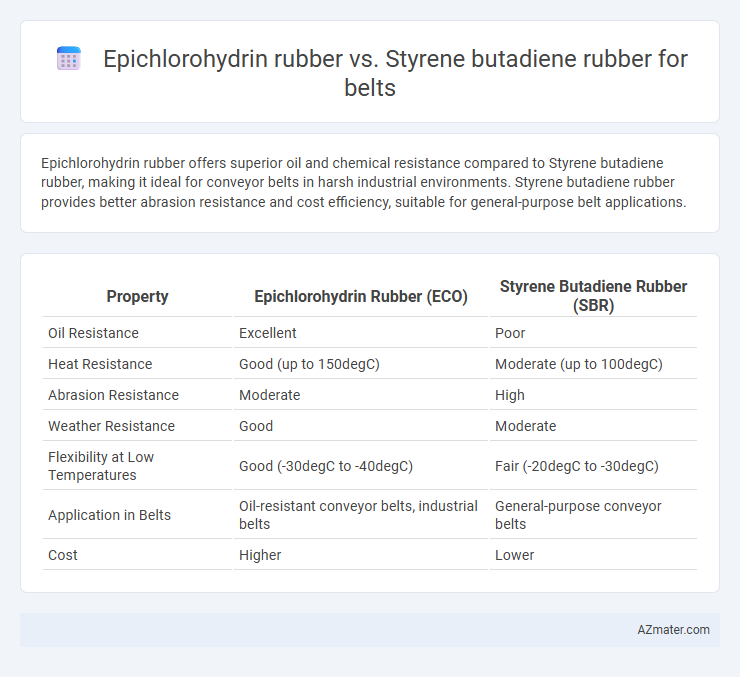
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior oil and chemical resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber, making it ideal for conveyor belts in harsh industrial environments. Styrene butadiene rubber provides better abrasion resistance and cost efficiency, suitable for general-purpose belt applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Resistance | Excellent | Poor |
| Heat Resistance | Good (up to 150degC) | Moderate (up to 100degC) |
| Abrasion Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Weather Resistance | Good | Moderate |
| Flexibility at Low Temperatures | Good (-30degC to -40degC) | Fair (-20degC to -30degC) |
| Application in Belts | Oil-resistant conveyor belts, industrial belts | General-purpose conveyor belts |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Epichlorohydrin Rubber and Styrene Butadiene Rubber
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) is a synthetic elastomer known for its outstanding oil, chemical, and ozone resistance, making it ideal for belts used in harsh industrial environments. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, commonly utilized in conveyor belts for general-purpose applications. Both rubbers provide unique benefits, with Epichlorohydrin excelling in durability under exposure to oils and SBR favored for mechanical wear resistance.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) is a copolymer of epichlorohydrin and ethylene oxide, characterized by its polar chlorine atoms that enhance oil, fuel, and chemical resistance. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) consists of styrene and butadiene monomers, providing excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability but lower chemical resistance compared to ECO. The presence of polar groups in epichlorohydrin rubber gives superior impermeability and resistance to ozone and weathering, making it a preferred choice for belts exposed to harsh chemicals and oils.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers superior oil resistance, compression set, and ozone resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for durable belts in harsh environments. SBR exhibits good abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness but falls short in chemical resistance and aging stability relative to ECO. Mechanical properties such as tensile strength, elongation at break, and tear resistance are higher in Epichlorohydrin rubber, resulting in longer service life and enhanced belt performance in demanding applications.
Temperature Resistance Performance
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior temperature resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber, maintaining elasticity and mechanical strength at temperatures up to 120degC. In contrast, Styrene butadiene rubber typically performs well only up to around 70degC before degradation begins, limiting its use in high-temperature belt applications. This makes Epichlorohydrin rubber ideal for industrial belts exposed to elevated thermal conditions, ensuring longer service life and reduced maintenance.
Oil and Chemical Resistance
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior oil and chemical resistance compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), making it ideal for conveyor belts exposed to harsh oils and solvents. Its molecular structure provides excellent resistance to hydrocarbons, ozone, and weathering, whereas SBR tends to degrade faster when in contact with oils and chemicals. This enhanced durability of epichlorohydrin rubber ensures longer service life and reduced maintenance costs in industrial applications.
Durability and Lifespan in Belt Applications
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior chemical resistance and low gas permeability, making it highly durable in harsh belt applications exposed to oils, solvents, and extreme temperatures. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides good abrasion resistance but has lower resistance to heat and chemicals, resulting in a shorter lifespan in demanding industrial environments. For belt applications requiring long-term durability and exposure to aggressive substances, Epichlorohydrin rubber belts significantly outperform SBR belts.
Flexibility and Elasticity
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent resistance to oil and ozone, making it ideal for belts exposed to harsh chemicals and low temperatures. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides moderate elasticity and abrasion resistance, suitable for general-purpose belts requiring good wear resistance. For applications demanding high elasticity and oil resistance, Epichlorohydrin rubber outperforms SBR in maintaining belt integrity and flexibility under stress.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers superior resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering, making it cost-efficient in industrial belt applications due to its longer lifespan despite a higher initial price. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) is more widely available and generally cheaper, suited for less demanding belt environments but may require more frequent replacement due to lower chemical resistance. Balancing cost efficiency and availability, ECO belts reduce maintenance expenses in harsh conditions, while SBR provides an economical option for standard applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) demonstrates superior chemical resistance and durability, contributing to longer belt lifespan and reduced waste compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), which tends to degrade faster under harsh conditions. ECO production involves chlorinated compounds that pose environmental challenges, including higher toxic emissions and difficulty in recycling, whereas SBR, derived from petroleum, has a lower environmental footprint during manufacturing but suffers from limited biodegradability. Sustainable belt applications favor ECO for performance longevity but require careful management of its environmental impact, while SBR offers more eco-friendly production with trade-offs in durability and replacement frequency.
Application Suitability in Belt Manufacturing
Epichlorohydrin rubber demonstrates superior oil resistance and ozone stability, making it highly suitable for belts used in automotive and industrial machinery where exposure to oils and chemicals is frequent. Styrene butadiene rubber offers excellent abrasion resistance and low-temperature flexibility, ideal for conveyor and drive belts operating in dry, cold environments. Selecting between Epichlorohydrin and Styrene butadiene rubber depends on the belt's exposure conditions and performance requirements in manufacturing applications.
Infographic: Epichlorohydrin rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com