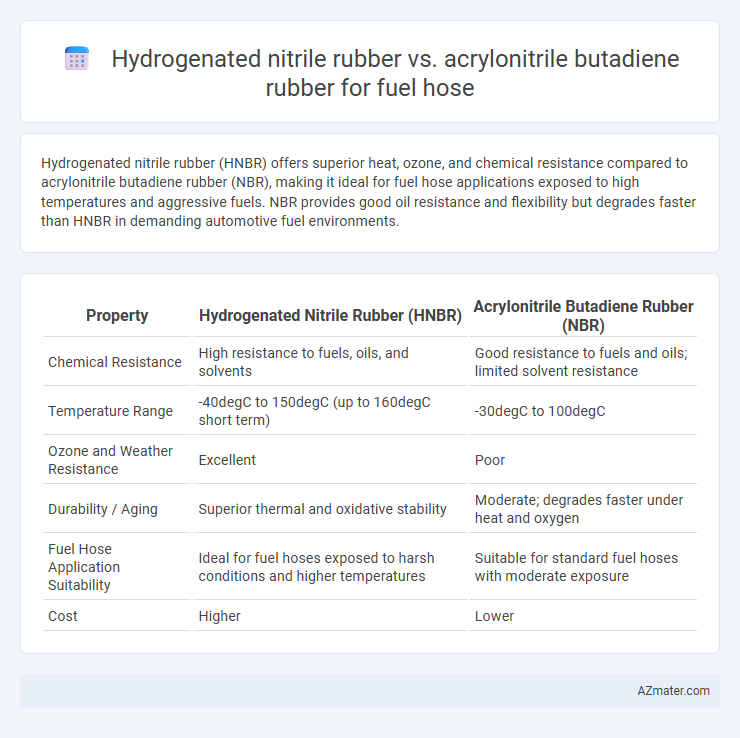
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat, ozone, and chemical resistance compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), making it ideal for fuel hose applications exposed to high temperatures and aggressive fuels. NBR provides good oil resistance and flexibility but degrades faster than HNBR in demanding automotive fuel environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to fuels, oils, and solvents | Good resistance to fuels and oils; limited solvent resistance |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC (up to 160degC short term) | -30degC to 100degC |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Excellent | Poor |
| Durability / Aging | Superior thermal and oxidative stability | Moderate; degrades faster under heat and oxygen |
| Fuel Hose Application Suitability | Ideal for fuel hoses exposed to harsh conditions and higher temperatures | Suitable for standard fuel hoses with moderate exposure |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and enhanced abrasion resistance, making it ideal for demanding fuel hose applications. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) provides excellent fuel and oil resistance with good mechanical properties, but its performance decreases at higher temperatures compared to HNBR. Both materials are widely used in fuel hose manufacturing, with HNBR preferred for extreme conditions and NBR suitable for standard applications.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) features a saturated backbone achieved by hydrogenating the double bonds in the nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) structure, enhancing its resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals compared to standard acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR). The higher acrylonitrile content in HNBR contributes to improved polarity and fuel resistance, making it ideal for fuel hoses exposed to aggressive hydrocarbons and elevated temperatures. In contrast, NBR's unsaturated polymer chain offers good oil resistance but limited thermal stability, resulting in quicker degradation under fuel and heat stress.
Fuel Resistance Performance
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior fuel resistance compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) due to its enhanced saturation and hydrogenation process, which improves its resistance to hydrocarbons, fuels, and oils. HNBR maintains dimensional stability and mechanical properties after prolonged exposure to gasoline, diesel, and ethanol blends, making it ideal for fuel hose applications in harsh environments. NBR, while effective, tends to swell and degrade faster when exposed to modern biofuels and aggressive fuel additives, limiting its durability and service life in fuel delivery systems.
Temperature Stability and Operating Range
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior temperature stability with an operating range typically from -40degC to 150degC, making it highly suitable for fuel hose applications exposed to extreme heat. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) generally performs well within a narrower temperature window of -30degC to 100degC but exhibits lower resistance to heat and oxidative aging compared to HNBR. HNBR's enhanced thermal resistance and longer service life under high-temperature conditions provide a clear advantage for critical fuel delivery systems.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior mechanical properties and enhanced durability compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) for fuel hose applications, offering higher tensile strength and improved abrasion resistance. HNBR's saturation of the polymer backbone provides excellent thermal stability and resistance to ozone and chemical degradation, resulting in longer service life under harsh fuel and oil exposure. NBR, while cost-effective and flexible, demonstrates lower heat aging resistance and mechanical strength, making HNBR preferable for high-performance fuel hoses demanding rigorous mechanical endurance and extended durability.
Ozone and Weathering Resistance Comparison
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior ozone and weathering resistance compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), making it ideal for fuel hoses exposed to harsh environmental conditions. HNBR's saturated molecular structure enhances its durability against ozone cracking and UV degradation, whereas NBR's unsaturated bonds are more prone to ozone attack and deterioration over time. For fuel hose applications requiring long-term performance in outdoor or high-ozone environments, HNBR provides significantly improved longevity and reliability.
Compatibility with Automotive Fuels and Additives
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior compatibility with automotive fuels and additives compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) due to its enhanced resistance to heat, oxygen, and ozone degradation, which extends fuel hose durability in aggressive fuel environments. HNBR maintains excellent swelling resistance and chemical stability when exposed to ethanol-blended fuels, biofuels, and common fuel additives like detergents and corrosion inhibitors, reducing the risk of hose degradation and leakage. NBR, while effective with conventional petroleum-based fuels, tends to absorb higher amounts of fuel and additives, leading to faster aging and reduced mechanical properties in modern fuel systems.
Manufacturing and Processing Considerations
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior oil, heat, and abrasion resistance compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), making it more suitable for demanding fuel hose applications requiring long-term durability. HNBR requires higher curing temperatures and longer vulcanization times, which can increase manufacturing complexity and cost but yields improved mechanical properties and chemical resistance. In contrast, NBR processes more easily at lower temperatures and with faster cure cycles, resulting in more cost-effective production but limited performance under high temperature and aggressive fuel environments.
Cost Analysis and Economic Impact
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior fuel resistance and durability compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), leading to longer fuel hose lifespans and reduced replacement frequency. Although HNBR exhibits higher initial material costs, its enhanced chemical stability and resistance to heat and oil degradation translate into lower long-term maintenance and downtime expenses. The economic impact of choosing HNBR for fuel hoses includes improved total cost of ownership (TCO) despite upfront investment, making it a cost-effective solution in high-performance and safety-critical fuel systems.
Application Suitability in Fuel Hose Industry
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior resistance to heat, oil, and fuel degradation compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), making it highly suitable for high-performance fuel hoses in automotive and industrial applications. HNBR's enhanced chemical stability and abrasion resistance extend hose service life under aggressive fuel exposure and elevated temperatures, whereas NBR offers cost-effective solutions for standard fuel transport with moderate temperature and chemical exposure. The fuel hose industry prefers HNBR in environments demanding durability and compliance with stringent automotive fuel system standards such as SAE J30 R9 and ISO 18752.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber for Fuel hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com