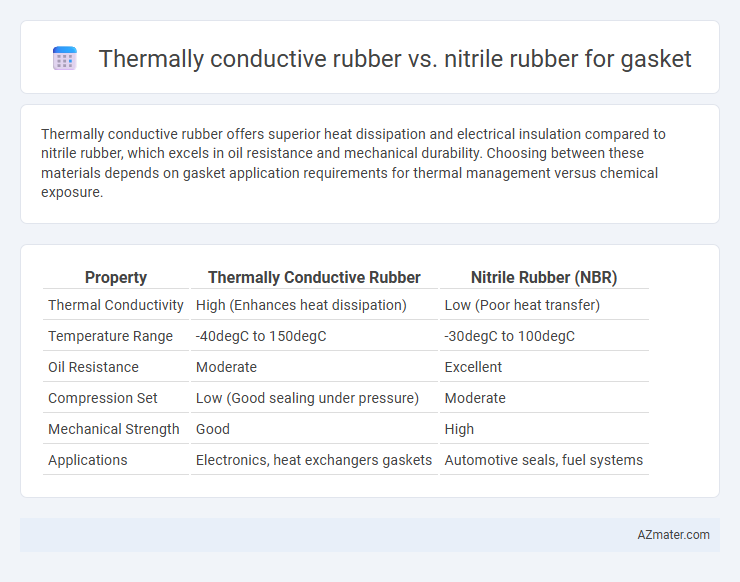
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior heat dissipation and electrical insulation compared to nitrile rubber, which excels in oil resistance and mechanical durability. Choosing between these materials depends on gasket application requirements for thermal management versus chemical exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermally Conductive Rubber | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | High (Enhances heat dissipation) | Low (Poor heat transfer) |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -30degC to 100degC |
| Oil Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Compression Set | Low (Good sealing under pressure) | Moderate |
| Mechanical Strength | Good | High |
| Applications | Electronics, heat exchangers gaskets | Automotive seals, fuel systems |
Introduction to Gasket Materials
Thermally conductive rubber offers enhanced heat dissipation properties, making it ideal for applications requiring efficient thermal management in gasket materials. Nitrile rubber, known for its exceptional oil and chemical resistance, provides durability and sealing performance in harsh environments. Selecting between these materials depends on the specific requirements for thermal conductivity, chemical resistance, and operational temperature range in gasket applications.
Overview of Thermally Conductive Rubber
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior heat dissipation properties compared to standard nitrile rubber, making it ideal for applications requiring efficient thermal management. Its formulation incorporates thermally conductive fillers like silicone or ceramic particles, enhancing thermal conductivity while maintaining flexibility and sealing performance. This material balances electrical insulation with effective heat transfer, providing reliable gasket solutions in electronic and automotive industries.
Understanding Nitrile Rubber Properties
Nitrile rubber, known for its excellent resistance to oil, fuel, and other chemicals, provides strong sealing capabilities and durability in gasket applications where exposure to aggressive fluids is common. While thermally conductive rubber offers enhanced heat dissipation for high-temperature conditions, nitrile rubber maintains superior compressive strength and flexibility at moderate temperatures, making it ideal for environments requiring chemical resistance and mechanical resilience. The material's ability to maintain its integrity under varying pressures and temperature ranges ensures reliable performance in automotive, aerospace, and industrial sealing solutions.
Thermal Conductivity: A Comparative Analysis
Thermally conductive rubber exhibits significantly higher thermal conductivity, typically ranging from 1 to 10 W/m*K, compared to nitrile rubber's much lower rate of around 0.2 W/m*K, making it more effective for heat dissipation in gasket applications. This enhanced thermal conductivity enables thermally conductive rubber gaskets to manage and transfer heat efficiently in electronic devices and automotive systems, reducing thermal resistance and preventing overheating. In contrast, nitrile rubber gaskets, while providing excellent chemical and oil resistance, are less suitable for applications requiring rapid heat transfer due to their limited thermal conductivity.
Mechanical Performance in Sealing Applications
Thermally conductive rubber exhibits superior mechanical performance in sealing applications due to its enhanced heat dissipation properties and excellent flexibility, reducing thermal stress and deformation under fluctuating temperatures. Nitrile rubber offers strong resistance to oils and fuels with good mechanical strength but lacks the thermal conductivity needed for high-temperature sealing environments. In critical gasket applications where mechanical durability and temperature management are essential, thermally conductive rubber provides a more reliable seal and longer service life compared to standard nitrile rubber.
Chemical and Oil Resistance Comparison
Thermally conductive rubber typically exhibits moderate chemical resistance but excels in heat dissipation, making it suitable for applications requiring both thermal management and sealing. Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, particularly hydrocarbons, making it the preferred choice for gaskets exposed to aggressive oil-based environments. While nitrile rubber provides exceptional oil resistance and durability, it lacks the thermal conductivity properties found in thermally conductive rubbers, limiting its use where heat transfer is critical.
Temperature Range Suitability
Thermally conductive rubber typically operates efficiently within a temperature range of -40degC to 150degC, offering enhanced heat dissipation for gaskets in high-thermal environments. Nitrile rubber, while resistant to oils and chemicals, generally suits lower temperature applications, functioning effectively between -30degC and 120degC but lacking superior thermal conductivity. Selecting thermally conductive rubber ensures reliable gasket performance in elevated temperature conditions where heat transfer is critical.
Longevity and Durability Considerations
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior heat dissipation properties, significantly enhancing gasket longevity in high-temperature applications by reducing thermal degradation compared to nitrile rubber. Nitrile rubber, known for its excellent resistance to oils and fuels, can experience accelerated wear and reduced durability under continuous thermal stress. Choosing thermally conductive rubber gaskets ensures extended service life and consistent performance in environments with elevated operating temperatures.
Cost-Effectiveness and Practical Applications
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior heat dissipation ideal for high-temperature gasket applications but at a higher cost compared to nitrile rubber, which remains a budget-friendly choice for general sealing tasks due to its excellent resistance to oils and fuels. Nitrile rubber gaskets excel in automotive and industrial environments where cost-effectiveness and chemical resistance are priorities, while thermally conductive rubber suits electronics and machinery requiring temperature regulation. Balancing budget constraints with functional requirements leads many manufacturers to select nitrile rubber for widespread use and thermally conductive rubber for specialized thermal management applications.
Choosing the Best Rubber for Your Gasket Needs
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior heat dissipation and electrical insulation, making it ideal for gaskets in electronics and high-temperature applications. Nitrile rubber provides excellent oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, suitable for automotive and industrial gaskets exposed to harsh fluids. Selecting the best rubber depends on operational temperature, chemical exposure, and thermal management requirements specific to your gasket application.
Infographic: Thermally conductive rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com