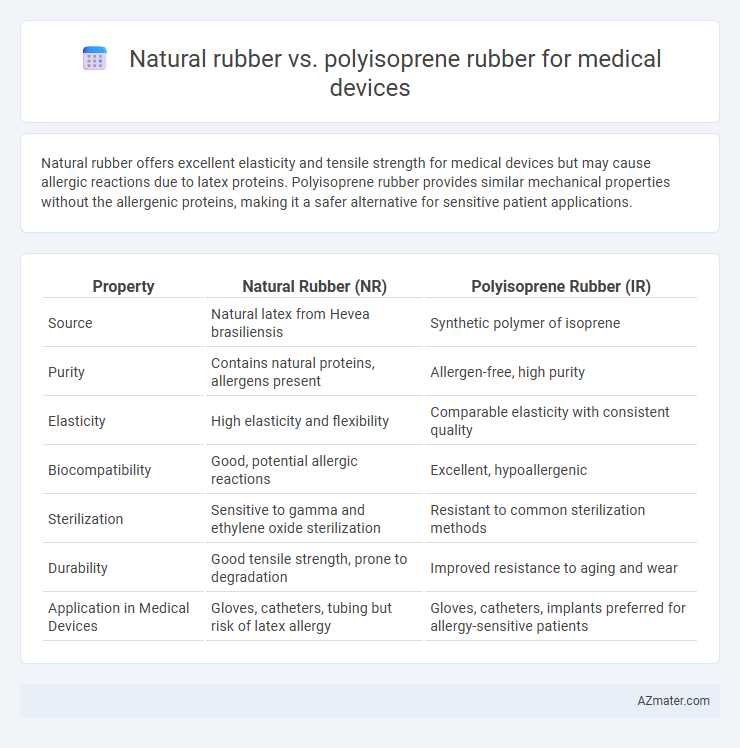
Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and tensile strength for medical devices but may cause allergic reactions due to latex proteins. Polyisoprene rubber provides similar mechanical properties without the allergenic proteins, making it a safer alternative for sensitive patient applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Natural Rubber (NR) | Polyisoprene Rubber (IR) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural latex from Hevea brasiliensis | Synthetic polymer of isoprene |
| Purity | Contains natural proteins, allergens present | Allergen-free, high purity |
| Elasticity | High elasticity and flexibility | Comparable elasticity with consistent quality |
| Biocompatibility | Good, potential allergic reactions | Excellent, hypoallergenic |
| Sterilization | Sensitive to gamma and ethylene oxide sterilization | Resistant to common sterilization methods |
| Durability | Good tensile strength, prone to degradation | Improved resistance to aging and wear |
| Application in Medical Devices | Gloves, catheters, tubing but risk of latex allergy | Gloves, catheters, implants preferred for allergy-sensitive patients |
Introduction to Medical-Grade Rubbers
Medical-grade natural rubber offers excellent elasticity, resilience, and biocompatibility, making it suitable for devices requiring flexibility and durability, such as gloves and catheters. Polyisoprene rubber, synthetic yet chemically similar to natural rubber, provides consistent purity and reduced allergenic risks, crucial for sensitive applications in medical devices. Both materials meet stringent regulatory standards, but polyisoprene is often preferred when latex allergies must be minimized without sacrificing performance.
What is Natural Rubber?
Natural rubber, derived from the latex sap of Hevea brasiliensis trees, is a biodegradable polymer primarily composed of cis-1,4-polyisoprene. It exhibits excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and barrier properties, making it widely used in medical devices like gloves and catheters. Despite its superior performance characteristics, natural rubber carries a risk of latex allergies, prompting the exploration of synthetic alternatives such as polyisoprene rubber.
What is Polyisoprene Rubber?
Polyisoprene rubber is a synthetic elastomer closely resembling natural rubber in molecular structure and physical properties, making it an ideal choice for medical devices requiring high elasticity and biocompatibility. Unlike natural rubber, polyisoprene is manufactured to reduce protein content, minimizing allergic reactions in sensitive patients. Its consistent quality, excellent tensile strength, and resistance to sterilization processes ensure reliable performance in products such as surgical gloves, catheters, and tubing.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Natural rubber consists primarily of cis-1,4-polyisoprene, a polymer with a high degree of cis-configuration contributing to its elasticity and resilience in medical devices. Synthetic polyisoprene rubber mimics the chemical structure of natural rubber but offers greater purity and consistency by eliminating proteins that can cause allergic reactions. The subtle differences in polymer chain structure and the absence of non-rubber components in polyisoprene enhance biocompatibility and make it preferable for sensitive medical applications.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Natural rubber exhibits excellent elasticity and tensile strength, making it a preferred material for medical devices requiring flexibility and durability. Polyisoprene rubber closely mimics the physical properties of natural rubber but offers improved purity and lower allergenic potential, which is critical for sensitive medical applications. Both materials demonstrate high resilience and abrasion resistance, yet polyisoprene's consistent molecular structure enhances its mechanical performance and biocompatibility in medical devices.
Biocompatibility and Allergenicity
Natural rubber and polyisoprene rubber both offer excellent elasticity and resilience for medical devices, but polyisoprene rubber is preferred for enhanced biocompatibility and reduced allergenicity. Natural rubber contains proteins that can trigger latex allergies in sensitive patients, posing risks in medical settings. Polyisoprene rubber is a synthetic alternative that mimics the physical properties of natural rubber while eliminating protein-related allergenic concerns, making it safer for long-term patient contact.
Sterilization Methods and Resistance
Natural rubber exhibits variable resistance to sterilization methods such as gamma radiation and ethylene oxide, often leading to degradation and reduced mechanical properties in medical devices. Polyisoprene rubber demonstrates superior stability under common sterilization processes, maintaining tensile strength and elasticity after exposure to autoclaving, gamma irradiation, and ethylene oxide sterilization. This enhanced resistance makes polyisoprene a preferred material for medical devices requiring repeated sterilization without compromising performance or patient safety.
Performance in Medical Device Applications
Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and biocompatibility, making it suitable for medical devices requiring flexibility and durability. Polyisoprene rubber provides similar mechanical properties but with reduced allergenic potential, enhancing patient safety in sensitive applications such as gloves and catheters. Both materials perform well in medical device manufacturing, but polyisoprene is often preferred for hypoallergenic requirements without compromising the physical performance needed for reliable device function.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Natural rubber, derived from rubber trees, offers cost advantages due to its widespread availability and established global supply chains, making it a competitive option for medical devices. Polyisoprene rubber, synthesized chemically to mimic natural rubber's properties, tends to be more expensive due to complex manufacturing processes and lower production volumes. Availability of natural rubber can fluctuate based on agricultural factors, while polyisoprene provides consistency and purity essential for sensitive medical applications despite higher costs.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Medical Devices
Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and resilience, making it suitable for medical devices requiring high flexibility and durability, but its potential for allergenic reactions necessitates careful consideration. Polyisoprene rubber provides similar physical properties without the latex proteins that cause allergies, making it ideal for hypoallergenic medical applications such as gloves and tubing. Selecting the right rubber hinges on balancing biocompatibility, mechanical performance, and patient safety requirements.
Infographic: Natural rubber vs Polyisoprene rubber for Medical device
 azmater.com
azmater.com