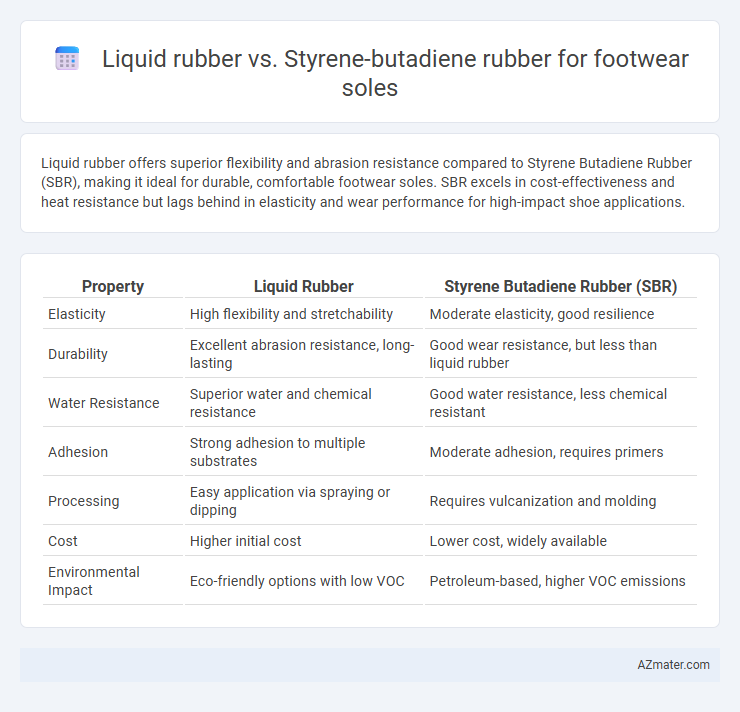
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and abrasion resistance compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), making it ideal for durable, comfortable footwear soles. SBR excels in cost-effectiveness and heat resistance but lags behind in elasticity and wear performance for high-impact shoe applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Liquid Rubber | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Elasticity | High flexibility and stretchability | Moderate elasticity, good resilience |
| Durability | Excellent abrasion resistance, long-lasting | Good wear resistance, but less than liquid rubber |
| Water Resistance | Superior water and chemical resistance | Good water resistance, less chemical resistant |
| Adhesion | Strong adhesion to multiple substrates | Moderate adhesion, requires primers |
| Processing | Easy application via spraying or dipping | Requires vulcanization and molding |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, widely available |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly options with low VOC | Petroleum-based, higher VOC emissions |
Introduction to Liquid Rubber and Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Liquid rubber is a versatile polymer known for its excellent flexibility, waterproof properties, and strong adhesion, making it ideal for durable footwear soles that require high abrasion resistance and comfort. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), a synthetic rubber widely used in shoe soles, offers good wear resistance, aging stability, and cost-effectiveness, contributing to reliable performance in various environmental conditions. Comparing liquid rubber and SBR highlights key differences in elasticity, durability, and processing methods critical for optimizing footwear sole manufacturing.
Material Composition and Properties
Liquid rubber, composed primarily of polyacrylate or polyurethane-based polymers, offers superior flexibility and excellent abrasion resistance compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), which is a synthetic copolymer of styrene and butadiene known for its high tensile strength and good wear resistance. Liquid rubber's low viscosity ensures better molding precision and seamless sole construction, while SBR provides greater resilience and aging resistance under varying temperature conditions. The hydrophobic nature of liquid rubber enhances water resistance for footwear soles, whereas SBR delivers balanced shock absorption and traction, making the choice dependent on specific performance requirements and environmental exposure.
Manufacturing Processes for Footwear Soles
Liquid rubber offers a versatile manufacturing process for footwear soles, allowing seamless molding through injection or spray applications that enhance precision and reduce material waste. Styrene butadiene rubber, commonly used in traditional sole production, relies heavily on vulcanization and extrusion methods, which provide durability but involve more energy-intensive steps and longer curing times. The liquid rubber's process supports rapid prototyping and customization, making it ideal for innovative sole designs with complex geometries.
Durability and Wear Resistance Comparison
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent abrasion resistance, making it highly durable for footwear soles subjected to constant bending and flexing. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides robust wear resistance and toughness, particularly effective in resisting cuts and tears under heavy use. When comparing durability, liquid rubber outperforms in flexibility retention over time, while SBR excels in long-term wear resistance on rough surfaces.
Flexibility and Comfort in Footwear Applications
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and cushioning compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), enhancing comfort in footwear soles by adapting better to foot movements and providing a softer underfoot feel. SBR, while durable and abrasion-resistant, tends to be stiffer, which can compromise flexibility and reduce overall comfort during prolonged wear. Footwear soles made from liquid rubber materials excel in environments requiring enhanced flexibility and shock absorption, making them ideal for athletic and casual shoes prioritizing comfort.
Slip Resistance and Traction Performance
Liquid rubber offers superior slip resistance and traction performance for footwear soles due to its excellent flexibility and ability to form a uniform, textured surface that enhances grip on wet and oily surfaces. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), while durable and cost-effective, typically provides less effective traction because its harder, less flexible compound can reduce contact with uneven or slippery surfaces. For applications requiring enhanced slip resistance, liquid rubber soles deliver optimal performance and safety benefits.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Liquid rubber offers a more eco-friendly alternative to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) in footwear soles due to its lower volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and better biodegradability. Styrene Butadiene Rubber, derived from petroleum-based sources, has a higher carbon footprint and limited recyclability, contributing to environmental pollution. Choosing liquid rubber supports sustainability by reducing toxic waste and enhancing the lifecycle performance of footwear products.
Cost Efficiency and Production Scalability
Liquid rubber offers superior cost efficiency for footwear soles due to lower raw material expenses and simplified processing, reducing overall manufacturing costs. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides high production scalability with established industrial frameworks but often incurs higher costs from longer curing times and complex molding processes. Manufacturers aiming for large-scale, cost-effective sole production benefit from liquid rubber's rapid curing and streamlined application capabilities compared to SBR's traditional methods.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
Liquid rubber and styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) dominate the footwear sole market, with liquid rubber gaining traction due to its superior flexibility, waterproofing, and eco-friendly attributes. Market trends reveal a growing consumer preference for sustainable and durable materials, propelling liquid rubber's adoption in athletic and casual footwear sectors. Styrene butadiene rubber remains favored for its cost-effectiveness and abrasion resistance, maintaining strong demand in budget-conscious and high-performance shoe segments.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Footwear Soles
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent waterproofing properties, making it ideal for footwear soles requiring high durability and resistance to environmental factors. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides good abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness but may lack the same level of elasticity and water resistance. Selecting the right rubber depends on balancing performance needs like flexibility, durability, and moisture protection with budget considerations for optimal footwear sole functionality.
Infographic: Liquid rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Footwear sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com