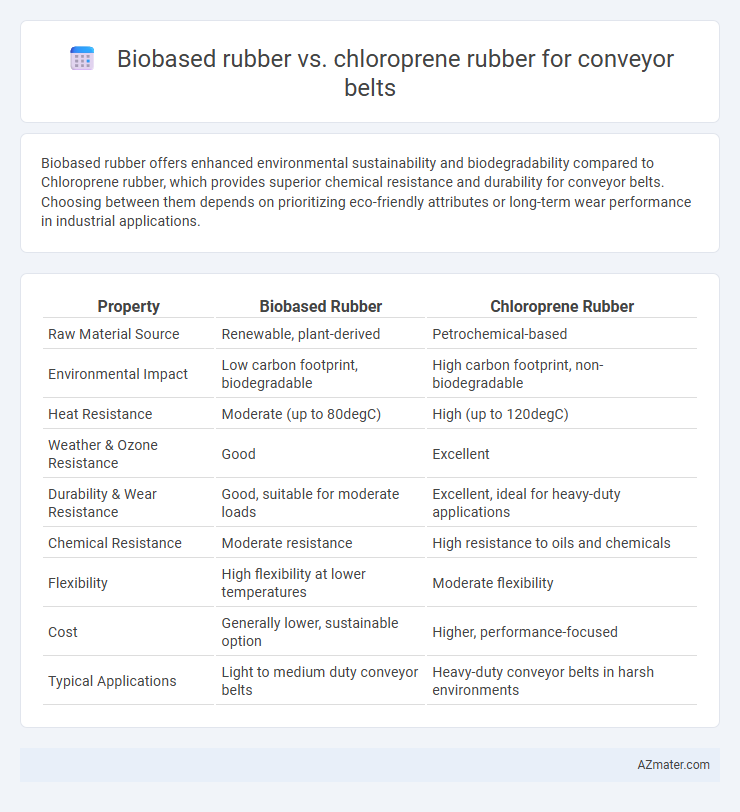
Biobased rubber offers enhanced environmental sustainability and biodegradability compared to Chloroprene rubber, which provides superior chemical resistance and durability for conveyor belts. Choosing between them depends on prioritizing eco-friendly attributes or long-term wear performance in industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Biobased Rubber | Chloroprene Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Source | Renewable, plant-derived | Petrochemical-based |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | High carbon footprint, non-biodegradable |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate (up to 80degC) | High (up to 120degC) |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Durability & Wear Resistance | Good, suitable for moderate loads | Excellent, ideal for heavy-duty applications |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance | High resistance to oils and chemicals |
| Flexibility | High flexibility at lower temperatures | Moderate flexibility |
| Cost | Generally lower, sustainable option | Higher, performance-focused |
| Typical Applications | Light to medium duty conveyor belts | Heavy-duty conveyor belts in harsh environments |
Introduction to Conveyor Belt Rubber Materials
Conveyor belt rubber materials predominantly include biobased rubber and chloroprene rubber, each offering distinct performance characteristics. Biobased rubber provides eco-friendly benefits through renewable resources while maintaining flexibility and abrasion resistance. Chloroprene rubber excels in resistance to oil, chemicals, and extreme temperatures, making it ideal for heavy-duty conveyor belt applications in harsh industrial environments.
What is Biobased Rubber?
Biobased rubber is a sustainable alternative derived from natural sources such as plant oils and biomass instead of petrochemicals, offering enhanced environmental benefits like biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint. In conveyor belt applications, biobased rubber provides comparable flexibility, abrasion resistance, and durability to chloroprene rubber while minimizing reliance on fossil fuels. This innovative material supports eco-friendly manufacturing and aligns with growing demands for sustainable industrial components.
Overview of Chloroprene Rubber
Chloroprene rubber, also known as polychloroprene or neoprene, is a synthetic elastomer renowned for its excellent resistance to oil, chemicals, and weathering, making it ideal for heavy-duty conveyor belts in harsh environments. Its balanced properties include good tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and flexibility at low temperatures, which outperform many biobased rubbers in industrial applications. Chloroprene rubber's durability and long service life contribute to reduced maintenance costs and improved conveyor reliability in sectors like mining, construction, and manufacturing.
Environmental Impact: Biobased vs Chloroprene
Biobased rubber for conveyor belts significantly reduces carbon footprint by utilizing renewable natural resources, unlike chloroprene rubber, which is derived from petroleum-based chemicals with high greenhouse gas emissions. The biodegradability and lower toxicity of biobased rubber contribute to reduced environmental pollution during production and disposal phases. In contrast, chloroprene rubber releases harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and poses challenges in recycling, increasing its overall environmental impact.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Biobased rubber for conveyor belts offers enhanced tensile strength and improved elongation at break compared to chloroprene rubber, contributing to superior flexibility and durability under dynamic loads. Chloroprene rubber exhibits higher abrasion resistance and better chemical stability, making it suitable for harsh industrial environments where oil and weather resistance are critical. Mechanical properties such as tear resistance and resilience favor chloroprene rubber for extended service life, while biobased rubber supports sustainability without compromising essential performance metrics.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Biobased rubber for conveyor belts offers enhanced environmental benefits and competitive durability, with natural polymer structures that provide resistance to abrasion and fatigue over extended use. Chloroprene rubber, known for excellent chemical resistance and weathering properties, delivers superior longevity in harsh industrial environments, maintaining tensile strength and elasticity under heavy load stress. Comparative durability analyses indicate chloroprene rubber typically outperforms biobased variants in longevity, especially in exposure to oils, ozone, and extreme temperatures, while biobased options excel in sustainability without significant compromise to service life.
Performance in Industrial Applications
Biobased rubber offers enhanced environmental sustainability with comparable abrasion resistance and flexibility to chloroprene rubber in conveyor belt applications. Chloroprene rubber excels in chemical resistance and heat tolerance, making it suitable for demanding industrial environments with exposure to oils and solvents. Both materials provide high tensile strength and durability, but chloroprene typically outperforms biobased rubber in extreme temperature stability and resistance to environmental degradation.
Cost Comparison and Economic Viability
Biobased rubber offers a competitive cost advantage over chloroprene rubber in conveyor belt manufacturing due to lower raw material expenses and reduced dependency on petrochemicals. The economic viability of biobased rubber is enhanced by growing demand for sustainable materials and potential government incentives, resulting in improved long-term cost savings. Chloroprene rubber, while traditionally favored for its durability and resistance properties, incurs higher production costs linked to synthetic chemical processes and fluctuating petroleum prices.
Sustainability and Regulatory Compliance
Biobased rubber conveyor belts offer enhanced sustainability by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions compared to traditional chloroprene rubber, which is derived from petrochemicals. Regulatory compliance is increasingly stringent for chloroprene rubber due to its association with environmental pollutants and potential health risks, prompting industries to favor biobased alternatives that align with global environmental standards such as REACH and EPA regulations. The shift towards biobased rubber supports circular economy initiatives and facilitates adherence to corporate sustainability goals while maintaining comparable durability and performance in conveyor belt applications.
Future Trends in Conveyor Belt Materials
Future trends in conveyor belt materials highlight a shift towards biobased rubber due to its sustainability, renewable sourcing, and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional chloroprene rubber. Advances in biobased rubber enhance durability, chemical resistance, and mechanical performance, positioning it as a competitive alternative for heavy-duty conveyor applications. Innovations in polymer blends and eco-friendly processing technologies are expected to further improve the functionality and lifecycle of biobased conveyor belts.
Infographic: Biobased rubber vs Chloroprene rubber for Conveyor belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com