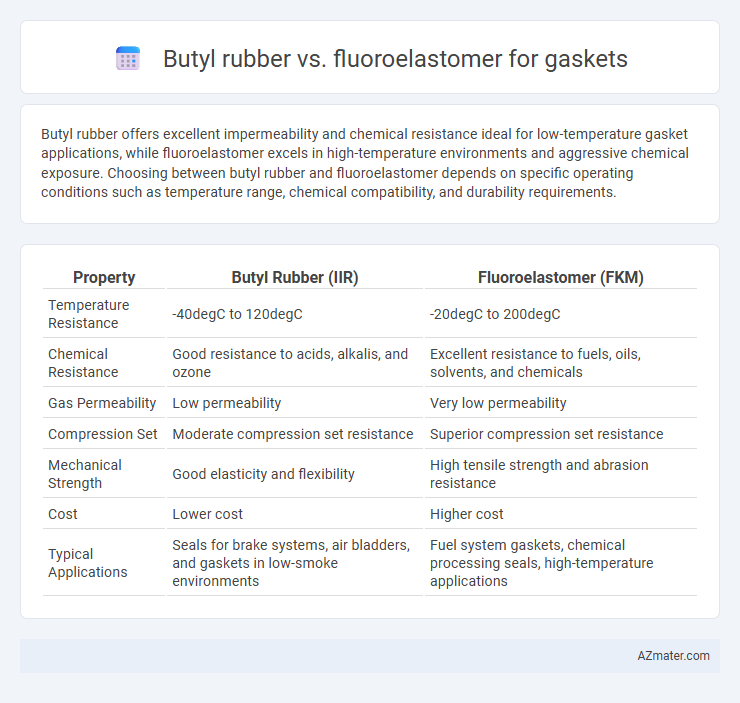
Butyl rubber offers excellent impermeability and chemical resistance ideal for low-temperature gasket applications, while fluoroelastomer excels in high-temperature environments and aggressive chemical exposure. Choosing between butyl rubber and fluoroelastomer depends on specific operating conditions such as temperature range, chemical compatibility, and durability requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Butyl Rubber (IIR) | Fluoroelastomer (FKM) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | -40degC to 120degC | -20degC to 200degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids, alkalis, and ozone | Excellent resistance to fuels, oils, solvents, and chemicals |
| Gas Permeability | Low permeability | Very low permeability |
| Compression Set | Moderate compression set resistance | Superior compression set resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | Good elasticity and flexibility | High tensile strength and abrasion resistance |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Typical Applications | Seals for brake systems, air bladders, and gaskets in low-smoke environments | Fuel system gaskets, chemical processing seals, high-temperature applications |
Introduction to Gasket Materials
Butyl rubber and fluoroelastomer are popular gasket materials known for their unique chemical and physical properties, making them suitable for different sealing applications. Butyl rubber offers excellent resistance to air, ozone, and weather aging, ideal for gasketing in HVAC systems and water sealing, while fluoroelastomers excel in high-temperature resistance and chemical inertness, commonly used in automotive and aerospace gaskets. Selecting between these materials depends on factors like operating temperature, chemical exposure, and environmental conditions specific to the gasket application.
Overview of Butyl Rubber
Butyl rubber is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent impermeability to gases, making it ideal for gasket applications that require airtight sealing. Its high resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemicals ensures durability in harsh environments, outperforming many other elastomers in longevity. Compared to fluoroelastomers, butyl rubber offers superior flexibility and cost-effectiveness, although it has lower temperature resistance and chemical tolerance.
Overview of Fluoroelastomer
Fluoroelastomers are synthetic rubber materials known for their exceptional chemical resistance, high temperature tolerance up to 200-250degC, and excellent durability in harsh environments, making them ideal for gasket applications in automotive, aerospace, and chemical industries. Unlike butyl rubber, which offers good impermeability and flexibility but lower resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents, fluoroelastomers provide superior sealing performance against aggressive media and maintain integrity under extreme conditions. Their resistance to aging, ozone, and weathering contributes to longer gasket lifespan, reducing maintenance costs and improving system reliability.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Butyl rubber exhibits excellent resistance to polar solvents, acids, and alkalis, making it suitable for gaskets exposed to water, steam, and mild chemicals. Fluoroelastomers (FKM), however, offer superior chemical resistance against a broader range of aggressive chemicals, including hydrocarbons, oils, fuels, and solvents, maintaining integrity at elevated temperatures up to 200degC. For applications demanding high-performance chemical resistance, especially in harsh environments involving strong chemicals and high heat, fluoroelastomer gaskets provide a more durable and reliable sealing solution compared to butyl rubber.
Temperature Performance Analysis
Butyl rubber gaskets exhibit excellent low-temperature flexibility, maintaining performance down to -40degC, but their heat resistance is limited to approximately 120degC, making them less suitable for high-temperature applications. Fluoroelastomer gaskets, such as Viton, outperform with a wide temperature range from -20degC to 230degC, offering superior chemical stability and thermal resistance. The temperature performance analysis favors fluoroelastomers for environments requiring prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures and aggressive chemicals, whereas butyl rubber is ideal for lower-temperature, ozone-resistant conditions.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Butyl rubber offers excellent flexibility, low gas permeability, and good resistance to weathering, making it ideal for gaskets requiring airtight seals and moderate chemical resistance. Fluoroelastomers exhibit superior mechanical strength, high temperature tolerance up to 200degC, and exceptional chemical and oil resistance, which significantly enhance gasket durability in harsh environments. The choice between butyl rubber and fluoroelastomer depends on the application's mechanical stress, temperature range, and exposure to aggressive chemicals.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Butyl rubber gaskets typically cost 30-50% less than fluoroelastomer counterparts due to lower raw material and manufacturing expenses. Fluoroelastomers offer superior chemical resistance and temperature tolerance, justifying higher initial investment in critical applications with aggressive media or extreme environments. Economically, butyl rubber suits general-purpose sealing needs where budget constraints prevail, while fluoroelastomer gaskets provide long-term value by reducing maintenance and replacement costs in demanding industrial settings.
Typical Applications in Industry
Butyl rubber gaskets are widely used in automotive fuel systems, HVAC sealing, and chemical processing due to their excellent resistance to air, moisture, and many chemicals. Fluoroelastomer gaskets are preferred in aerospace, pharmaceutical, and oil and gas industries for their high-temperature tolerance and superior resistance to aggressive chemicals and fuels. Choosing between these materials depends on specific application requirements such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical durability.
Environmental and Safety Factors
Butyl rubber gaskets offer excellent ozone and weather resistance, making them suitable for outdoor applications with minimal environmental degradation and low toxicity. Fluoroelastomer gaskets provide superior chemical resistance, including to oils and fuels, enhancing safety in harsh chemical environments but may pose higher environmental concerns due to their fluorinated compounds. Both materials require proper disposal protocols to mitigate environmental impact, with butyl rubber being more biodegradable and fluoroelastomers demanding specialized recycling or incineration to prevent toxic emissions.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Gasket Needs
Butyl rubber offers excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and gas permeability, making it ideal for seals in HVAC systems and pharmaceutical industries. Fluoroelastomer excels in chemical resistance, high temperatures up to 200degC, and fuel compatibility, suitable for automotive and aerospace gaskets exposed to harsh environments. Selecting the right gasket material depends on operating temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress, ensuring optimal durability and performance in specific applications.
Infographic: Butyl rubber vs Fluoroelastomer for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com