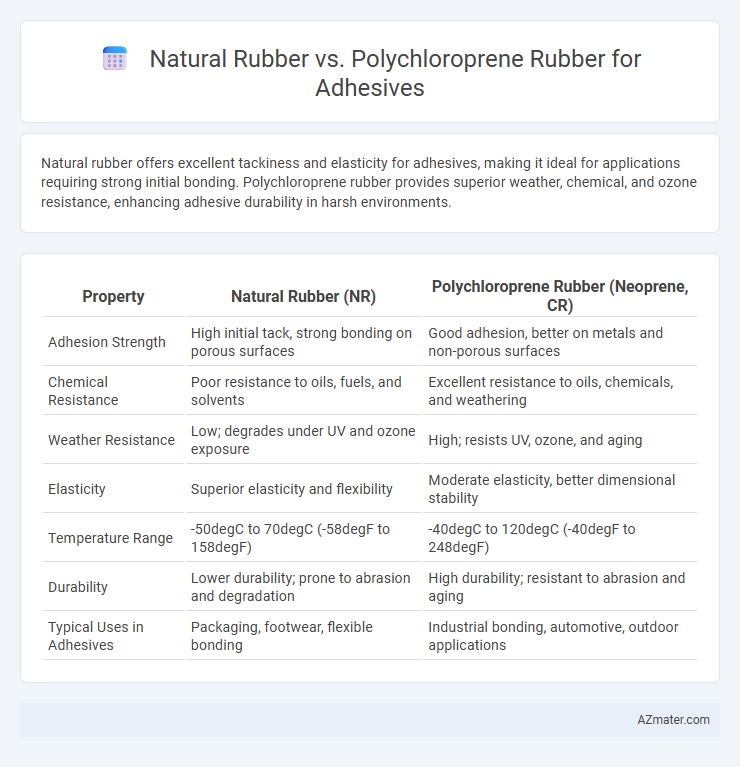
Natural rubber offers excellent tackiness and elasticity for adhesives, making it ideal for applications requiring strong initial bonding. Polychloroprene rubber provides superior weather, chemical, and ozone resistance, enhancing adhesive durability in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Natural Rubber (NR) | Polychloroprene Rubber (Neoprene, CR) |
|---|---|---|
| Adhesion Strength | High initial tack, strong bonding on porous surfaces | Good adhesion, better on metals and non-porous surfaces |
| Chemical Resistance | Poor resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents | Excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering |
| Weather Resistance | Low; degrades under UV and ozone exposure | High; resists UV, ozone, and aging |
| Elasticity | Superior elasticity and flexibility | Moderate elasticity, better dimensional stability |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 70degC (-58degF to 158degF) | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) |
| Durability | Lower durability; prone to abrasion and degradation | High durability; resistant to abrasion and aging |
| Typical Uses in Adhesives | Packaging, footwear, flexible bonding | Industrial bonding, automotive, outdoor applications |
Introduction to Rubber-Based Adhesives
Natural rubber offers superior elasticity and tackiness, making it ideal for pressure-sensitive adhesives requiring strong initial bonding. Polychloroprene rubber provides enhanced resistance to heat, oils, and weathering, suitable for industrial adhesives exposed to harsh environments. Both rubbers serve as essential polymer bases in formulating diverse adhesive products tailored to specific application needs.
What is Natural Rubber?
Natural rubber is a polymer derived from the latex sap of Hevea brasiliensis trees, primarily composed of cis-1,4-polyisoprene, known for its excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and adhesion properties. It is widely used in adhesive formulations due to its tackiness and ability to bond well with various substrates, especially in pressure-sensitive adhesives and flexible bonds. Compared to polychloroprene rubber, natural rubber offers superior natural biodegradability and lower chemical resistance, influencing its application in environments where environmental impact and exposure to solvents are critical factors.
What is Polychloroprene Rubber?
Polychloroprene rubber, commonly known by the brand name Neoprene, is a synthetic elastomer widely used in adhesives for its excellent chemical stability, weather resistance, and adhesive strength. Unlike natural rubber, which is derived from latex of rubber trees and is prone to degradation by oils and ozone, polychloroprene offers superior durability and resistance to environmental factors. Its balanced combination of flexibility and toughness makes polychloroprene an ideal choice for high-performance adhesive applications in automotive, industrial, and marine sectors.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Natural rubber, composed primarily of polyisoprene, features a cis-1,4-polyisoprene structure that imparts excellent elasticity, tackiness, and tensile strength, making it highly effective for pressure-sensitive adhesives. Polychloroprene rubber (neoprene) contains chlorinated polyisoprene chains, which introduce enhanced chemical stability, oil resistance, and weathering durability due to the presence of chlorine atoms in its polymer backbone. The chemical structure differences lead to natural rubber exhibiting superior flexibility and adhesion to porous surfaces, while polychloroprene offers improved resistance to heat, solvents, and aging, making it suitable for more demanding adhesive applications.
Adhesion Strength: Natural Rubber vs Polychloroprene
Natural rubber exhibits high tack and excellent initial adhesion strength, making it ideal for quick bonding applications and flexible surfaces. Polychloroprene, also known as Neoprene, provides superior long-term adhesion strength with enhanced resistance to environmental factors such as heat, ozone, and chemicals. The choice between natural rubber and polychloroprene adhesives depends largely on application requirements for durability versus immediate adhesion performance.
Flexibility and Elasticity Differences
Natural rubber offers superior elasticity due to its high molecular structure, enabling excellent stretch and recovery essential for flexible adhesives. Polychloroprene rubber provides enhanced flexibility with improved resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering, making it suitable for adhesives in harsher environments. The elasticity of natural rubber surpasses polychloroprene, but polychloroprene's balanced flexibility delivers durability and consistent performance under varied conditions.
Resistance to Heat, Oils, and Chemicals
Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and tensile strength but shows limited resistance to heat, oils, and many chemicals, making it less suitable for demanding adhesive applications exposed to harsh environments. Polychloroprene rubber (neoprene) provides superior resistance to heat up to approximately 120degC, along with enhanced chemical and oil resistance, maintaining adhesive integrity in automotive, industrial, and marine settings. The choice between these rubbers depends on specific environmental conditions, with polychloroprene preferred for applications requiring durable, heat- and chemical-resistant adhesive bonds.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Natural rubber, derived from Hevea brasiliensis trees, is biodegradable and renewable, making it a more environmentally sustainable choice for adhesives. Polychloroprene rubber, a synthetic polymer produced from petrochemicals, has a higher carbon footprint and generates hazardous byproducts during manufacturing. The biodegradability and renewable sourcing of natural rubber significantly reduce long-term environmental impact compared to the non-biodegradable, fossil-fuel-based polychloroprene.
Common Applications in Adhesive Products
Natural rubber is widely used in adhesive products for applications requiring high elasticity and strong initial tack, such as contact adhesives, pressure-sensitive tapes, and footwear bonding. Polychloroprene rubber, known as Neoprene, offers superior resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering, making it ideal for industrial adhesives used in automotive, marine, and construction sectors. Both rubbers serve critical roles in adhesive formulations, with natural rubber favored for flexibility and cost-effectiveness, while polychloroprene provides enhanced durability and environmental resistance.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Adhesive Needs
Natural rubber offers excellent tack, flexibility, and tensile strength, making it ideal for applications requiring strong initial bonding and elasticity. Polychloroprene rubber, also known as Neoprene, provides superior resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering, which enhances adhesive durability in harsh environments. Selecting the right rubber depends on balancing performance factors like adhesion strength, environmental resistance, and flexibility according to specific adhesive application requirements.
Infographic: Natural rubber vs Polychloroprene rubber for Adhesive
 azmater.com
azmater.com