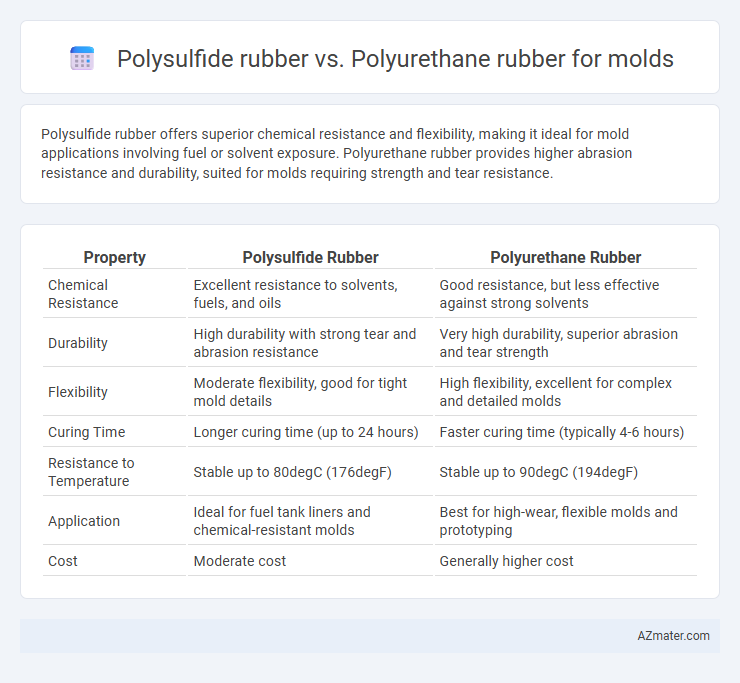
Polysulfide rubber offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for mold applications involving fuel or solvent exposure. Polyurethane rubber provides higher abrasion resistance and durability, suited for molds requiring strength and tear resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfide Rubber | Polyurethane Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to solvents, fuels, and oils | Good resistance, but less effective against strong solvents |
| Durability | High durability with strong tear and abrasion resistance | Very high durability, superior abrasion and tear strength |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, good for tight mold details | High flexibility, excellent for complex and detailed molds |
| Curing Time | Longer curing time (up to 24 hours) | Faster curing time (typically 4-6 hours) |
| Resistance to Temperature | Stable up to 80degC (176degF) | Stable up to 90degC (194degF) |
| Application | Ideal for fuel tank liners and chemical-resistant molds | Best for high-wear, flexible molds and prototyping |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Generally higher cost |
Introduction to Mold Making Materials
Polysulfide rubber offers excellent flexibility and chemical resistance, making it ideal for molds requiring high durability and tear strength, especially in casting resins and waxes. Polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance and faster cure times, suitable for molds with fine details and high reproduction accuracy in prototyping and small batch production. Selecting between these materials depends on the molding application's demands for elasticity, hardness, and resistance to environmental factors.
Overview of Polysulfide Rubber
Polysulfide rubber is a highly flexible and chemically resistant sealing material commonly used in mold applications due to its excellent oil, solvent, and fuel resistance. Its outstanding elongation and tensile strength provide superior durability and flexibility for complex mold geometries, preventing leakage and enhancing mold longevity. Polysulfide rubber also offers excellent resistance to weathering and aging, making it suitable for long-term mold sealing solutions compared to polyurethane rubber.
Overview of Polyurethane Rubber
Polyurethane rubber is a versatile elastomer known for its exceptional abrasion resistance, high tear strength, and superior flexibility, making it ideal for mold applications requiring durability and detailed surface finishes. Unlike polysulfide rubber, polyurethane cures faster and provides better resistance to oils, solvents, and weathering, ensuring longer mold life in industrial environments. Its ability to produce precise, high-quality molds with excellent dimensional stability makes polyurethane the preferred choice for prototyping and manufacturing complex parts.
Key Differences: Polysulfide vs Polyurethane Rubber
Polysulfide rubber offers superior chemical resistance and excellent fuel and solvent impermeability, making it ideal for molds in harsh chemical environments, whereas polyurethane rubber excels in abrasion resistance and tear strength, suitable for durable, high-wear molds. Polysulfide rubber typically cures slower and has lower tensile strength compared to polyurethane, which provides faster curing times and higher mechanical durability. The choice between polysulfide and polyurethane rubber depends on specific mold application requirements, including chemical exposure, flexibility, and longevity.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polysulfide rubber exhibits excellent flexibility and chemical resistance, making it highly effective for molds requiring dimensional stability and solvent resistance. Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance, higher tensile strength, and better tear resistance, suitable for molds subjected to repetitive mechanical stress and wear. The choice between polysulfide and polyurethane rubber depends on the specific mechanical demands, with polysulfide favoring chemical resilience and polyurethane excelling in durability and toughness.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Polysulfide rubber offers superior chemical resistance against fuels, oils, and solvents, making it ideal for molds exposed to aggressive chemicals. Polyurethane rubber provides enhanced durability with excellent abrasion and tear resistance, suitable for molds requiring long service life under mechanical stress. Choosing between these materials depends on the specific chemical exposure and mechanical demands of the molding application.
Ease of Use and Processing
Polysulfide rubber offers excellent flexibility and chemical resistance but requires longer curing times and careful mixing to avoid inconsistencies, making its processing more challenging. Polyurethane rubber cures faster and has a wider processing window, allowing for more straightforward handling and quicker demolding. Ease of use in polyurethane molds is generally superior due to faster set times and less sensitivity to moisture during processing.
Cost Analysis: Polysulfide vs Polyurethane
Polysulfide rubber typically offers a lower initial material cost compared to polyurethane rubber, making it a cost-effective choice for budget-sensitive mold applications. Polyurethane rubber, while more expensive upfront, provides superior durability and tear resistance, potentially reducing long-term maintenance and replacement costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including lifespan and performance under specific molding conditions, is critical for selecting between polysulfide and polyurethane rubbers.
Ideal Applications for Each Rubber Type
Polysulfide rubber is ideal for applications requiring excellent chemical resistance and flexibility in sealing joints exposed to fuels, solvents, and weathering, such as in aerospace and automotive gasket molds. Polyurethane rubber excels in abrasion resistance and toughness, making it suitable for molds used in casting, prototyping, and parts requiring high impact durability and tear strength. Selecting between polysulfide and polyurethane rubbers depends on specific mold performance needs, with polysulfide favored for chemical endurance and polyurethane for mechanical strength.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Mold Making
Polysulfide rubber offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for molds requiring durability and repeated use with aggressive materials. Polyurethane rubber provides superior tear strength and faster curing times, suited for high-detail molds and short production runs. Selecting between polysulfide and polyurethane rubber depends on balancing mold longevity, detail accuracy, and environmental resistance specific to the molding application.
Infographic: Polysulfide rubber vs Polyurethane rubber for Mold
 azmater.com
azmater.com