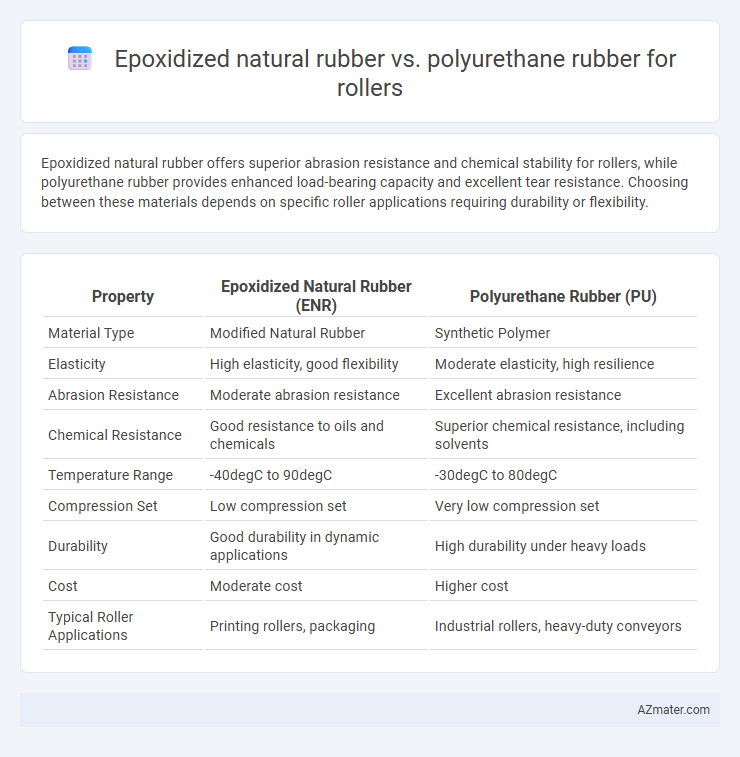
Epoxidized natural rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and chemical stability for rollers, while polyurethane rubber provides enhanced load-bearing capacity and excellent tear resistance. Choosing between these materials depends on specific roller applications requiring durability or flexibility.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) | Polyurethane Rubber (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Modified Natural Rubber | Synthetic Polymer |
| Elasticity | High elasticity, good flexibility | Moderate elasticity, high resilience |
| Abrasion Resistance | Moderate abrasion resistance | Excellent abrasion resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and chemicals | Superior chemical resistance, including solvents |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 90degC | -30degC to 80degC |
| Compression Set | Low compression set | Very low compression set |
| Durability | Good durability in dynamic applications | High durability under heavy loads |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost |
| Typical Roller Applications | Printing rollers, packaging | Industrial rollers, heavy-duty conveyors |
Introduction to Roller Materials
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced oil resistance, improved mechanical strength, and superior abrasion resistance, making it suitable for rollers in demanding industrial applications. Polyurethane rubber provides exceptional toughness, high load-bearing capacity, and excellent wear resistance, often preferred for heavy-duty roller components subjected to high stress and impact. Choosing between ENR and polyurethane rubber depends on specific performance requirements such as chemical exposure, load conditions, and operational environment.
Overview of Epoxidized Natural Rubber
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) is derived from natural rubber through epoxidation, introducing oxygen groups into the polymer chain, enhancing oil resistance, gas impermeability, and adhesion properties. ENR exhibits better heat and chemical resistance compared to traditional natural rubber, making it a valuable material for demanding roller applications where durability and elasticity are required. Compared to polyurethane rubber, ENR offers improved flexibility and resistance to swelling in oils, although polyurethane provides superior abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity for heavy-duty roller use.
Overview of Polyurethane Rubber
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent elasticity compared to epoxidized natural rubber, making it ideal for roller applications requiring durability and load-bearing capacity. Its resistance to oils, solvents, and chemicals enhances roller longevity in industrial settings involving harsh environments. Polyurethane's customizable hardness and resilience allow precise performance tuning, outperforming epoxidized natural rubber in wear resistance and dimensional stability.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits enhanced tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to conventional natural rubber, making it highly suitable for rollers subjected to heavy wear. Polyurethane rubber outperforms ENR in tear resistance and compressive strength, providing superior durability under high-stress and repetitive loading conditions. While ENR offers better elasticity and resilience, polyurethane's mechanical robustness ensures longer service life for industrial roller applications.
Chemical Resistance Performance
Epoxidized natural rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents due to the polar epoxy groups that enhance its molecular structure, making it less prone to swelling and degradation. Polyurethane rubber provides excellent resistance to abrasion and mechanical wear but is generally less effective against aggressive chemicals, particularly aromatic hydrocarbons and chlorinated solvents. For roller applications requiring high chemical durability, epoxidized natural rubber offers enhanced longevity and performance in harsh chemical environments compared to polyurethane rubber.
Abrasion and Wear Resistance
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior abrasion resistance due to its enhanced polarity and crosslink density, making it highly effective for roller applications subject to friction and wear. Polyurethane rubber exhibits excellent wear resistance owing to its high tensile strength and toughness, providing durability under heavy load conditions. Compared to polyurethane, ENR delivers better grip and reduced surface cracking, while polyurethane generally outperforms in oil resistance and mechanical stress endurance.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers lower raw material costs compared to polyurethane rubber, making it a more economical choice for rollers in cost-sensitive applications. ENR exhibits good abrasion resistance and flexibility, reducing maintenance expenses over time, while polyurethane provides superior durability and chemical resistance but at a higher initial investment. Choosing between ENR and polyurethane involves balancing upfront material costs against long-term performance and replacement frequency to optimize total cost of ownership.
Application Suitability in Roller Manufacturing
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers excellent oil resistance, high tensile strength, and superior abrasion resistance, making it suitable for rollers used in printing, laminating, and rubber processing industries where chemical exposure and durability are critical. Polyurethane rubber provides outstanding load-bearing capacity, excellent abrasion resistance, and superior mechanical properties, ideal for rollers in heavy-duty applications such as conveyor systems, industrial machinery, and material handling. ENR excels in environments requiring chemical compatibility and elasticity, while polyurethane is preferred for rollers demanding high resilience and wear resistance under intense mechanical stress.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior biodegradability and lower carbon footprint compared to polyurethane rubber, which relies heavily on petrochemical sources and emits more greenhouse gases during production. ENR's renewable origin from natural latex contributes to reduced environmental pollution and enhanced sustainability in roller applications. Polyurethane, while durable, poses challenges in recycling and disposal, making ENR a more eco-friendly choice for industries prioritizing green manufacturing practices.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Rollers
Epoxidized natural rubber offers superior chemical resistance and improved thermal stability, making it ideal for environments requiring durability against oils and solvents. Polyurethane rubber provides exceptional abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, suitable for heavy-duty roller applications with high mechanical stress. Selecting the right rubber depends on specific operational needs, where ENR excels in chemical and heat resistance, while polyurethane outperforms in wear resistance and mechanical strength.
Infographic: Epoxidized natural rubber vs Polyurethane rubber for Roller
 azmater.com
azmater.com