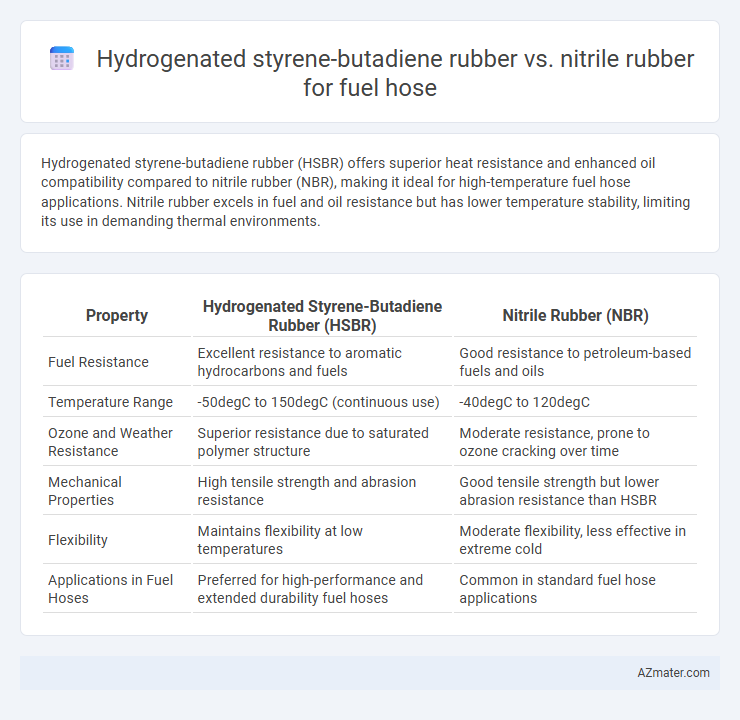
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior heat resistance and enhanced oil compatibility compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), making it ideal for high-temperature fuel hose applications. Nitrile rubber excels in fuel and oil resistance but has lower temperature stability, limiting its use in demanding thermal environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Resistance | Excellent resistance to aromatic hydrocarbons and fuels | Good resistance to petroleum-based fuels and oils |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 150degC (continuous use) | -40degC to 120degC |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Superior resistance due to saturated polymer structure | Moderate resistance, prone to ozone cracking over time |
| Mechanical Properties | High tensile strength and abrasion resistance | Good tensile strength but lower abrasion resistance than HSBR |
| Flexibility | Maintains flexibility at low temperatures | Moderate flexibility, less effective in extreme cold |
| Applications in Fuel Hoses | Preferred for high-performance and extended durability fuel hoses | Common in standard fuel hose applications |
Overview of Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR)
Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) offers superior aging resistance, chemical stability, and heat resistance compared to traditional styrene-butadiene rubber, making it highly suitable for fuel hose applications exposed to harsh environments. HSBR's enhanced saturation in the polymer backbone improves resistance to oxidation and ozone, leading to longer service life in fuel hoses subjected to aggressive fuels and elevated temperatures. This material exhibits excellent flexibility and mechanical strength, ensuring reliable performance while maintaining fuel impermeability and elasticity.
Introduction to Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a synthetic rubber copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene, widely used for fuel hoses due to its excellent resistance to petroleum-based fluids, oils, and fuels. Compared to hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR), NBR offers superior fuel resistance and durability under high temperatures commonly found in automotive and industrial fuel systems. Its strong barrier properties and resistance to swelling ensure reliable performance and extended service life in fuel hose applications.
Chemical Resistance: HSBR vs NBR in Fuel Hose Applications
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits superior chemical resistance to aromatic hydrocarbons and fuels compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), making HSBR more suitable for fuel hose applications exposed to aggressive fuels and additives. HSBR's enhanced saturation level in the polymer backbone provides improved resistance to degradation by fuels, oils, and ozone, extending the hose service life under demanding chemical environments. NBR offers good resistance to aliphatic hydrocarbons but is less effective against aromatic fuels, resulting in faster swelling and material breakdown in fuel hose systems.
Mechanical Properties Comparison: Strength and Flexibility
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits superior tensile strength and improved abrasion resistance compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), making it more durable under high mechanical stress in fuel hose applications. NBR offers excellent flexibility and elongation at break, providing better resistance to fuel swelling and maintaining pliability in cold temperatures. Combining high strength and moderate flexibility, HSBR is preferred for heavy-duty fuel hoses, while NBR is suitable for applications requiring enhanced flexibility and chemical resistance.
Temperature Performance: HSBR vs NBR Fuel Hoses
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior temperature resistance for fuel hoses, maintaining flexibility and performance at continuous temperatures up to 125degC and intermittent peaks around 150degC. Nitrile rubber (NBR) fuel hoses typically withstand temperatures up to 100degC continuously, with degradation occurring more rapidly above this threshold due to its lower heat resistance. HSBR's saturated polymer structure provides enhanced thermal stability compared to NBR's unsaturated nitrile copolymer, making HSBR fuel hoses preferable in high-temperature environments.
Ozone and Weathering Resistance Considerations
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior ozone and weathering resistance compared to nitrile rubber, making it more suitable for fuel hose applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. HSBR's saturated polymer backbone resists ozone cracking and aging effects caused by UV radiation, extending the service life of fuel hoses in outdoor or high-ozone environments. Nitrile rubber, while excellent for fuel and oil resistance, tends to degrade faster under prolonged ozone exposure and weathering, limiting its durability when used in external fuel hose applications.
Cost Analysis: HSBR vs NBR for Fuel Hose Manufacturing
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) generally incurs higher raw material costs than nitrile rubber (NBR) due to specialized hydrogenation processing, impacting overall fuel hose manufacturing expenses. NBR offers cost advantages with lower production costs and widespread availability, making it economically favorable for standard fuel hose applications. However, HSBR's superior fuel and heat resistance may justify its premium price in high-performance or long-life fuel hoses where durability reduces replacement frequency.
Compatibility with Alternative Fuels and Biofuels
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior resistance to swelling and degradation when exposed to alternative fuels and biofuels, making it highly compatible with ethanol blends and biodiesel. Nitrile rubber (NBR), while effective in traditional fuel environments, tends to absorb biofuels, leading to decreased mechanical properties and shorter service life. The enhanced chemical stability of HSBR under fluctuating biofuel compositions ensures better durability and performance in modern fuel hose applications.
Longevity and Maintenance Requirements
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior resistance to heat, ozone, and fuel aging, resulting in extended longevity for fuel hoses compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), which is more prone to degradation from prolonged exposure to hydrocarbons. HSBR demonstrates improved tensile strength and elasticity, reducing the need for frequent maintenance or replacement in high-temperature fuel systems. NBR, while cost-effective and resistant to oil, generally requires more regular inspection and maintenance due to its lower thermal and oxidative stability.
Summary: Choosing the Right Rubber for Fuel Hose Applications
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior heat resistance and enhanced abrasion durability, making it ideal for fuel hoses exposed to high temperatures and mechanical stress. Nitrile rubber (NBR) excels in fuel and oil resistance due to its strong affinity for hydrocarbons, providing excellent sealing and chemical stability in fuel hose applications. Selecting between HSBR and NBR depends on specific performance needs, such as thermal endurance for HSBR or superior fuel compatibility and flexibility for NBR.
Infographic: Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Fuel hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com