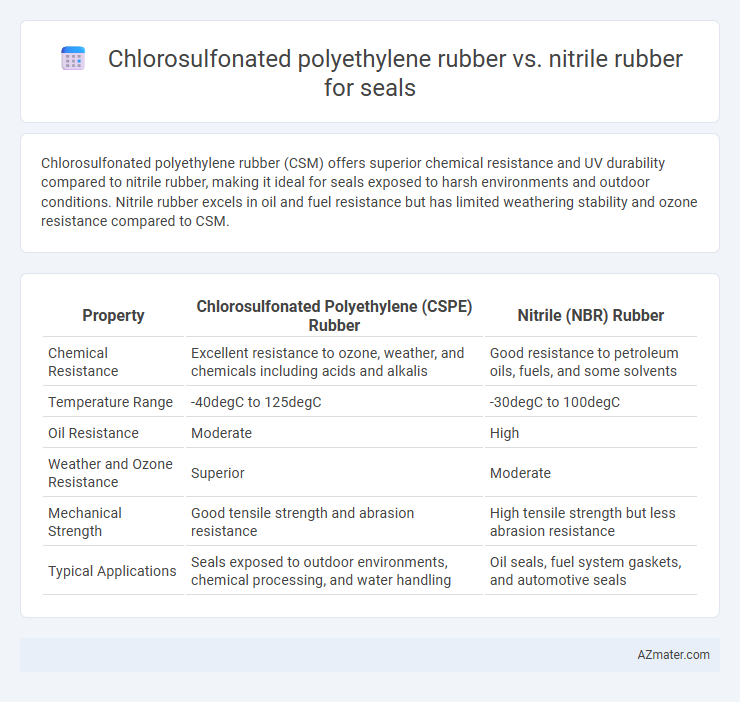
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) offers superior chemical resistance and UV durability compared to nitrile rubber, making it ideal for seals exposed to harsh environments and outdoor conditions. Nitrile rubber excels in oil and fuel resistance but has limited weathering stability and ozone resistance compared to CSM.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSPE) Rubber | Nitrile (NBR) Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to ozone, weather, and chemicals including acids and alkalis | Good resistance to petroleum oils, fuels, and some solvents |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 125degC | -30degC to 100degC |
| Oil Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Weather and Ozone Resistance | Superior | Moderate |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength and abrasion resistance | High tensile strength but less abrasion resistance |
| Typical Applications | Seals exposed to outdoor environments, chemical processing, and water handling | Oil seals, fuel system gaskets, and automotive seals |
Introduction to Seal Materials: CSM vs NBR
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) offers superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and chemicals, making it ideal for seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Nitrile rubber (NBR) excels in oil resistance and mechanical strength, making it a preferred choice for seals in automotive and industrial hydraulic applications. Selection between CSM and NBR depends on the specific sealing environment, including exposure to chemicals, temperature ranges, and mechanical stress requirements.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber features a polyethylene backbone with chlorosulfonyl functional groups enhancing chemical resistance and ozone durability, while nitrile rubber (NBR) consists of a copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene, delivering excellent resistance to oils and fuels due to its polar nitrile groups. The incorporation of sulfonyl chloride groups in CSM facilitates crosslinking and improves resistance to weathering and chemicals like acids and alkalis, whereas the acrylonitrile content in nitrile rubber determines its polarity and fuel resistance but limits its ozone and weathering performance. CSM's unique chemical structure offers versatility in sealing applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions, whereas nitrile rubber excels in environments requiring strong hydrocarbon resistance.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Flexibility
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers superior tensile strength and excellent resistance to abrasion, making it highly durable for sealing applications under mechanical stress. Nitrile rubber (NBR) provides outstanding flexibility and resilience, especially in dynamic seals exposed to oils and fuels, maintaining elasticity across a broad temperature range. While CSM excels in chemical and weather resistance, NBR's lower tensile strength is compensated by its excellent elongation and compression set performance, making each suitable for different sealing demands depending on mechanical and environmental conditions.
Resistance to Chemicals, Oils, and Fuels
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and solvents, making it highly suitable for harsh chemical environments. Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and aliphatic hydrocarbons, commonly found in automotive and industrial applications, but tends to degrade when exposed to ozone and weathering. For seals requiring prolonged exposure to oils and fuels, NBR provides better performance, whereas CSM rubber is preferred in applications demanding broad chemical resistance and durability against environmental degradation.
Temperature Performance and Thermal Stability
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) exhibits superior temperature performance with a continuous service range of -40degC to 130degC and excellent thermal stability, resisting degradation and maintaining elasticity under prolonged heat exposure. Nitrile rubber (NBR) performs well within a temperature range of approximately -40degC to 100degC but shows reduced thermal stability, prone to hardening and cracking when exposed to elevated temperatures over time. For seals requiring higher thermal resistance and stability in harsh environments, CSM is typically preferred over NBR.
Weathering, UV, and Ozone Resistance
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior weathering, UV, and ozone resistance compared to nitrile rubber, making it ideal for outdoor seal applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. CSM maintains flexibility and physical integrity over prolonged sun exposure and ozone attack, whereas nitrile rubber tends to degrade and crack under similar factors. The enhanced molecular structure of CSM confers exceptional durability and longevity in sealing solutions requiring high environmental resilience.
Compression Set and Sealing Performance
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber exhibits superior resistance to compression set compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), maintaining elasticity and shape under prolonged compression, which enhances long-term sealing performance in dynamic applications. Nitrile rubber, while offering excellent oil and fuel resistance, tends to have a higher compression set, leading to potential seal relaxation and leakage over extended service periods. The low compression set and resistance to weathering of CSM make it ideal for sealing in harsh chemical and ozone-exposed environments, ensuring consistent sealing integrity.
Applications in Industrial Sealing
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) excels in applications requiring superior chemical resistance and weatherability, making it ideal for outdoor industrial seals exposed to harsh environments and UV radiation. Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers outstanding resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels, making it the preferred choice for seals in automotive, hydraulic, and oil industry applications. Both materials provide excellent sealing performance, but selection depends on the specific exposure conditions and required durability in industrial sealing systems.
Cost, Availability, and Processing Considerations
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers superior chemical resistance and weathering properties compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), but typically comes at a higher cost, impacting overall seal manufacturing budgets. Nitrile rubber remains widely available and is favored for its excellent oil resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for seals in automotive and industrial applications. Processing CSM requires specialized equipment and careful control due to its vulcanization with sulfur, whereas nitrile rubber benefits from more straightforward processing techniques with established industrial protocols.
Summary Table: CSM vs NBR for Seal Selection
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and chemicals compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), making it ideal for harsh environmental seals. NBR excels in oil, fuel, and hydraulic fluid resistance but underperforms in UV and ozone exposure. For seal selection, CSM is preferred in outdoor and chemical-heavy conditions, while NBR suits petroleum-based applications with moderate environmental stress.
Infographic: Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com