Butyl rubber offers superior impermeability and excellent resistance to weathering and ozone, making it ideal for roofing membranes in harsh climates. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber provides outstanding flexibility, UV resistance, and cost-effectiveness for large-scale commercial roofing applications.
Table of Comparison
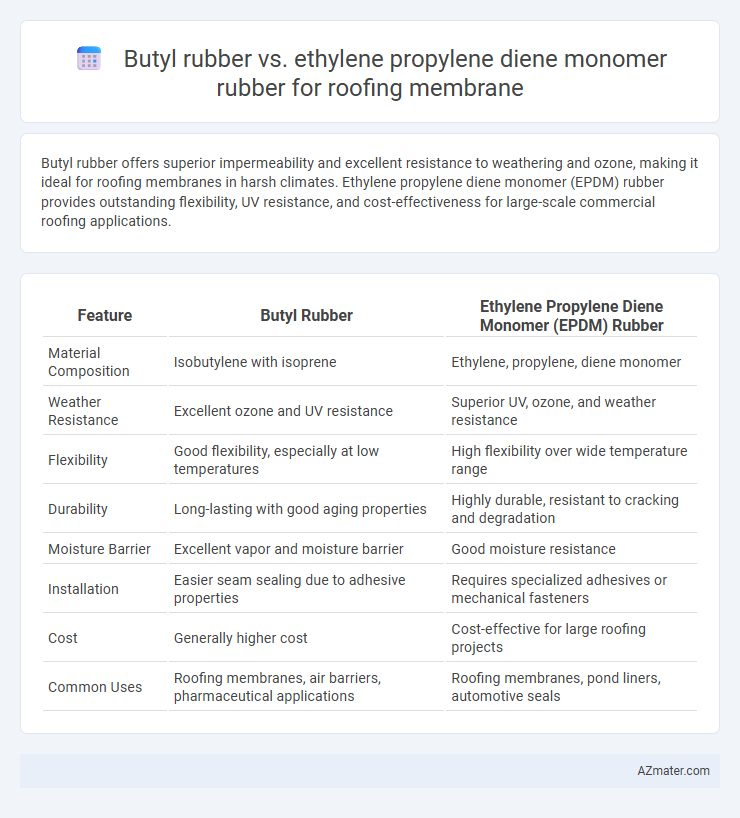
| Feature | Butyl Rubber | Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Isobutylene with isoprene | Ethylene, propylene, diene monomer |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent ozone and UV resistance | Superior UV, ozone, and weather resistance |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility, especially at low temperatures | High flexibility over wide temperature range |
| Durability | Long-lasting with good aging properties | Highly durable, resistant to cracking and degradation |
| Moisture Barrier | Excellent vapor and moisture barrier | Good moisture resistance |
| Installation | Easier seam sealing due to adhesive properties | Requires specialized adhesives or mechanical fasteners |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | Cost-effective for large roofing projects |
| Common Uses | Roofing membranes, air barriers, pharmaceutical applications | Roofing membranes, pond liners, automotive seals |
Introduction to Roofing Membranes
Roofing membranes like Butyl rubber and Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) are essential for waterproofing and durability in commercial and residential roofing systems. Butyl rubber membranes offer superior impermeability and excellent resistance to ozone and UV radiation, enhancing roof longevity. EPDM membranes are favored for their flexibility, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making them popular for various roofing applications in different climates.
Overview of Butyl Rubber (IIR)
Butyl rubber (IIR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent impermeability to gases and superior weather resistance, making it a reliable choice for roofing membranes. Its low permeability to air and moisture helps prevent water infiltration and enhances roof longevity compared to other materials. Butyl rubber's flexibility and resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and extreme temperatures contribute to durable, long-lasting roofing solutions in various climates.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) Rubber
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber is a highly durable synthetic elastomer widely used in roofing membranes due to its excellent resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and extreme weather conditions. EPDM exhibits superior flexibility and elasticity over a broad temperature range, making it ideal for various climates and ensuring long-lasting waterproofing performance. Its chemical composition, based on ethylene and propylene monomers with a diene component for crosslinking, provides enhanced tensile strength and resistance to aging compared to Butyl rubber alternatives.
Comparative Weather Resistance
Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber exhibits superior weather resistance compared to Butyl rubber, making it more suitable for roofing membranes exposed to prolonged sunlight, ozone, and temperature extremes. EPDM's molecular structure provides exceptional resistance to UV radiation, oxidative aging, and thermal cycling, while Butyl rubber tends to degrade faster under these harsh environmental conditions. This enhanced durability of EPDM contributes to longer lifespan and reduced maintenance costs in roofing applications.
Durability and Longevity
Butyl rubber roofing membranes exhibit superior durability with exceptional resistance to ozone, weathering, and UV degradation, ensuring a lifespan of 20 to 30 years under harsh environmental conditions. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber offers excellent flexibility and resistance to extreme temperatures but may have slightly lower longevity, typically ranging from 15 to 25 years, depending on formulation and installation quality. Both materials resist water and chemical exposure effectively; however, butyl's lower permeability to gases provides enhanced protection against oxidation, contributing to its longer service life in roofing applications.
Installation Process Differences
Butyl rubber roofing membranes require solvent-based adhesives for installation, which demands careful surface preparation and extended curing times to ensure proper bonding. Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) membranes utilize either adhesive, peel-and-stick, or mechanically fastened installation methods, allowing for faster and more versatile application on various substrates. EPDM's flexible seam welding and option for liquid adhesives reduce labor intensity compared to Butyl rubber's more sensitive adhesive handling and slower set times.
Cost Comparison Analysis
Butyl rubber roofing membranes typically have a higher upfront cost compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber due to their enhanced impermeability and UV resistance. EPDM roofing offers a more budget-friendly option with lower material and installation expenses, although it may require more frequent maintenance over its lifespan. Long-term cost analysis reveals Butyl rubber's durability can offset initial expenses through reduced repair and replacement rates, whereas EPDM presents savings in short-term projects or tighter budget constraints.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Butyl rubber roofing membranes offer excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and UV radiation, with moderate environmental impact due to limited recyclability and reliance on petroleum-based raw materials. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber membranes provide superior sustainability benefits, being highly durable, energy-efficient through excellent solar reflectance, and often available in recyclable form, reducing landfill waste. EPDM's longer lifespan and lower environmental toxicity make it a preferable choice for eco-friendly roofing solutions compared to butyl rubber.
Typical Applications in Roofing
Butyl rubber is highly effective for roofing membranes due to its excellent impermeability to air and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for single-ply roofing systems in commercial and industrial buildings. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber is widely used in roofing applications requiring outstanding UV and ozone resistance, typically applied in flat or low-slope roofs of both residential and commercial structures. EPDM's flexibility and durability make it a preferred choice for waterproofing roofs exposed to extreme temperature fluctuations and prolonged sun exposure.
Choosing the Right Membrane for Your Roof
Butyl rubber offers superior waterproofing and excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and UV radiation, making it a reliable choice for roofing membranes in harsh climates. Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in flexibility and durability, with strong resistance to temperature extremes and chemical exposure, ideal for long-lasting roof protection. Selecting the right membrane depends on factors like environmental conditions, expected roof lifespan, and maintenance requirements to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Infographic: Butyl rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber for Roofing membrane
 azmater.com
azmater.com