Thermally conductive rubber enhances heat dissipation in tire inner liners, improving performance and preventing overheating. Butyl rubber, known for its excellent air impermeability and flexibility, is commonly used for tire inner liners but lacks significant thermal conductivity.
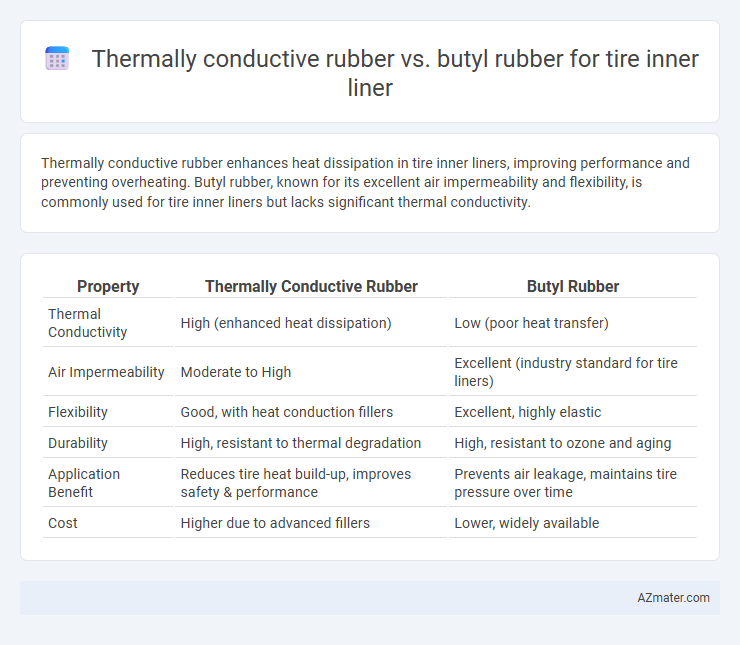
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermally Conductive Rubber | Butyl Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | High (enhanced heat dissipation) | Low (poor heat transfer) |
| Air Impermeability | Moderate to High | Excellent (industry standard for tire liners) |
| Flexibility | Good, with heat conduction fillers | Excellent, highly elastic |
| Durability | High, resistant to thermal degradation | High, resistant to ozone and aging |
| Application Benefit | Reduces tire heat build-up, improves safety & performance | Prevents air leakage, maintains tire pressure over time |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced fillers | Lower, widely available |
Introduction to Tire Inner Liner Materials
Thermally conductive rubber enhances heat dissipation in tire inner liners, improving tire durability and performance under high-temperature conditions. Butyl rubber, widely used for tire inner liners, offers excellent air impermeability and flexibility, ensuring consistent tire pressure and long-term sealing. Comparing these materials highlights trade-offs between thermal management and airtightness critical for optimizing tire inner liner functionality.
What is Thermally Conductive Rubber?
Thermally conductive rubber is a specialized elastomer designed to efficiently dissipate heat while maintaining flexibility and durability, making it ideal for tire inner liners that require enhanced thermal management. Unlike traditional butyl rubber, which primarily offers excellent air retention and chemical resistance, thermally conductive rubber incorporates fillers such as boron nitride or aluminum oxide to improve heat transfer properties. This thermal conductivity helps prevent tire overheating, reduces the risk of blowouts, and extends tire lifespan by optimizing temperature regulation within the inner liner.
Overview of Butyl Rubber in Tire Applications
Butyl rubber, a synthetic rubber known for its exceptional air impermeability and chemical resistance, is widely used in tire inner liners to maintain tire pressure and extend tire life. Its low gas permeability compared to natural rubber prevents air leakage, while its resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering enhances durability under varying environmental conditions. Though less thermally conductive than thermally conductive rubber alternatives, butyl rubber's balance of flexibility and impermeability remains critical for reliable tire inner liner performance.
Properties Comparison: Thermally Conductive vs. Butyl Rubber
Thermally conductive rubber offers enhanced heat dissipation and improved thermal management compared to butyl rubber, making it ideal for high-performance tire inner liners subjected to elevated temperatures. Butyl rubber excels in impermeability and air retention, providing superior airtightness and excellent resistance to gas permeability, essential for maintaining tire pressure. While thermally conductive rubber prioritizes thermal stability and heat transfer, butyl rubber remains unmatched in chemical resistance and durability under static environmental conditions.
Thermal Conductivity: Impact on Tire Performance
Thermally conductive rubber significantly enhances heat dissipation within the tire inner liner, reducing the risk of overheating and improving overall tire durability and safety. Butyl rubber, known for its excellent air impermeability, has lower thermal conductivity, which can lead to higher internal temperatures during prolonged use or high-speed conditions. Improved thermal management from thermally conductive rubber contributes to better tire performance by maintaining optimal tire pressure and minimizing thermal degradation.
Air Retention and Permeability Characteristics
Thermally conductive rubber exhibits enhanced heat dissipation properties while maintaining low air permeability, contributing to superior air retention in tire inner liners compared to butyl rubber. Butyl rubber, renowned for its excellent impermeability to gases, offers exceptional air retention due to its dense molecular structure, but typically lacks thermal conductivity. The trade-off between thermally conductive rubber's improved temperature management and butyl rubber's proven air impermeability impacts the overall performance and longevity of tire inner liners under various operating conditions.
Durability and Longevity in Real-World Conditions
Thermally conductive rubber offers enhanced heat dissipation properties, reducing thermal degradation and extending tire inner liner lifespan compared to traditional butyl rubber. Butyl rubber provides excellent air impermeability and chemical resistance but may suffer from faster aging under high-temperature conditions typical in heavy-duty or high-speed use. Real-world durability tests demonstrate that thermally conductive rubber maintains structural integrity and flexibility longer, improving overall tire performance and reducing maintenance frequency.
Manufacturing and Cost Considerations
Thermally conductive rubber in tire inner liners enhances heat dissipation during manufacturing, reducing cycle times and improving overall tire durability but often incurs higher raw material costs compared to traditional butyl rubber. Butyl rubber remains a cost-effective choice with proven air impermeability and ease of processing, making it a standard in mass production despite less efficient thermal management. Manufacturers must balance the premium cost of thermally conductive rubber against potential gains in tire performance and production efficiency based on application requirements.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Thermally conductive rubber used in tire inner liners offers improved heat dissipation, potentially extending tire life and reducing environmental waste by lowering the frequency of replacements. Butyl rubber, known for its exceptional air retention and durability, contributes to tire longevity but presents challenges in recycling due to its complex chemical composition. The recyclability of thermally conductive rubber is evolving with newer formulations designed for easier breakdown, whereas butyl rubber recycling remains limited, impacting environmental sustainability efforts in tire disposal and reuse.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Rubber for Tire Inner Liners
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior heat dissipation, enhancing tire performance and longevity by reducing thermal degradation in the inner liner. Butyl rubber excels in air impermeability and chemical resistance, ensuring optimal air retention and durability under various conditions. Selecting the best rubber depends on balancing thermal management needs with airtightness, where thermally conductive rubber suits high-performance tires, while butyl rubber remains ideal for standard applications demanding reliable sealing.
Infographic: Thermally conductive rubber vs Butyl rubber for Tire inner liner
 azmater.com
azmater.com