |
| Cost | Higher - More specialized material | Lower - Widely available |
| Common Use | Inner tubes requiring superior air retention | Inner tubes exposed to oils or fuels |
Introduction to Inner Tube Materials
Inner tubes are commonly manufactured using butyl rubber and nitrile rubber, each offering distinct advantages for tire performance and durability. Butyl rubber is prized for its excellent air retention and chemical resistance, making it ideal for maintaining consistent tire pressure over time. Nitrile rubber provides superior resistance to oil, fuel, and abrasion, enhancing inner tube longevity in demanding applications such as motorcycles and heavy machinery.
Overview of Butyl Rubber
Butyl rubber, a synthetic rubber known for its excellent air impermeability, is widely used in inner tubes due to its superior resistance to gas diffusion and good flexibility at low temperatures. It provides outstanding chemical stability and resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it more durable compared to nitrile rubber. Butyl rubber's low permeability to air ensures longer inflation retention, enhancing the performance and lifespan of inner tubes in various vehicles.
Overview of Nitrile Rubber
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a synthetic elastomer renowned for its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for inner tubes exposed to harsh conditions. It offers superior abrasion resistance and good flexibility at low temperatures compared to butyl rubber, enhancing durability and performance in demanding environments. Though butyl rubber provides better air retention, nitrile rubber's enhanced chemical resistance and toughness ensure longer service life in industrial and automotive inner tube applications.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Butyl rubber, primarily composed of isobutylene with a small amount of isoprene, offers excellent impermeability to gases and superior resistance to weathering, making it ideal for inner tubes requiring airtight performance. Nitrile rubber consists mainly of acrylonitrile and butadiene, providing superior oil and fuel resistance but lower gas impermeability compared to butyl rubber. The chemical composition of butyl rubber enhances its flexibility and air retention, whereas nitrile rubber's polar acrylonitrile content improves chemical resistance but reduces its effectiveness as a tire inner tube material.
Air Retention Capabilities
Butyl rubber offers superior air retention capabilities compared to nitrile rubber due to its low permeability to gases, making it the preferred material for inner tubes in automotive and bicycle tires. Its molecular structure effectively minimizes air leakage over time, ensuring longer inflation periods and improved durability. Nitrile rubber, while resistant to oils and chemicals, exhibits higher gas permeability, resulting in faster air loss and less efficient performance in inner tube applications.
Resistance to Temperature and Weather
Butyl rubber offers superior resistance to extreme temperatures and excellent weathering properties, making it ideal for inner tubes exposed to prolonged sunlight and harsh environmental conditions. Nitrile rubber, while providing good heat resistance and moderate weather resistance, is more prone to degradation under intense UV exposure. The enhanced impermeability and durability of butyl rubber ensure longer lifespan and reliable performance in varying climatic conditions compared to nitrile rubber.
Flexibility and Elasticity Differences
Butyl rubber offers superior elasticity, enabling inner tubes to maintain shape and absorb impacts effectively, while nitrile rubber provides greater flexibility with enhanced resistance to oils and punctures. The molecular structure of butyl rubber allows for excellent gas retention and elastic recovery, making it ideal for high-pressure inner tubes. Nitrile rubber's flexibility supports better movement under stress but sacrifices some elasticity, which can affect the tube's long-term durability and airtightness.
Durability and Longevity
Butyl rubber offers superior air retention and excellent resistance to ozone, heat, and weathering, making it highly durable for inner tubes subjected to prolonged use and harsh conditions. Nitrile rubber provides exceptional resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, enhancing longevity in environments where inner tubes are exposed to such substances. When evaluating inner tube materials, butyl rubber generally ensures longer service life through better durability against environmental factors, while nitrile rubber excels in applications demanding chemical and oil resistance.
Cost Analysis of Butyl vs Nitrile Rubber
Butyl rubber offers a lower material cost compared to nitrile rubber, making it a more economical choice for inner tube production where budget constraints are critical. Nitrile rubber, while generally more expensive, provides superior resistance to oils and chemicals, which can justify the higher price in applications requiring enhanced durability. Manufacturers must weigh the cost savings of butyl against the performance benefits of nitrile to determine the most cost-effective material for their specific inner tube requirements.
Best Applications for Each Material
Butyl rubber excels in inner tubes for bicycle, motorcycle, and truck tires due to its superior air retention, excellent impermeability to gases, and resistance to weathering and ozone. Nitrile rubber is best suited for inner tubes in industrial and heavy-duty applications where oil, fuel, and chemical resistance are critical factors. Both materials offer durability, but butyl is favored for long-lasting inflation while nitrile provides enhanced performance in harsh environments prone to hydrocarbon exposure.
Infographic: Butyl rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Inner tube
 azmater.com
azmater.com