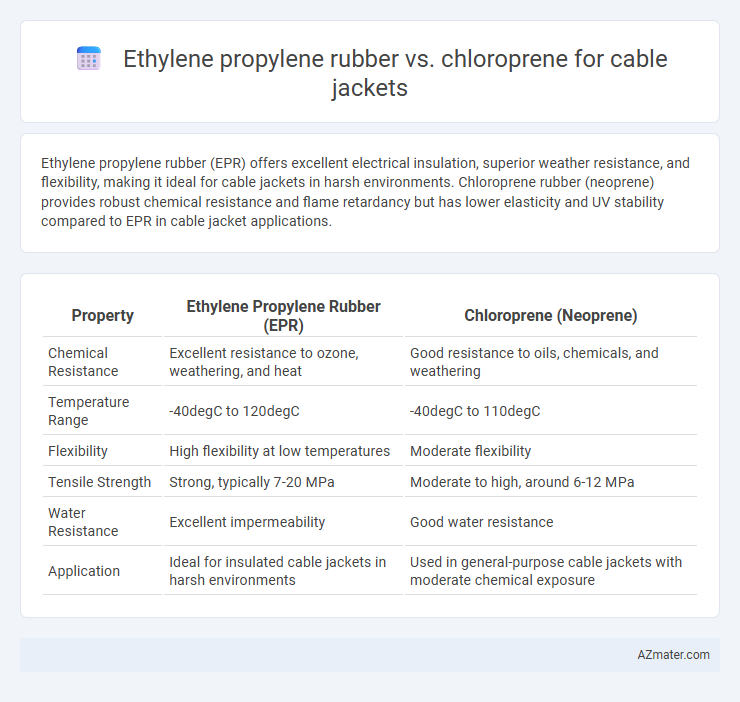
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers excellent electrical insulation, superior weather resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for cable jackets in harsh environments. Chloroprene rubber (neoprene) provides robust chemical resistance and flame retardancy but has lower elasticity and UV stability compared to EPR in cable jacket applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) | Chloroprene (Neoprene) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and heat | Good resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -40degC to 110degC |
| Flexibility | High flexibility at low temperatures | Moderate flexibility |
| Tensile Strength | Strong, typically 7-20 MPa | Moderate to high, around 6-12 MPa |
| Water Resistance | Excellent impermeability | Good water resistance |
| Application | Ideal for insulated cable jackets in harsh environments | Used in general-purpose cable jackets with moderate chemical exposure |
Introduction to Cable Jacket Materials
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers excellent electrical insulation, weather resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for cable jackets in harsh environments. Chloroprene, also known as neoprene, provides superior oil resistance, flame retardance, and mechanical durability, which enhances cable performance under mechanical stress and exposure to chemicals. Selecting between EPR and chloroprene depends on the specific application requirements, including environmental conditions, chemical exposure, and mechanical demands of the cable jacket.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR)
Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) is a highly flexible and durable elastomer widely used as a cable jacket material due to its excellent resistance to heat, ozone, weathering, and electrical insulation properties. EPR offers superior thermal stability up to 90degC continuous operating temperature and exceptional resistance to moisture and chemicals, making it ideal for underground and outdoor power cables. Compared to Chloroprene, EPR provides enhanced flexibility and aging resistance, contributing to longer cable life and superior performance in harsh environments.
Overview of Chloroprene Rubber (CR)
Chloroprene Rubber (CR), also known as Neoprene, is a synthetic elastomer widely used for cable jackets due to its excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering. It offers good flexibility, flame resistance, and durability in harsh environments, making it suitable for outdoor and industrial cable applications. Compared to Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR), Chloroprene provides superior mechanical strength and resistance to ozone and oxidation, enhancing the lifespan of cable insulation.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) exhibits superior flexibility and excellent abrasion resistance, making it highly effective for cable jackets subjected to mechanical stress and bending. Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers greater tensile strength and enhanced resistance to tearing and weathering, providing durability in harsh environments. Comparing mechanical properties, EPR excels in elongation and flexibility, while chloroprene delivers higher hardness and better resistance to oils and chemicals.
Thermal Resistance and Performance
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior thermal resistance with continuous operating temperatures up to 130degC, making it ideal for high-temperature cable jackets compared to chloroprene, which typically withstands up to 105degC. EPR's excellent heat aging resistance and electrical insulating properties enhance cable longevity and performance in harsh environments. While chloroprene provides good mechanical strength and weather resistance, EPR's enhanced thermal stability ensures better durability under prolonged thermal stress.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) exhibits superior chemical resistance to acids, alkalis, and polar solvents, making it highly durable in harsh industrial environments. Chloroprene rubber (CR), also known as neoprene, offers excellent resistance to oils, ozone, and weathering, but is less effective against strong acids and alkalis compared to EPR. In terms of environmental resistance, EPR withstands water and steam exposure better, while CR provides enhanced toughness and resistance to UV radiation and atmospheric aging.
Flexibility and Installation Characteristics
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior flexibility and excellent resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for cable jackets that require frequent bending and twisting during installation. Chloroprene rubber (Neoprene) provides good flexibility with enhanced chemical and weather resistance, but its stiffness can challenge tight bending applications. The ease of installation for EPR jackets is often preferred in environments needing high flexibility, whereas chloroprene excels in harsh outdoor conditions requiring durability.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) generally offers a lower cost and better availability compared to chloroprene rubber (CR), making it a preferred choice for budget-sensitive cable jacket applications. EPR's widespread production and stable supply chains ensure more consistent pricing and easier procurement, especially for large-scale projects. Chloroprene, while offering excellent chemical resistance, tends to be more expensive and less readily available due to complex manufacturing processes and fluctuating raw material costs.
Typical Applications in Cable Manufacturing
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) is widely used in cable jackets for its excellent electrical insulation, weather resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for medium to high voltage power cables in underground or industrial environments. Chloroprene rubber (CR), known for its durability and resistance to oil, chemicals, and ozone, is commonly employed in control, instrumentation, and industrial cables exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Both materials offer distinct advantages; EPR excels in electrical performance and thermal aging, while chloroprene provides enhanced mechanical strength and chemical resistance suited for rugged applications.
Conclusion: Choosing Between EPR and CR for Cable Jackets
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior electrical insulation, excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for high-voltage cable jackets in harsh environments. Chloroprene rubber (CR), known for its exceptional oil, chemical, and abrasion resistance, is better suited for cables exposed to mechanical stresses and chemical exposures. Selecting between EPR and CR depends on balancing the required electrical performance with environmental and mechanical durability needs for the specific cable application.
Infographic: Ethylene propylene rubber vs Chloroprene for Cable jacket
 azmater.com
azmater.com