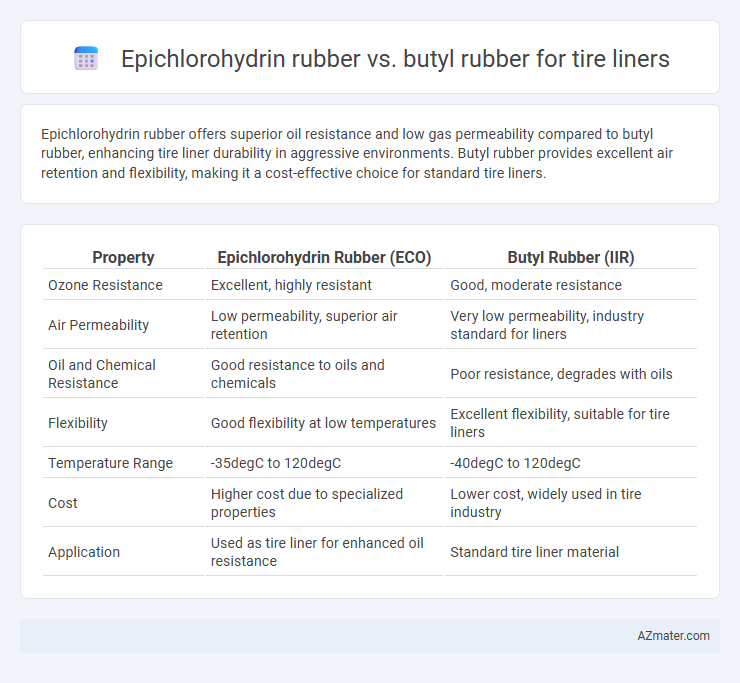
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior oil resistance and low gas permeability compared to butyl rubber, enhancing tire liner durability in aggressive environments. Butyl rubber provides excellent air retention and flexibility, making it a cost-effective choice for standard tire liners.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) | Butyl Rubber (IIR) |
|---|---|---|
| Ozone Resistance | Excellent, highly resistant | Good, moderate resistance |
| Air Permeability | Low permeability, superior air retention | Very low permeability, industry standard for liners |
| Oil and Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and chemicals | Poor resistance, degrades with oils |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at low temperatures | Excellent flexibility, suitable for tire liners |
| Temperature Range | -35degC to 120degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized properties | Lower cost, widely used in tire industry |
| Application | Used as tire liner for enhanced oil resistance | Standard tire liner material |
Introduction to Tire Liner Materials
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent resistance to oil, ozone, and weathering, making it a durable choice for tire liners in industrial and truck tires. Butyl rubber is highly impermeable to gases and provides superior air retention, which is essential for maintaining tire pressure over extended periods. Both materials contribute distinct properties to tire liners, balancing durability and airtightness in tire construction.
Overview of Epichlorohydrin Rubber
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers excellent oil, fuel, and ozone resistance, making it ideal for tire liners exposed to harsh chemical environments. Its low permeability to gases and superior flexibility at low temperatures provide enhanced durability and airtightness compared to butyl rubber. ECO's chemical structure, featuring chlorinated epoxy groups, results in improved adhesion properties and resistance to heat aging, outperforming traditional butyl rubber in demanding tire applications.
Overview of Butyl Rubber
Butyl rubber is a synthetic elastomer characterized by its excellent impermeability to gases, making it ideal for tire liners that require airtight properties to maintain consistent tire pressure. Its unique polymer structure, primarily composed of isobutylene with a small amount of isoprene, offers superior resistance to heat, chemicals, and ozone compared to epichlorohydrin rubber. This combination of durability and low permeability enhances the overall performance and longevity of tires, giving butyl rubber a significant advantage in tire liner applications.
Key Properties of Epichlorohydrin Rubber
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) exhibits exceptional oil resistance, superior impermeability to gases, and excellent flexibility at low temperatures, making it highly suitable for tire liners that require durability against fuel and chemical exposure. Its high resilience and resistance to ozone, weathering, and heat contribute to extended tire life, outperforming butyl rubber in oil resistance and chemical stability. While butyl rubber offers excellent air retention and good abrasion resistance, epichlorohydrin rubber's enhanced impermeability and chemical durability provide significant advantages in demanding automotive applications.
Key Properties of Butyl Rubber
Butyl rubber offers superior air impermeability and excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and chemicals, making it ideal for tire liners. Its high damping capacity and flexibility improve tire performance by enhancing ride comfort and durability. Compared to epichlorohydrin rubber, butyl rubber provides better resistance to gas permeability and aging, which extends tire life and safety.
Comparative Air Permeability
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits significantly lower air permeability compared to butyl rubber, enhancing tire liner airtightness and extending tire life. The tightly cross-linked molecular structure of Epichlorohydrin rubber reduces gas transmission rates, making it superior for preventing air loss in pneumatic tires. In contrast, butyl rubber offers moderate air impermeability but typically allows higher oxygen and nitrogen diffusion, impacting long-term tire pressure retention.
Chemical and Ozone Resistance Comparison
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance, particularly against oils, fuels, and solvents, making it highly effective for tire liners exposed to harsh chemical environments. Butyl rubber, while offering exceptional ozone and weathering resistance due to its saturated polymer backbone, shows less chemical resistance compared to Epichlorohydrin rubber. The ozone resistance of Butyl rubber surpasses that of Epichlorohydrin, minimizing cracking and degradation in outdoor applications, whereas Epichlorohydrin provides a balanced performance in both chemical and moderate ozone exposure conditions.
Flexibility and Durability in Tire Liners
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent resistance to ozone and weathering, making it ideal for tire liners requiring enhanced elastic properties. Butyl rubber provides exceptional air impermeability and remarkable durability against heat and aging, ensuring long-lasting tire pressure retention. Combining the flexibility of Epichlorohydrin with the durability of Butyl rubber creates tire liners optimized for both comfort and extended lifespan.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent chemical resistance and impermeability, making it a cost-effective choice for tire liners in applications where fuel and oil resistance are critical. Butyl rubber, while generally more expensive due to its specialized synthesis and higher raw material costs, provides superior air retention and flexibility crucial for tire performance. Manufacturing Epichlorohydrin rubber involves simpler polymerization processes compared to the more complex isobutylene-based production of Butyl rubber, impacting overall production costs and scalability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Ideal Tire Liner Material
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to ozone, fuel, and chemicals, making it ideal for high-performance tire liners requiring excellent impermeability and durability. Butyl rubber provides outstanding air retention and flexibility, ensuring long-lasting tire inflation and enhanced ride comfort. Selecting between Epichlorohydrin and Butyl rubber depends on specific tire performance demands, environmental exposure, and cost considerations.
Infographic: Epichlorohydrin rubber vs Butyl rubber for Tire liner
 azmater.com
azmater.com