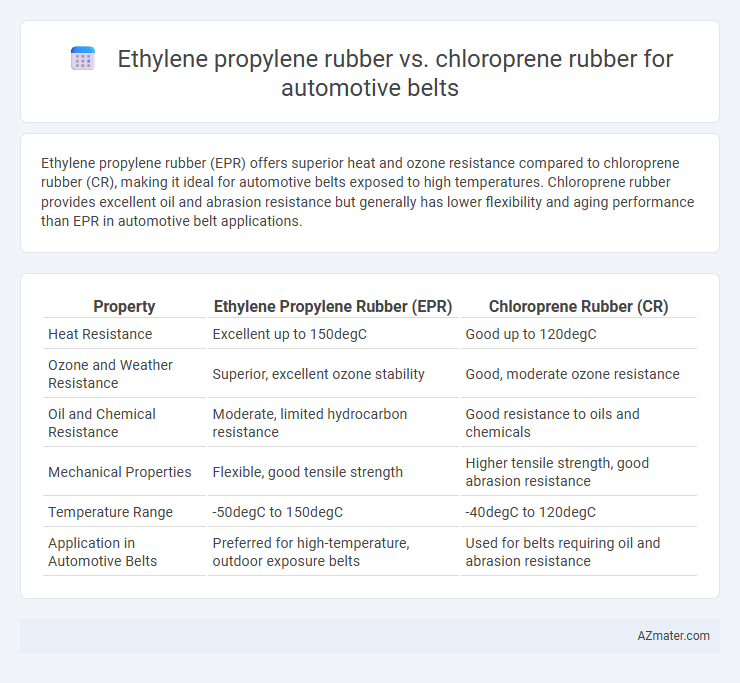
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior heat and ozone resistance compared to chloroprene rubber (CR), making it ideal for automotive belts exposed to high temperatures. Chloroprene rubber provides excellent oil and abrasion resistance but generally has lower flexibility and aging performance than EPR in automotive belt applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Excellent up to 150degC | Good up to 120degC |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Superior, excellent ozone stability | Good, moderate ozone resistance |
| Oil and Chemical Resistance | Moderate, limited hydrocarbon resistance | Good resistance to oils and chemicals |
| Mechanical Properties | Flexible, good tensile strength | Higher tensile strength, good abrasion resistance |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 150degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Application in Automotive Belts | Preferred for high-temperature, outdoor exposure belts | Used for belts requiring oil and abrasion resistance |
Introduction: Overview of Automotive Belt Materials
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) and chloroprene rubber (CR) are prominent materials used in automotive belt manufacturing due to their distinct physical and chemical properties. EPR offers excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for belts requiring durability under high-temperature conditions. Chloroprene rubber provides superior abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, enhancing belt longevity in demanding automotive applications.
Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR): Properties and Benefits
Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) offers excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for automotive belts exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Its superior flexibility and good electrical insulation properties enhance belt durability and performance in engine compartments. Compared to Chloroprene Rubber, EPR provides better chemical resistance and longer service life under high-temperature applications in automotive systems.
Chloroprene Rubber (CR): Characteristics and Advantages
Chloroprene rubber (CR), commonly known as Neoprene, offers exceptional resistance to oil, heat, and weathering, making it ideal for automotive belts in demanding environments. Its superior mechanical strength and excellent abrasion resistance ensure long-lasting performance under continuous stress and exposure to chemicals. Compared to ethylene propylene rubber (EPR), CR maintains flexibility at low temperatures and provides enhanced durability against ozone and UV radiation, crucial for automotive belt longevity.
Heat and Temperature Resistance Comparison
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior heat resistance, maintaining flexibility and performance at temperatures up to 150degC, making it ideal for automotive belts exposed to high engine heat. Chloroprene rubber (CR), also known as neoprene, exhibits good temperature resistance but typically operates effectively up to 120degC, with slightly lower heat aging properties than EPR. For automotive belts requiring extended durability in high-temperature environments, EPR provides enhanced thermal stability and resistance to heat-induced degradation compared to chloroprene rubber.
Chemical and Oil Resistance: EPR vs CR
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) demonstrates superior chemical resistance, particularly against polar solvents, acids, and alkalis, making it highly effective in automotive belt applications exposed to harsh chemicals. Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers excellent oil and fuel resistance due to its balanced polarity and molecular structure, ensuring durability in environments with petroleum-based fluids. When comparing EPR vs CR for automotive belts, EPR excels in resisting a wider range of chemicals, while CR provides enhanced oil resistance, crucial for engine compartment performance.
Durability and Longevity in Automotive Applications
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) exhibits superior resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, resulting in enhanced durability and extended longevity for automotive belts compared to chloroprene rubber. Chloroprene rubber offers moderate resistance to oil and abrasion but tends to degrade faster under high-temperature conditions common in automotive engine environments. For long-lasting automotive belt performance, EPR provides better stability and endurance, reducing maintenance frequency and overall replacement costs.
Performance in Harsh Environmental Conditions
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers exceptional resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for automotive belts exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Chloroprene rubber (CR) provides excellent oil, chemical, and abrasion resistance but may degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and extreme temperatures. For automotive belts requiring durability against ozone, heat, and moisture, EPR generally delivers superior long-term performance compared to chloroprene rubber.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior cost-effectiveness for automotive belts due to its lower raw material expenses and extended service life, reducing overall maintenance costs. Chloroprene rubber (CR), while more expensive, provides excellent oil resistance and durability, but its higher production costs impact price competitiveness. Availability-wise, EPR is more widely accessible globally, facilitating easier sourcing and consistent supply chains in automotive manufacturing.
Applications in Modern Automotive Belts
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPM/EPDM) excels in automotive belt applications due to its superior resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for serpentine belts and timing belts exposed to harsh engine environments. Chloroprene rubber (Neoprene) offers excellent oil, chemical, and abrasion resistance, which helps maintain belt durability in contact with engine oils and coolant fluids. Modern automotive belts often leverage the thermal stability of EPDM alongside the mechanical resilience of chloroprene to optimize performance under varying operational conditions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Automotive Belts
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior heat resistance and excellent weathering properties, making it ideal for automotive belts exposed to high temperatures and harsh environmental conditions. Chloroprene rubber (CR), with its strong oil resistance and good mechanical strength, is better suited for applications requiring durability against petroleum-based fluids and mechanical stress. Selecting the right rubber depends on the specific automotive belt requirements, where EPR excels in thermal and environmental resilience, while CR delivers enhanced oil and abrasion resistance.
Infographic: Ethylene propylene rubber vs Chloroprene rubber for Automotive belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com