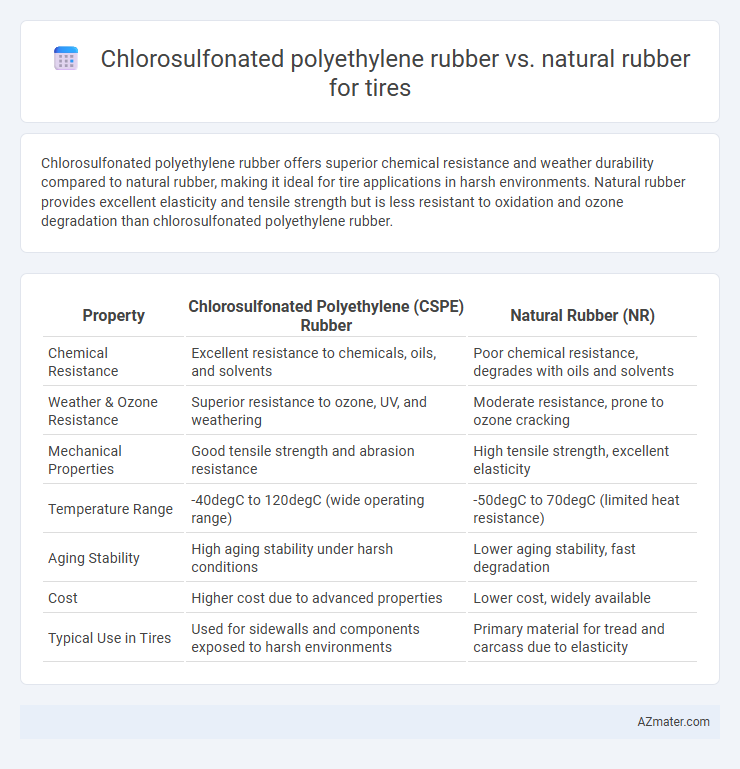
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber offers superior chemical resistance and weather durability compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for tire applications in harsh environments. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and tensile strength but is less resistant to oxidation and ozone degradation than chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSPE) Rubber | Natural Rubber (NR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to chemicals, oils, and solvents | Poor chemical resistance, degrades with oils and solvents |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | Superior resistance to ozone, UV, and weathering | Moderate resistance, prone to ozone cracking |
| Mechanical Properties | Good tensile strength and abrasion resistance | High tensile strength, excellent elasticity |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC (wide operating range) | -50degC to 70degC (limited heat resistance) |
| Aging Stability | High aging stability under harsh conditions | Lower aging stability, fast degradation |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost, widely available |
| Typical Use in Tires | Used for sidewalls and components exposed to harsh environments | Primary material for tread and carcass due to elasticity |
Introduction to Tire Rubber Compounds
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers superior chemical resistance and weatherability compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for tire compounds exposed to harsh environments. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and tensile strength, essential for tire performance and durability in general use. Combining these materials in tire formulations enhances overall wear resistance, aging stability, and traction on varying road surfaces.
Overview of Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber is a synthetic elastomer known for its exceptional resistance to chemicals, ozone, and weathering, making it highly suitable for harsh environments encountered in tire applications. Unlike natural rubber, CSM offers superior tensile strength and aging stability, enhancing tire durability and lifespan, especially in industrial and off-road tires. Its low gas permeability and excellent resistance to oils and solvents provide improved performance under extreme conditions, differentiating it from the more elastic but less chemically resistant natural rubber.
Natural Rubber: Properties and Applications
Natural rubber exhibits exceptional elasticity, tensile strength, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for tire manufacturing, especially in high-performance and off-road applications. Its excellent grip and resilience under varying temperatures enhance tire durability and safety, while its natural composition offers better environmental sustainability compared to synthetic alternatives. Applications extend beyond tires to include footwear, adhesives, and industrial products, highlighting its versatility in diverse industries.
Chemical Structure Differences
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber features a saturated polyethylene backbone with chlorosulfonyl functional groups (-SO2Cl) that enhance chemical resistance and weatherability, unlike natural rubber which consists primarily of cis-1,4-polyisoprene with unsaturated double bonds prone to oxidation and degradation. The incorporation of chlorine and sulfonyl groups in CSM provides superior resistance to ozone, chemicals, and heat, making it ideal for demanding tire applications requiring durability. In contrast, the natural rubber's unsaturated hydrocarbon chains offer excellent elasticity and tensile strength but lack the chemical stability inherent in CSM's modified polymer structure.
Mechanical Performance Comparison
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior resistance to abrasion, ozone, and chemical degradation compared to natural rubber, making it highly durable for tire applications. Natural rubber provides excellent tensile strength, elasticity, and tear resistance, contributing to better fatigue life and impact resilience under dynamic loads. Despite natural rubber's superior mechanical flexibility, CSM's enhanced weathering stability and heat resistance improve tire longevity in harsh environmental conditions.
Resistance to Heat, Ozone, and Chemicals
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior resistance to heat, ozone, and chemicals compared to natural rubber, making it highly suitable for tire applications exposed to harsh environments. CSM's molecular structure provides enhanced stability at elevated temperatures, preventing degradation and maintaining performance. Natural rubber, while highly elastic and offering excellent tensile strength, is more prone to ozone cracking and chemical attack, limiting its durability in demanding conditions.
Durability and Wear Characteristics
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers superior chemical resistance and exceptional durability in tire applications compared to natural rubber, making it more resistant to ozone, weathering, and UV degradation. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance, which contributes to better wear performance under dynamic loads and high traction conditions. Tires combining CSM's robust environmental stability with natural rubber's resilience achieve enhanced lifespan and reduced tread wear in diverse driving environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) offers superior resistance to chemicals, ozone, and weathering compared to natural rubber, resulting in longer tire lifespan and reduced waste generation. Natural rubber, derived from renewable Hevea brasiliensis latex, supports sustainable farming practices and carbon sequestration, but its production can contribute to deforestation and biodiversity loss if unmanaged. Life cycle assessments indicate that CSM tires have a higher environmental footprint due to synthetic polymer production, whereas natural rubber tires provide a more eco-friendly profile when sourced from certified sustainable plantations.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber generally incurs higher production costs than natural rubber due to its complex synthesis and specialized chemical properties, impacting overall tire manufacturing expenses. Natural rubber remains more widely available and economically viable, benefiting from established global supply chains and renewable harvesting methods. Tire manufacturers often favor natural rubber for cost-efficiency and availability, while CSM rubber is selected selectively for enhanced chemical resistance despite its premium price.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Tires
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber offers superior resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering, making it ideal for tires exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and abrasion resistance, ensuring optimal performance in standard tire applications. Selecting the right rubber depends on balancing durability requirements with cost-efficiency to achieve the best tire performance for specific usage scenarios.
Infographic: Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber vs Natural rubber for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com