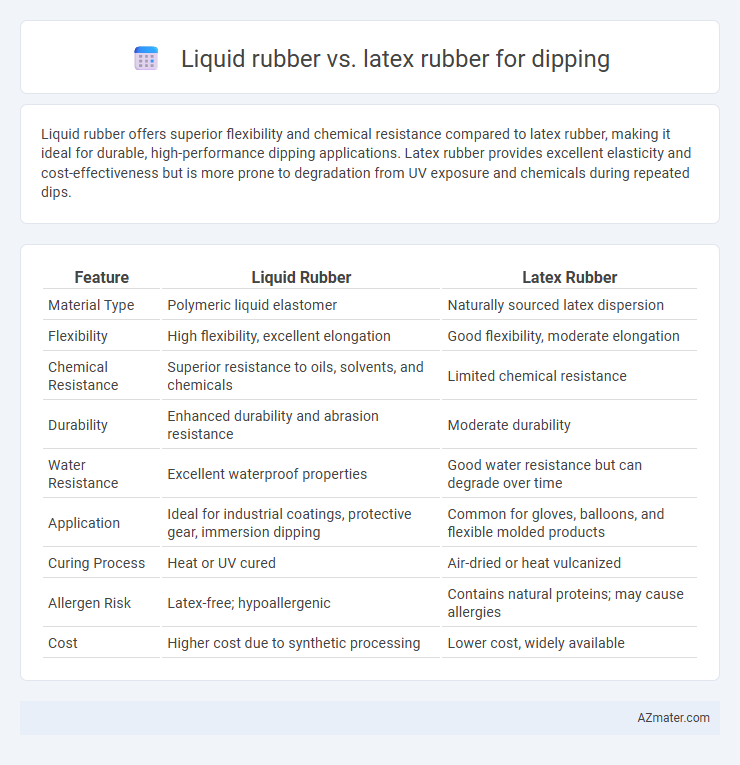
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and chemical resistance compared to latex rubber, making it ideal for durable, high-performance dipping applications. Latex rubber provides excellent elasticity and cost-effectiveness but is more prone to degradation from UV exposure and chemicals during repeated dips.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Liquid Rubber | Latex Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polymeric liquid elastomer | Naturally sourced latex dispersion |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, excellent elongation | Good flexibility, moderate elongation |
| Chemical Resistance | Superior resistance to oils, solvents, and chemicals | Limited chemical resistance |
| Durability | Enhanced durability and abrasion resistance | Moderate durability |
| Water Resistance | Excellent waterproof properties | Good water resistance but can degrade over time |
| Application | Ideal for industrial coatings, protective gear, immersion dipping | Common for gloves, balloons, and flexible molded products |
| Curing Process | Heat or UV cured | Air-dried or heat vulcanized |
| Allergen Risk | Latex-free; hypoallergenic | Contains natural proteins; may cause allergies |
| Cost | Higher cost due to synthetic processing | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Liquid Rubber and Latex Rubber
Liquid rubber is a versatile polymer material widely used in industrial dipping processes for coatings, seals, and protective films, offering excellent chemical resistance and durability. Latex rubber, a natural or synthetic milky fluid, forms flexible, elastic coatings typically preferred for their softness and biodegradability but with limited chemical resistance compared to liquid rubber. Both materials are essential in dipping applications, with liquid rubber favored for tougher, long-lasting performance and latex rubber chosen for applications requiring elasticity and comfort.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Liquid rubber typically consists of synthetic polymers such as nitrile or styrene-butadiene, characterized by a molecular structure designed for enhanced chemical resistance and durability during dipping processes. Latex rubber is composed primarily of natural cis-1,4-polyisoprene, featuring a highly elastic and flexible molecular network ideal for producing smooth, stretchable coatings. The choice between liquid rubber and latex rubber for dipping depends on the chemical composition's impact on adhesion, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors.
Common Applications in Dipping
Liquid rubber, typically made from synthetic materials like neoprene or nitrile, is widely used in industrial dipping applications such as coating automotive parts, protective gloves, and medical devices due to its chemical resistance and durability. Latex rubber, derived from natural sources, is preferred for producing flexible, lightweight items like balloons, gloves, and catheters, emphasizing elasticity and biocompatibility. Both materials support seamless dipping processes but differ significantly in chemical resistance, flexibility, and end-use performance requirements.
Flexibility and Durability Comparison
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility compared to latex rubber, making it ideal for applications requiring extensive material stretch and movement without cracking. In terms of durability, liquid rubber provides enhanced resistance to oils, chemicals, and UV exposure, resulting in longer-lasting protective coatings than latex rubber. Latex rubber, while more cost-effective, typically exhibits less resilience under extreme environmental conditions and repetitive flexing.
Ease of Use and Application Process
Liquid rubber offers superior ease of use for dipping due to its lower viscosity, allowing smoother and more even coatings without the need for extensive thinning. Latex rubber requires careful mixing and often multiple thin layers to prevent uneven texture and extended drying times. The dipping application process with liquid rubber is faster and more efficient, making it ideal for high-volume production settings.
Safety Considerations and Allergen Risks
Liquid rubber formulated from synthetic polymers generally presents fewer allergen risks compared to natural latex rubber, which contains proteins known to trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Safety considerations favor liquid synthetic rubber for dipping applications in environments requiring hypoallergenic materials, as it reduces the incidence of Type I hypersensitivity reactions. Despite this advantage, proper ventilation and protective equipment remain essential when handling both types to minimize exposure to potentially harmful chemicals and fumes.
Cost Comparison: Liquid Rubber vs Latex Rubber
Liquid rubber generally costs more than latex rubber due to its advanced formulation and enhanced durability, making it a preferred choice for long-term applications despite higher initial investment. Latex rubber, being a natural and widely available material, offers a more economical option for short-term or disposable dipping projects. Cost efficiency depends on the project's durability requirements and volume, with latex suited for budget-conscious tasks and liquid rubber for premium protective coatings.
Environmental Impact and Disposal
Liquid rubber used for dipping often consists of synthetic polymers like polyurethane or nitrile, which can be more resistant to degradation and may release harmful chemicals if not disposed of properly. Latex rubber, a natural product derived from rubber trees, is biodegradable and generally has a lower environmental impact due to its renewable source and ease of disposal through natural decomposition. Choosing latex over synthetic liquid rubber reduces landfill waste and lowers the risk of toxic pollution, making it a more eco-friendly option for dipping applications.
Performance Under Different Conditions
Liquid rubber offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for harsh environments and prolonged exposure to oils and solvents. Latex rubber excels in elasticity and tear resistance, providing excellent performance in applications requiring high stretchability and quick curing. Under varying temperatures, liquid rubber maintains durability better in cold and UV-exposed conditions, while latex rubber performs optimally in moderate thermal settings with faster recovery.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Dipping Projects
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and durability for dipping projects, making it ideal for applications requiring long-lasting, waterproof coatings. Latex rubber provides excellent elasticity and cost-effectiveness, suited for creating thin, detailed layers in molds or protective coatings. Selecting the right rubber depends on the project's need for toughness, stretchability, and environmental resistance.
Infographic: Liquid rubber vs Latex rubber for Dipping
 azmater.com
azmater.com